
Advances in Sample Preparation: Removing Phospholipids from Biological Samples

Advances in Sample Preparation: Removing Phospholipids from Biological Samples
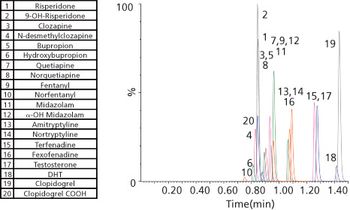

Fast, flexible platforms for peptide quantification are needed, particularly for a discovery setting. This type of methodology would be especially advantageous in the case of amyloid beta (a?) peptides.

The growing market for biotherapeutic peptides and the development of quantitative methods for those analytes has brought to light the challenges facing the analysis of this broad range of compounds. Market forces and regulatory requirements are encouraging analytical groups to develop methodologies that are time- and cost-effective, while still producing assays that are sensitive enough to cope with biological matrices.
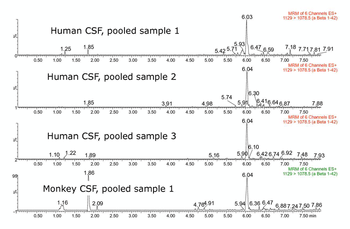

Streamlined sample prep, LC and MS method development.

Streamlined sample prep, LC and MS method development.

Zhe Yin, Kenneth J. Fountain, Erin E. Chambers and Diane M. Diehl, Waters Corporation, Milford, Massachusetts, USA.

Morphine is an effective pain-relieving drug that is primarily metabolized into morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G) and morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G). The highly potent M6G may have adverse effects, such as respiratory depression and renal failure, if accumulated in the body. As morphine abuse continues to affect modern society, an effective method must be established to analyse morphine and its structurally related compounds in biological fluid samples. In this work, a UPLC–MS-MS method was developed to separate six morphine-related compounds on a 2.1 Ã- 100 mm, 1.8 μm ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 column in a single run using an ACQUITY UPLC system connected to a fast-scanning triple-quadrupole MS detector (TQD). The method achieved adequate retention of these very polar compounds by reversed-phase (RP) chromatography in an 8-min total run time.

A highly sensitive analytical method for the analysis of tamsulosin in human plasma has been developed for use in bioanalytical studies. The solid-phase extraction (SPE) and UPLC–MS–MS methodologies are described, as well as performance against validation parameters.

Several common birth control formulations contain both drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol. A highly selective and sensitive analytical method for the analysis of drospirenone in human plasma has been developed for use in bioequivalence studies. The solid-phase extraction (SPE) and UPLC–MS–MS methodologies are described as well as performance against validation parameters.

Several common birth control formulations contain both drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol. A highly selective and sensitive analytical method for the analysis of drospirenone in human plasma has been developed for use in bioequivalence studies. The solid-phase extraction (SPE) and UPLC®–MS–MS methodologies are described as well as performance against validation parameters.

Using ACQUITY UPLC technology with triple quadrupole MS detection enhances the selectivity, sensitivity and throughput in quantitative bioanalytical studies. Detection limits for these methods are being driven lower and lower as drugs become more potent.

The use of 30 mm UPLC columns coupled with Oasis SPE in µElution format was investigated to increase the speed of quantitative bioanalytical methods while maintaining sensitivity and resolution of closely related analytes.

Published: December 2nd 2012 | Updated:

Published: April 1st 2011 | Updated:

Published: March 2nd 2010 | Updated:

Published: March 2nd 2010 | Updated:

Published: September 1st 2010 | Updated: