Glyphosate Analysis in Soy Beans, Corn, and Sunflower Seeds by HPLC with Post-Column Derivatization and Fluorescence Detection
The Application Notebook
Glyphosate is a broad-spectrum herbicide widely used around the world. Monitoring of glyphosate in crops and water is mandated in many countries.
Glyphosate is a broad-spectrum herbicide widely used around the world. Monitoring of glyphosate in crops and water is mandated in many countries. We describe a sensitive and robust HPLC method for analysis of glyphosate in soy beans, corn, and sunflower seeds. This method utilizes a simplified sample preparation procedure that has proven to be effective even for challenging matrices.

Supplies for Sample Preparation
Methylene Chloride, HPLC Grade
Acidic Modifier Solution (16 g KH2PO4, 160 mL of water, 40 ml of Methanol, 13.4 mL of conc. HCl)
Elution Solution (160 mL of water, 40 mL of Methanol, 2.7 mL of HCl)
RESTORE™
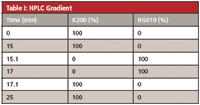
Table I: HPLC Gradient
SPE sample clean-up cartridges P/N 1705-0001
Sample Preparation
Extraction
To 25 g of homogenized sample, add enough water (after estimating moisture content) such that the total volume of water is 125 mL. Blend at high speed for 3–5 min and centrifuge for 10 min. Transfer 20 mL of the aqueous extract into a centrifuge tube and add 15 mL of methylene chloride. Shake for 2–3 min and centrifuge for 10 min. Transfer 4.5 mL of aqueous layer to another centrifuge tube and add 0.5 mL of acidic modifier solution. Shake and centrifuge for 10 min. Filter through a 0.45 μm filter.
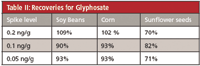
Table II: Recoveries for Glyphosate
Matrix-Specific Modifications
Matrix with high 1) Water; 2) Protein; 3) Fat Content:
1) For samples that absorb large amounts of water, reduce test portion to 12.5 g while keeping water volume the same.
2) For samples with high protein content, add 100 μL of concentrated HCl to 20 mL of crude extract. Shake and centrifuge for 10 min.
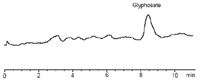
Figure 1: Chromatogram of soy beans sample spiked with Glyphosate at 0.1 ppb level.
3) For samples with high fat content, do the methylene chloride partitioning twice.
SPE Cleanup
Remove the top cap first, then the bottom cap of the SPE columns and place them into the manifold. Drain the solution to the top of the resin bed. Transfer 1 mL of extract into the column and elute to the top of the resin bed. Add 0.7 mL of the elution solution and discard the effluent. Repeat with a second 0.7 mL portion of the elution solution and discard the effluent. Elute glyphosate with 12 mL of the elution solution and collect the effluent in a round bottom flask. Evaporate to dryness at 40 °C using a rotary evaporator. Dissolve the residue in 2.0 mL of a solution of 10% RESTORE™ in water (use 1.5 mL for dry samples), filter through a 0.45 μm syringe filter and inject onto the HPLC column. Extracts can be stored refrigerated for up to seven days before the evaporation step.
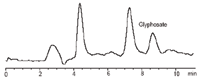
Figure 2: Chromatogram of corn sample spiked with Glyphosate at 0.1 ppb level.
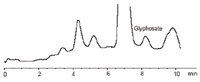
Figure 3: Chromatogram of sunflower seeds sample spiked with Glyphosate at 0.1 ppb level.
Pickering Laboratories
1280 Space Park Way, Mountain View, CA 94043
tel. (800) 654-3330, fax (408) 694-6700
Website: www.pickeringlabs.com

Investigating 3D-Printable Stationary Phases in Liquid Chromatography
May 7th 20253D printing technology has potential in chromatography, but a major challenge is developing materials with both high porosity and robust mechanical properties. Recently, scientists compared the separation performances of eight different 3D printable stationary phases.
Detecting Hyper-Fast Chromatographic Peaks Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry
May 6th 2025Ion mobility spectrometers can detect trace compounds quickly, though they can face various issues with detecting certain peaks. University of Hannover scientists created a new system for resolving hyper-fast gas chromatography (GC) peaks.
University of Oklahoma and UC Davis Researchers Probe Lipidomic Profiles with RP-LC–HRMS/MS
May 6th 2025A joint study between the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center (Oklahoma City, Oklahoma) and the UC Davis West Coast Metabolomics Center (Davis, California) identified differentially regulated lipids in type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity through the application of reversed-phase liquid chromatography-accurate mass tandem mass spectrometry (RP-LC-accurate MS/MS).

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)


















