Advantages of Shodex NH2P Series, Polymer-Based Amino HILIC Column, Over Silica-Based Amino HILIC Columns
The Application Notebook
Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) has become a popularly used separation mode for carbohydrate HPLC method. There are wide variations in HILIC stationary phase.
Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) has become a popularly used separation mode for carbohydrate HPLC method. There are wide variations in HILIC stationary phase. The base material can be silica or polymer, and they are modified with different types of polar functionalities such as amide, amino, diol, and cyano. Shodex™ Asahipak NH2P series column is filled with a polyvinyl alcohol based gel, modified with polyamine. In this article, we compare the performance of a NH2P series column and a silica-based amino HILIC column.
Experimental Conditions
A NH2P-50 4E column and a silica-based amino column, obtained from another company, were compared for their analytical performances. Mobile phase consisted of a mixture of acetonitrile and water. A conventional HPLC system was used with a Shodex™ RI detector.
Results
When acetonitrile concentration was increased, NH2P-50 4E provided stronger retention and a higher theoretical plate number for all saccharides and sugar-alcohols. In contrast, the silica-based amino column showed nonconsistent changes in the theoretical plate number and sensitivity to some saccharides. This was more obvious for galactose measurement that showed considerably lower sensitivity with a silica-based amino column (Figure 1).
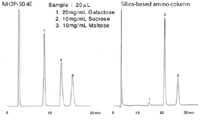
Figure 1: Comparison of saccharides analysis by a NH2P-50 4 E and a silica-based amino column. Column dimensions; 4.6 à 250 mm, Eluent; CH3CN/H2O = 75/25, Flow rate; 1.0 mL/min, Temp.; 25 °C, Detector; Shodex⢠RI.
In addition to saccharide separations, NH2P columns are suitable for sugar-alcohol and saccharides separations. Separation of some sugar-alcohol and saccharide pairs (for example, sorbitol and glucose) is difficult by a silica-based HILIC column, whereas a NH2P column provides a base-line separation of those two.
Another advantage of polymer-based NH2P columns is the inherent chemical stability, solving the deterioration problem over time that conventional silica-based columns have. One proof of high chemical tolerance is its wide pH working capability (2–13). This allows a large selection of usable eluents including different cleaning solvents. The performance tests under very extreme conditions (over 60 h of 0.1 N H2SO4 and over 160 h of 0.005 N NaOH at pH 11.4) showed no considerable deterioration of the column. Thus, it is also suitable for the method that requires an alkaline condition, such as separation of pyridylamino-derivatives.
Moreover, very small "bleeding" of particles has been reported in NH2P series column. Consequently, this reduces the back-ground noise level. This is especially beneficial when coupling the HPLC with a corona charged aerosol detection or an evaporative light scattering detector systems.
Conclusions
Advantages of polymer-based amino column, Shodex™ NH2P series, over conventional silica-based amino columns are: (i) no adsorption of particular saccharides or sugar-alcohols, (ii) tolerances towards wide range of working conditions, and (iii) small bleeding. Using those advantages, the possible applications of NH2P series include analysis of carbohydrates in food stuff, and in biomedical areas such as analysis of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Shodex/Showa Denko America, Inc.
420 Lexington Avenue Suite 2850, New York, NY, 10170
tel. (212) 370-0033, fax (212) 370-4566
Website: www.shodex.net
Email: support@shodex.net

Detecting Hyper-Fast Chromatographic Peaks Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry
May 6th 2025Ion mobility spectrometers can detect trace compounds quickly, though they can face various issues with detecting certain peaks. University of Hannover scientists created a new system for resolving hyper-fast gas chromatography (GC) peaks.
University of Oklahoma and UC Davis Researchers Probe Lipidomic Profiles with RP-LC–HRMS/MS
May 6th 2025A joint study between the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center (Oklahoma City, Oklahoma) and the UC Davis West Coast Metabolomics Center (Davis, California) identified differentially regulated lipids in type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity through the application of reversed-phase liquid chromatography-accurate mass tandem mass spectrometry (RP-LC-accurate MS/MS).
Automated Sample Preparation (ISO 20122) for MOSH/MOAH in Seasoning Oils
May 6th 2025This work presents an Automated Sample Preparation procedure for MOSH/MOAH analysis of Seasoning Oils. We compare results from a manual epoxidation procedure compliant with DIN 16995 with results based on fully automated sample preparation (epoxidation and saponification) compliant with ISO 20122. In both cases, online clean-up via activated aluminum oxide (AlOx) are used to remove interfering n-alkanes from the MOSH fraction during the HPLC run. Automated data evaluation using a dedicated software (GERSTEL ChroMOH) is presented.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)


















