Sensitive Detection of IgG Aggregation using On-line Fluorescent Dye Detection in HP-SEC and AF4
To guide the development of aggregate free protein formulations, there is an urgent need for complementary methods that allow a sensitive detection, characterization and quantification of different types of protein aggregates.
To guide the development of aggregate free protein formulations, there is an urgent need for complementary methods that allow a sensitive detection, characterization and quantification of different types of protein aggregates. Our aim was to use size exclusion chromatography (HP-SEC) and asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation (AF4) in combination with UV, fluorescence and multiangle laser light scattering (MALS) detection to quantify and characterize monoclonal antibody (IgG) aggregates in heat stressed formulations. For fluorescence detection the extrinsic fluorescent dye Bis-ANS (600 nM) was added to the mobile phase and detected using an excitation of 385 nm and an emission of 488 nm.
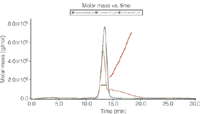
Figure 1: UV detection (280 nm) and molar mass calculated from the MALS signal of AF4 separation of non-stressed IgG, 10 min 75°C stressed and 10?min 80 °C stressed IgG.
The UV signal at 280 nm was used to calculate the relative amount of monomer and aggregates and the total recovery of the method using an extinction coefficient of 1.5 mLmg–1 cm–1. HP-SEC resulted in a better separation of monomer and dimers. However, the recovery was below 50% for the 80 °C stressed samples, because of aggregates larger than the exclusion volume of the column. With AF4 these larger aggregates could be analysed and a higher recovery of > 90% was achieved. From the MALS and UV signal the molar mass of the monomer was calculated to be 150 kDa, the dimer 300 kDa and the larger aggregates higher than 400 kDa (Figure 1). Bis-ANS fluorescence detection represents a highly sensitive method to identify aggregated IgG (Figure 2). Bis-ANS exhibits an increase in fluorescence in a hydrophobic environment, which is frequently found wherever proteins aggregate or change conformation. In conclusion, the combination of different detectors for HP-SEC and AF4 analysis adds significant methodological comprehensiveness, thus achieving a reliable characterization of IgG samples.
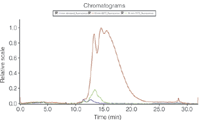
Figure 2: Fluorescence detection (excitation 385 nm, emission 488 nm) of AF4 separation of non-stressed IgG, 10 min 75 °C stressed and 10 min 80 °C stressed IgG.

Wyatt Technology
6300 Hollister Ave., Santa Barbara, California 93117, USA
tel. +1 805 681 9009 fax +1 805 681 0123
E-mail: info@wyatt.com
Website: www.wyatt.com

Accelerating Monoclonal Antibody Quality Control: The Role of LC–MS in Upstream Bioprocessing
This study highlights the promising potential of LC–MS as a powerful tool for mAb quality control within the context of upstream processing.
Using GC-MS to Measure Improvement Efforts to TNT-Contaminated Soil
April 29th 2025Researchers developing a plant microbial consortium that can repair in-situ high concentration TNT (1434 mg/kg) contaminated soil, as well as overcome the limitations of previous studies that only focused on simulated pollution, used untargeted metabolone gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to measure their success.
Prioritizing Non-Target Screening in LC–HRMS Environmental Sample Analysis
April 28th 2025When analyzing samples using liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry, there are various ways the processes can be improved. Researchers created new methods for prioritizing these strategies.
Potential Obstacles in Chromatographic Analyses Distinguishing Marijuana from Hemp
April 28th 2025LCGC International's April series for National Cannabis Awareness Month concludes with a discussion with Walter B. Wilson from the National Institute of Standard and Technology’s (NIST’s) Chemical Sciences Division regarding recent research his team conducted investigating chromatographic interferences that can potentially inflate the levels of Δ9-THC in Cannabis sativa plant samples, and possible solutions to avoid this problem.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



















