Hydroxyethylstarches (HES)
The Application Notebook
Hydroxyethylstarches (HES) are used increasingly as plasma expanders in medical applications. The HES's circulation time in the blood depends strongly on its molar mass distributions.
Hydroxyethylstarches (HES) are used increasingly as plasma expanders in medical applications. The HES's circulation time in the blood depends strongly on its molar mass distributions. Historically, polysaccharide characterization by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) has been problematic, especially if high molar mass components are present. Because of its superior separation capability, especially on molecules exceeding 50 kDa, flow field-flow fractionation (Flow-FFF) is an excellent separation alternative. By coupling this technology to a multi angle light scattering (MALS) detector, such as a DAWN or miniDAWN, absolute values can be determined without making any assumptions.
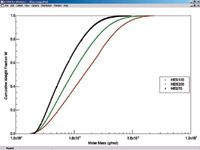
Figure 1: The fractograms of the three samples with their molar mass values overlaid.
We characterized 0.2% (w/v) HES solutions in doubly-distilled water. The HES types were 200/0.5, 130/0.42, and 70/0.5 from Serumwerk (Bernburg, Germany). The FFF system was an Eclipse connected to a DAWN EOS and an RI detector (Shodex 101). Volumes of 100 µL were injected into the 350-µm spacer channel containing a 10 kDa regenerated cellulose membrane. A channel flow of 1 mL/min was kept constant while the cross flow decreased linearly from 2 mL/min to 0 mL/min within 20 min. Data were evaluated using Wyatt's ASTRA software package.
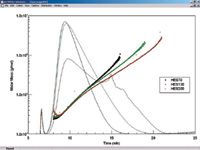
Figure 2: Three different HES samples shown on the cumulative weight fraction plot of ASTRA, indicating the large differences among them.
The aF-FFF/MALS fractograms of the HES types are compared in Figure 1. Corresponding to normal mode Flow-FFF theory, samples with smaller average molar mass elute faster. In Figure 2, the molar mass distributions are given as cumulative weight fraction plots. As is evident in the plots, monomodal distributions were successfully achieved. The values covered a range from approximately 20 kDa to approximately 600 kDa and up to 2 GDa in size, depending on the characterized HES type. Thus, the average molar mass value was mainly influenced by high molar mass fractions. This was also indicated by higher polydispersity values for HES types with higher molar mass.
Asymmetrical FFF/MALS is, therefore, an excellent method for characterizing medical polysaccharides such as HES. The main advantage of this technique is that molar mass distributions can be determined from absolute values over an extremely wide range of masses.
Wyatt Technology Corporation
6300 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, CA 93117
tel. (805) 681-9009, fax (805) 681-0123
E-mail: info@wyatt.com, Website: www.wyatt.com

Regulatory Deadlines and Supply Chain Challenges Take Center Stage in Nitrosamine Discussion
April 10th 2025During an LCGC International peer exchange, Aloka Srinivasan, Mayank Bhanti, and Amber Burch discussed the regulatory deadlines and supply chain challenges that come with nitrosamine analysis.




















