Latest from LCGC International
6 days ago
Deep In The Heart of Texas: Pittcon 2026Latest Content
LC–MS/MS Profiling of Salivary Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Persistent Covid Disease
Perioperative Endocannabinoid Profiling by LC–MS in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty

LC–MS Metabolomic Profiling of Mantle Tissue Reveals Pigment-Linked Pathways in Pacific Oyster Shell Coloration

Celebrating Women Advancing Science and Society in Chromatography

LC–MS–Based Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling Distinguishes Carbohydrate Restriction from Low Energy Availability in Elite Endurance Athletes

Shorts










Podcasts
Videos
All Content

On the International Day of Women and Girls in Science 2026, LCGC highlights the women shaping chromatography, their curiosity-driven journeys, technical contributions, and the importance of representation, mentorship, and confidence in building a more inclusive scientific future.

A University of Bologna study describes a validated LC–MS/MS method for quantifying 13 PFAS in porcine liver and muscle. Chromatographic analysis revealed pronounced hepatic accumulation, with PFOS and PFOA consistently detected in liver but largely absent from muscle, supporting liver-focused, risk-based biomonitoring strategies in pork production.

A recent study evaluated the anticancer potential of Israeli black scorpion venom (SFV) against colorectal cancer (CRC) using integrated biochemical, computational, and biological approaches. SFV components were characterized by gel electrophoresis, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and ultraviolet–visible (UV-vis) spectrometry, followed by in silico docking against CRC- and apoptosis-related targets.

Waters has announced the completion of its acquisition of BD’s Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions businesses.

Applying UHPLC–quadrupole-orbital trap MS–based untargeted metabolomics to evaluate psychrotrophic lactic acid bacteria as kimchi starters revealed strain-specific suppression of pathogen metabolic pathways, linking enhanced low-temperature antimicrobial performance to distinct metabolic inhibition mechanisms relevant for improving microbial safety in fermented foods.

A joint study between William & Mary (Williamsburg, Virginia) and James Madison University (Harrisonburg, Virginia) analyzed volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from commercially produced and locally sourced kombucha products using gas chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry and flame ionization detection (GC-TOF-MS/FID) and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled with TOF-MS and FID (GC×GC-TOF-MS/FID). LCGC International spoke with Sarah Foster, lead author of the paper resulting from this study, about the team’s findings and the key takeaways from this study.
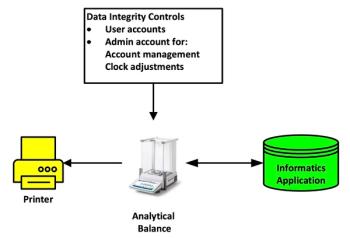
A new version of United States Pharmacopeia (USP) <41> Balances becomes effective in February 2026. This installment of “Questions of Quality” explores the impact of the changes this brings, along with developments in the Japanese and European Pharmacopoeias.

University of Erlangen–Nuremberg researchers applied a bottom-up proteomics workflow centered on microflow liquid chromatography (microLC) coupled to ion mobility quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (QTOF-MS) to authenticate walnut products and detect adulteration with cashew, hazelnut, and peanut.

Top articles published this week highlight troubleshooting issues close to the point of sample injection and the importance of continued collaboration between industry and academia.

The Pittsburgh Conference on Analytical Chemistry and Applied Spectroscopy (Pittcon) has served as a major international meeting for analytical scientists across academia, industry, and government laboratories for more than 75 years. Pittcon 2026 will take place March 7–11, 2026, at the Henry B. González Convention Center in San Antonio, Texas, under the conference theme The Scientific Frontier.

A liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) method for the determination of 39 emerging contaminants in water at ultra trace concentrations has been developed and validated.
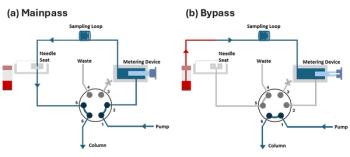
In this installment of “LC Troubleshooting,” we take a close look at how the commonly used “flow-through needle” sampler works, discuss how and where leaks can develop, and solutions to the problems when they do occur.
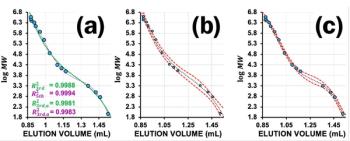
Bob Pirok discusses the use of R², adjusted R², and F-tests to pick the right SEC calibration curve polynomial to avoid overfitting.

Researchers compared leaf and in vitro callus extracts of Eucalyptus camaldulensis using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) to assess phytochemical composition and bioactivity. Callus extracts contained a greater diversity and higher abundance of secondary metabolites, including flavonoids and key volatiles such as 1,8-cineole, α-terpineol, and sabinene. Bioassays showed superior anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity in callus-derived oils, surpassing standard drugs, highlighting tissue culture as a powerful tool for enhancing natural therapeutic compounds.

LCGC International salutes Jack Henion and Bob W.J. Pirok, winners of the 19th annual LCGC Lifetime Achievement and Emerging Leader in Chromatography Awards, respectively.