Rapid Improvements for LC–MS-MS Analysis Using the New Phree Phospholipid Removal Plates
The Application Notebook
Phenomenex
When performing LC–MS-MS analysis, phospholipids are perhaps one of the most troublesome components of bioanalytical samples. The presence of phospholipids not only reduces the column lifetime and sensitivity but can also cause a phenomenon known as ion suppression.
This work compares the presence of phospholipids in plasma samples after two different sample preparation techniques, protein precipitation and simultaneous protein precipitation and phospholipid removal using a new product, Phree.
Experimental Conditions
Plasma samples from the same lot were prepared (Table 1) and were injected on a Kinetex® 2.6 µm C18 core–shell column coupled with an API 3000 MS (AB SCIEX) (Figure 1). A total phospholipid profile was monitored using m/z 184–184.
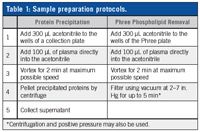
Table 1: Sample preparation protocols.
Results and Discussion
When monitoring the total phospholipid profile, the protein precipitated plasma showed a large amount of phospholipids. In comparison, the plasma sample that was prepared using Phree showed virtually no phospholipids (Figure 1).
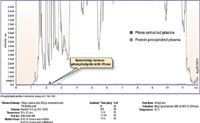
Figure 1: Total phospholipid profile.
We also studied analyte response by comparing diclofenac spiked plasma samples. After sample preparation, 20 µL samples were injected on a Kinetex® 2.6 µm C18 core–shell column. The diclofenac signal in the protein precipitated samples was immediately lower than the signal in the Phree extracted samples. The signal in the protein precipitated sample rapidly decreases. The Phree extracted sample shows a steadier signal and is able to withstand > 250 injections (Figure 2). The higher signal strength of the Phree extracted sample is due to the reduction of phospholipid induced ion suppression. The significant reduction in phospholipid build up on the column and MS source also resulted in an increase in column lifetime and a decrease in the amount of MS maintenance required.
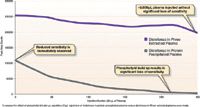
Figure 2: Column sensitivity after 250 injections.
Conclusion
By preparing samples with Phree, analysts can remove proteins and phospholipids in 4 short steps resulting in immediate improvements to their chromatography work.
For more information about Phree, visit www.phenomenex.com/Phree.
Phenomenex Inc.
411 Madrid Avenue, Torrance, California 90501, USA
tel. +1 (310) 212 0555 +1 (310) 328 7768
Website: www.phenomenex.com

New Method Explored for the Detection of CECs in Crops Irrigated with Contaminated Water
April 30th 2025This new study presents a validated QuEChERS–LC-MS/MS method for detecting eight persistent, mobile, and toxic substances in escarole, tomatoes, and tomato leaves irrigated with contaminated water.
Accelerating Monoclonal Antibody Quality Control: The Role of LC–MS in Upstream Bioprocessing
This study highlights the promising potential of LC–MS as a powerful tool for mAb quality control within the context of upstream processing.
University of Tasmania Researchers Explore Haloacetic Acid Determiniation in Water with capLC–MS
April 29th 2025Haloacetic acid detection has become important when analyzing drinking and swimming pool water. University of Tasmania researchers have begun applying capillary liquid chromatography as a means of detecting these substances.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



















