Rapid Analysis of Corn Stover Acid Hydrolysate for Estimation of Total Monosaccharide Content
The Application Notebook
Corn stover is the above-ground portion of the plant minus the kernels and it accounts for a large percentage of the global supply of lignocelluosic biomass available as feedstock for fermentation systems used for biofuel production.
Corn stover is the above-ground portion of the plant minus the kernels and it accounts for a large percentage of the global supply of lignocelluosic biomass available as feedstock for fermentation systems used for biofuel production. Acid hydrolysis of corn stover with sulphuric acid is a common method to release water-soluble carbohydrates for biofuel production. Monosaccharide concentrations released can vary with the feedstock, its pretreatment, hydrolysis and storage conditions. Knowledge of the monosaccharide content of acid-hydrolysed corn stover allows evaluation of the effectiveness of a new hydrolysis process and/or an estimation of the product yield.
Carbohydrates lack a good chromophore and, therefore, require high concentrations to be detected by UV absorbance or refractive index. Non-carbohydrate ingredients of acid-hydrolysed corn stover with good chromophoric properties can interfere with carbohydrate determinations. Pulsed amperometric detection (PAD) is selective for compounds that can be detected under a given set of electrochemical conditions and has a wide linear range for carbohydrates.
High-performance anion-exchange chromatography (HPAE) can separate glucose, galactose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, fructose, cellobiose, rhamnose, sucrose, mannitol and other carbohydrates typical of acid-hydrolysed plant-derived materials. The CarboPac PA1 anion-exchange column resolves monosaccharides and disaccharides from the unretained non-carbohydrate components using hydroxide eluent. Generally, at high hydroxide concentrations (e.g., 200 mM NaOH), monosaccharides elute rapidly and are poorly resolved. When the knowledge of the types of monosaccharides present in the acid-hydrolysed feed stock is not necessary, a rapid method that combines the total monosaccharides into one or two peaks for quantification may be more desirable.1 The method presented here allows estimation of total monosaccharides in undiluted corn stover acid hydrolysate in less than 10 min using HPAE-PAD.
Experimental
Dionex ICS-3000 chromatography system consisting of a pump, detector chromatography module (with electrochemical detector, gold working electrode with 15 mL PTFE gasket, 0.2 μL injection loop) and autosampler. The CarboPac PA1 column was used with 200 mM NaOH at 30 °C with a flow-rate of 1 mL/min. Corn stover acid hydrolysate was centrifuged at 16 k × g for 10 min to remove particulates, then directly injected.1
Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows the chromatograms of undiluted corn stover hydrolysate (blue trace) and standards (magenta trace). Panel B reveals greater detail. Arabinose (peak 1) is resolved from galactose, glucose, mannose and xylose (peak 2) and fructose (peak 3). The combined peak area for peaks 1, 2 and 3 is an estimate of the monosaccharide content of this sample.
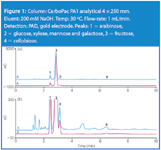
Figure 1
Reference
1. Dionex Corporation. Rapid Method for the Estimation of Total Free Monosaccharide Content in Corn Stover Hydrolysate Using HPAEPAD. Application Note 225, LPN 2190. Sunnyvale, California, USA.
CarboPac is a registered trademark of Dionex Corporation.
Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, PO Box 3603, Sunnyvale
California 94088, USA
tel. +1 408 737 0700 fax +1 408 730 9403
Website: www.dionex.com

Characterizing Plant Polysaccharides Using Size-Exclusion Chromatography
April 4th 2025With green chemistry becoming more standardized, Leena Pitkänen of Aalto University analyzed how useful size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) and asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation (AF4) could be in characterizing plant polysaccharides.
Investigating the Protective Effects of Frankincense Oil on Wound Healing with GC–MS
April 2nd 2025Frankincense essential oil is known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and therapeutic properties. A recent study investigated the protective effects of the oil in an excision wound model in rats, focusing on oxidative stress reduction, inflammatory cytokine modulation, and caspase-3 regulation; chemical composition of the oil was analyzed using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS).


















