Solid-Phase Extraction of Aflatoxins from Peanut Butter and Quantification Using Kinetex Core-Shell Technology by LC–MS–MS
The Application Notebook
As a result of their high toxicity and carcinogenicity, aflatoxins are of major concern for food producers, the food processing industry and consumers. Most countries have legislation setting maximum permissible limits for aflatoxins, which are in the low micrograms per kilogram for food matrices.
Introduction
As a result of their high toxicity and carcinogenicity, aflatoxins are of major concern for food producers, the food processing industry and consumers. Most countries have legislation setting maximum permissible limits for aflatoxins, which are in the low micrograms per kilogram for food matrices.
We demonstrate a new SPE protocol for aflatoxins analysis from peanut butter, which gives ultra-clean extracts, while maintaining absolute recoveries above 80%. Samples are analysed by LC–MS–MS using the new Kinetex core-shell particle technology achieving full resolution of all compounds in less than 2 minutes with great precision and accuracy.
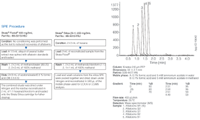
Figure 1: Instrumentation and chromatographic parameters.
Experimental Conditions
Extracts of peanut butter were spiked with aflatoxin standards at 50 ppb for LC–MS–MS for use with SPE. Data generated on the API 3000 LC–MS–MS was done at Phenomenex, Torrance, California, USA. Work on the API 3200 Q TRAP was done at ABI MDS Analytical Technologies in Toronto, Canada. Instruments and chromatographic parameters are found in Figure 1.
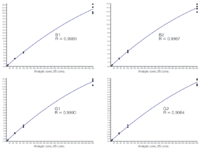
Figure 2: Spiked standard calibration curves.
Results and Discussion
Calibration curves for aflatoxins using the API 3200 Q TRAP were generated from 5 to 500 ppb. To better account for matrix interferences, calibration standards were prepared in a blank peanut butter matrix that had been processed using the Florisil SPE cartridges (Figure 2). Relative recoveries for the aflatoxins obtained using the extracted calibration curve were greater than 90% (Table 1).
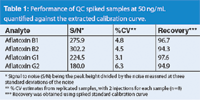
Table 1: Performance of QC spiked samples at 50 ng/mL quantified against the extracted calibration curve.
Because Kinetex core-shell particles consist of a nearly monodispered 1.9 μm solid silica core and a 0.35 μm porous silica shell, a very stable and homogeneous packed column bed is achieved (Figure 3). This newly developed LC particle significantly reduces peak dispersion because of eddy diffusion and resistance to mass transfer at reasonable back pressures (typically under 400 bar/6000 psi), allowing the benefits of ultra-high efficiency to be attained on any HPLC or UHPLC system.
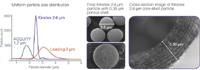
Figure 3: Kinetex core-shell technology.
Conclusions
The current work describes a quick and easy method for clean up and analysis of aflatoxins from peanut butter samples. The two-stage SPE procedure removes a majority of matrix interferences observed in LC–MS–MS chromatography. Combining the high efficiency Kinetex core-shell particle with the highly selective PFP chemistry enables ultrafast separation of all four aflatoxins on any LC–MS–MS system configuration. Precision and accuracy of this method were excellent when using a matrix-matched calibration curve. The estimated detection limits for each analyte are well below 5 ppb, which are more than sufficient to allow the method to be used for either confirmation or quantification.
References
1. H.P. van Egmond, Analytical Bioanalytical Chemistry, 378, 1152–1160 (2004).
2. Food and Agriculture Organization. Worldwide Regulations for Mycotoxins in Food and Feed, 2003, FAO Food and Nutr. Paper, 81 (2004).
3. M.C. Spanjer, P.M. Rensen and J.M. Scholten, Food Additives and Contaminants, 25, 472–489 (2008).
4. V.A. Vega, J. AOAC International, 88, 1383–1386 (2005).
5. M. Castegnaro et al., Mol. Nutr. Food Res., 50, 480–487 (2006).
6. V. Sobolev, J. Agric. Food Chem., 55, 2136–2141 (2007).
Phenomenex is not affiliated with Applied Biosystems.
Kinetex is a trademark of Phenomenex Inc.

Phenomenex Inc.
411 Madrid Avenue, Torrance, California 90501, USA
tel. +1 310 212 0555 fax +1 310 328 7768
E-mail: info@phenomenex.com
Website: www.phenomenex.com

Removing Double-Stranded RNA Impurities Using Chromatography
April 8th 2025Researchers from Agency for Science, Technology and Research in Singapore recently published a review article exploring how chromatography can be used to remove double-stranded RNA impurities during mRNA therapeutics production.
The Effect of Time and Tide On PFAS Concentrations in Estuaries
April 8th 2025Oliver Jones and Navneet Singh from RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia discuss a recent study they conducted to investigate the relationship between tidal cycles and PFAS concentrations in estuarine systems, and offer practical advice on the sample preparation and LC–MS/MS techniques they used to achieve the best results.



















