Simultaneous Extraction of Ethyl Glucuronide (EtG) and Ethyl Sulphate (EtS) from urine with EVOLUTE AX prior to LC–MS-MS analysis
The Application Notebook
Biotage AB
This application note describes the extraction of both ethyl glucuronide (EtG) and the lower concentration metabolite ethyl sulphate (EtS) from human urine using EVOLUTE AX columns followed by LC-MS-MS analysis. EtG and EtS are specific metabolites formed within the body after the ingestion of alcohol. EVOLUTE AX is a resin-based mixedmode sorbent with an optimized combination of non-polar (hydrophobic), polar (hydrophilic) and weak anion exchange interactions ideally constructed to extract acidic analytes such as ethyl glucuronide.
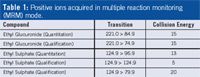
Table 1: Positive ions acquired in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode.
Extraction Conditions
Sample pre-treatment: Dilute urine samples with acetonitrile (1:9, v/v)
Column conditioning: Methanol (3 mL)
Column equilibration 1: Water (3 mL)
Column equilibration 2: Acetonitrile (3 mL)
Sample loading: Load pre-treated sample (2 mL total volume) onto EVOLUTE AX 100 mg/3 mL column (part number 6130010-B)
Interference elution 1: Acetonitrile (3 mL)
Interference elution 2: Methanol (3 mL)
Analyte elution: 2% HCl in acetonitrile (3 mL)
Evaporation: Evaporate to dryness at 40 °C
Reconstitution: Reconstitute in HPLC grade water (250 µL), vortex mix and add acetonitrile (250 µL), vortex mix
Analytical Conditions
Instrument: Waters Acquity UPLC with 20 µL injection loop interfaced to Premier XE triple quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with an electrospray interface for mass analysis.
Column: UPLC HSS C18 (150 mm × 1.8 µm × 2.1 mm i.d.)
Mobile phase: A = 0.05% Formic acid (aq) B = Acetonitrile
Flow rate: 0.2 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL (partial loop with overfill)
Sample temp: 10 °C
Column temp: 50 °C
Desolvation temp: 450 °C
Source temp: 100 °C
Results
Recoveries of > 90% were achieved for all EtG and > 80% for EtS, with relative standard deviation (RSD) < 10%. Limit of quantifications (LOQs) were 10 ng/mL for EtG and 2 ng/mL for EtS. Figure 1 shows both extracted ion chromatograms for both analytes at 100 ng/mL.

Figure 1: Extracted ion chromatograms EtG and EtS at 100 ng/mL.
Conclusions
Using a modified solid phase extraction protocol incorporating a polar aprotic solvent (ACN) demonstrates excellent extract cleanliness for both EtG and EtS. This protocol demonstrates a significant improvement over the established 'dilute and shoot' approach, increasing signal and reducing downtime on the LC–MS–MS.
Reference
(1) For complete details of this application, see Application Note AN755, available from www.biotage.com/applications
Biotage AB
Kungsgaten 76, SE-753, 18, Uppsala, Sweden
tel. +46 18 56 59 00 fax +46 18 59 19 22
E-mail: info@biotage.com Website: www.biotage.com

Regulatory Deadlines and Supply Chain Challenges Take Center Stage in Nitrosamine Discussion
April 10th 2025During an LCGC International peer exchange, Aloka Srinivasan, Mayank Bhanti, and Amber Burch discussed the regulatory deadlines and supply chain challenges that come with nitrosamine analysis.
Polysorbate Quantification and Degradation Analysis via LC and Charged Aerosol Detection
April 9th 2025Scientists from ThermoFisher Scientific published a review article in the Journal of Chromatography A that provided an overview of HPLC analysis using charged aerosol detection can help with polysorbate quantification.





















