An Improved SPE-LC–MS–MS Platform for the Simultaneous Quantification of Multiple Amyloid Peptides in Cerebrospinal Fluid for Preclinical or Biomarker Discovery
The Application Notebook
Fast, flexible platforms for peptide quantification are needed, particularly for a discovery setting. This type of methodology would be especially advantageous in the case of amyloid beta (a?) peptides.
Erin E. Chambers1, Mary E. Lame2, and Diane M. Diehl1, 1Waters Corporation and 2Pfizer, Neuroscience Research Unit
Fast, flexible platforms for peptide quantification are needed, particularly for a discovery setting. This type of methodology would be especially advantageous in the case of amyloid beta (aβ) peptides. The deposition/formation of insoluble aggregates, or plaques, of aβ peptides in the brain is considered to be a critical event in the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and thus has the attention of many researchers. A previous Waters application note (720003682en) described in detail the development of a fast, flexible SPE-LC–MS–MS platform for the quantification of multiple aβ peptides from human or monkey CSF for use in a biomarker or preclinical discovery setting. In this work, the mass spectrometry platform has been updated from the Xevo TQ MS to the Xevo TQ-S mass spectrometry system. This change facilitated both a 4× reduction in required sample size and a 4–5× increase in assay sensitivity. This work focuses on methods for the 1–38, 1–40, and 1–42 aβ, Table I.

Table I: Sequence, MW, and pI Information for Amyloid Peptides
Experimental Conditions
SPE-LC–MS–MS Conditions
LC system: Waters ACQUITY UPLC System
Column: ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 300 Å, 2.1 × 150 mm, 1.7 µm, Peptide Separation Technology
SPE: Oasis MCX µElution 96-well plate, 50 µL human or animal CSF
MS system: Waters Xevo TQ-S, ESI+
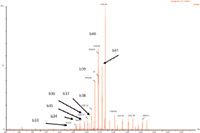
Figure 1: Representative ESI+ MS-MS spectrum for amyloid 1-42 with fragment sequence ions labeled.
Results and Conclusions
- An improved SPE-UPLC–MS–MS bioanalytical method was developed and validated for the simultaneous quantification of multiple amyloid β peptides in human CSF.
- MS was performed in positive ion mode since CID of the 4+ precursor ion yielded several distinct product ions corresponding to inherently specific b sequence ions (representative spectrum shown in Figure 1).
- UPLC separation of the three amyloid β peptides is shown in Figure 2.
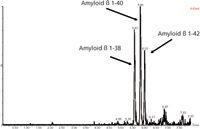
Figure 2: Representative UPLCâMSâMS analysis of amyloid 1-38, 1-40, and 1-42 peptides extracted from artificial CSF + 5% rat plasma.
- The increased sensitivity of the Xevo TQ-S triple quadrupole mass spectrometer facilitated the use of 4× less sample and a 4–5× improvement in quantification limits (Table II).
- Average basal levels and RSD values for all 3 aβ peptides in two sources of human CSF are shown in Table III and are lower or equal to 5%.
- Overspiked QC samples were prepared in triplicate in two sources of pooled human CSF at 0.04, 0.075, 0.15, 0.2, 0.8, 2, and 6 ng/mL. Accuracy and precision values met the regulatory criteria for LC–MS–MS assays. Results from QC sample analysis are shown in Table IV. Average deviation from expected is 2.3%.
- The method described herein eliminates time-consuming immunoassays or immunoprecipitation steps for preclinical work.
- The use of a single UPLC–MS–MS assay represents a significant advantage over an ELISA assay, which would require multiple assays with multiple antibodies to quantify each of the relevant peptides.
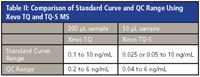
Table II: Comparison of Standard Curve and QC Range Using Xevo TQ and TQ-S MS
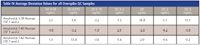
Table IV: Average Deviation Values for all Overspike QC Samples
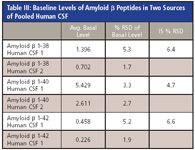
Table III: Baseline Levels of Amyloid β Peptides in Two Sources of Pooled Human CSF
Copyright 2010: ACQUITY UPLC, Oasis, The Science of What's Possible, Xevo are trademark of Waters Corporation.
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street, Milford, MA 01757
tel. (508) 478-2000, fax (508) 478-1990
Website: www.waters.com

Polysorbate Quantification and Degradation Analysis via LC and Charged Aerosol Detection
April 9th 2025Scientists from ThermoFisher Scientific published a review article in the Journal of Chromatography A that provided an overview of HPLC analysis using charged aerosol detection can help with polysorbate quantification.
Analyzing Vitamin K1 Levels in Vegetables Eaten by Warfarin Patients Using HPLC UV–vis
April 9th 2025Research conducted by the Universitas Padjadjaran (Sumedang, Indonesia) focused on the measurement of vitamin K1 in various vegetables (specifically lettuce, cabbage, napa cabbage, and spinach) that were ingested by patients using warfarin. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) equipped with an ultraviolet detector set at 245 nm was used as the analytical technique.
Removing Double-Stranded RNA Impurities Using Chromatography
April 8th 2025Researchers from Agency for Science, Technology and Research in Singapore recently published a review article exploring how chromatography can be used to remove double-stranded RNA impurities during mRNA therapeutics production.




















