Analysis of Phosphate Compounds with Agilent 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC system
The Application Notebook
Agilent
This application note shows that unspecific reaction of adenosine triphosphate can be completely prevented due to the iron and steel-free design using the Agilent 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC System.
Severe peak tailing of phosphate compounds is a well described issue in HPLC analysis. Interaction between stainless steel and phosphate groups were described by Liu et al. leading to the formation of phosphopeptide-Fe(III) complexes (1). The 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC System provides a complete metalfree sample flow path throughout the system. With this system, the user can analyse a variety of phosphate compounds without the emersion of peak tailing or other unspecific reaction due to phosphate–iron complexes.
Experimental Conditions
Solvents: 10 mM ammonium acetate with increasing amount of methanol
Sample: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), solved in H2Odd (5 mg/mL)
A PEEK restriction capillary was used instead of a stainless steel column.
Results
Significant peak tailing could be observed for ATP analysis in a stainless steel based system, the 1260 Infinity Quaternary LC System. With increasing amount of organic mobile phase, the retention of the phosphate compound was increasing to a huge extent, also resulting in relevant area reduction, see Figure 1.
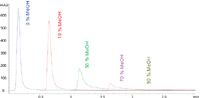
Figure 1: ATP analysis on Agilent 1260 Infinity Quaternary System.
With the 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC System, the unspecific reaction of the used phosphate sample could be completely prevented, resulting in good peak shapes without substantial peak tailing or area reduction, see Figure 2.
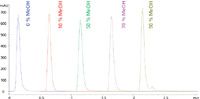
Figure 2: ATP analysis on the Agilent 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary System.
Conclusions
Unspecific reaction and peak tailing of adenosine triphosphate could be completely prevented when using the Agilent 1260 Infinity Bioinert Quaternary LC System. Due to the iron and steelfree design of the 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC system, phosphate compounds can be analyzed without any issues regarding the formation of phosphate–iron complexes as found with stainless steel systems.
Reference
(1) Liu et al., Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 19(19), 2747–2756 (2005).
Agilent Technologies Inc.
5301 Stevens Creek Blvd., Santa Clara, California 95051, USA
tel. (800) 227 9770 (Directory) fax (866) 497 1134
Website: www.agilent.com

Altering Capillary Gas Chromatography Systems Using Silicon Pneumatic Microvalves
May 5th 2025Many multi-column gas chromatography systems use two-position multi-port switching valves, which can suffer from delays in valve switching. Shimadzu researchers aimed to create a new sampling and switching module for these systems.
Studying Cyclodextrins with UHPLC-MS/MS
May 5th 2025Saba Aslani from the University of Texas at Arlington spoke to LCGC International about a collaborative project with Northwestern University, the University of Hong Kong, and BioTools, Inc., investigating mirror-image cyclodextrins using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS) and vibrational circular dichroism (VCD).

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)


















