Reversed-Phase Analyses of Monoclonal Antibodies Using High Temperatures
The Application Notebook
This application note shows how to achieve robust chromatographic results for two commercially available mAbs: Adalimumab (Humira®) and Bevacizumab (Avastin®).
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are immunological active proteins, which bind specifically to certain cells or proteins. This will stimulate the immune system to attack those targets.
mAbs are very important for the treatment of different kinds of cancer and autoimmune diseases. Nowadays, a broad variety of therapeutical antibodies are available on the market and several more are in research and development.
Due to their molecular weight of about 150 kDa, intact antibodies are usually analyzed by IEX, SEC, or HIC. In addition, reversedâphase methods are an easy tool as well.
However, a lack of sensitivity and resolution has been a hurdle in the past. With modern reversed phases addressing the requirements of these analytes, it is easy to find a suitable method.
Successful analysis in reversed-phase mode for mAbs is enhanced by employing a temperature stable (> 60 °C), widepore stationary phase.
This application note shows how to achieve robust chromatographic results for two commercially available mAbs: Adalimumab (Humira®) and Bevacizumab (Avastin®).
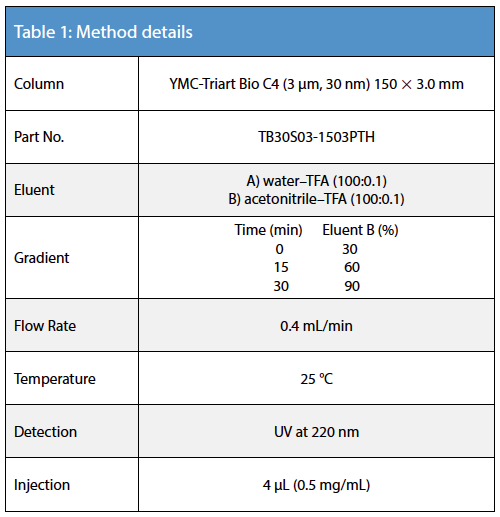
The increase in temperatures leads to higher sensitivity and a sharper peak of Adalimumab at temperatures >60 °C (Figure 1).
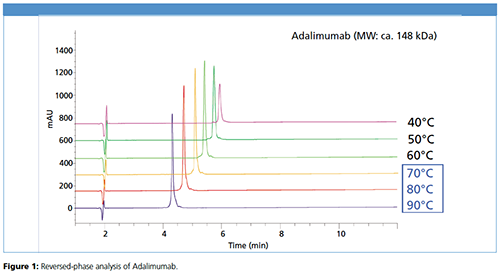
Bevacizumab shows robust results starting from 70 °C, whereas at lower temperatures no peak was detected (Figure 2).
With YMC-Triart Bio C4, elevated temperatures can easily be applied, due to stability up to 90 °C. In addition, the surface comprising 30 nm/300 Å is beneficial for resolution. In combination with a wide pH range of 1–10 YMC-Triart Bio C4 is a well-suited tool for any mAb (U)HPLC method.

YMC Europe GmbH
Tel.: +49 2064 4270
E-mail: info@ymc.de
Website: www.ymc.de

Measuring Procyanidin Concentration in Wines Using UHPLC
January 24th 2025Researchers from the University of Bordeaux (Villenave d'Ornon, France) report the development and validation of a rapid and quantitative analytical method measuring crown procyanidin concentration in red and white wines using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) coupled with a ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (Q-TOF) mass spectrometer.
The Next Frontier for Mass Spectrometry: Maximizing Ion Utilization
January 20th 2025In this podcast, Daniel DeBord, CTO of MOBILion Systems, describes a new high resolution mass spectrometry approach that promises to increase speed and sensitivity in omics applications. MOBILion recently introduced the PAMAF mode of operation, which stands for parallel accumulation with mobility aligned fragmentation. It substantially increases the fraction of ions used for mass spectrometry analysis by replacing the functionality of the quadrupole with high resolution ion mobility. Listen to learn more about this exciting new development.
The Complexity of Oligonucleotide Separations
January 9th 2025Peter Pellegrinelli, Applications Specialist at Advanced Materials Technology (AMT) explains the complexity of oligonucleotide separations due to the unique chemical properties of these molecules. Issues such as varying length, sequence complexity, and hydrophilic-hydrophobic characteristics make efficient separations difficult. Separation scientists are addressing these challenges by modifying mobile phase compositions, using varying ion-pairing reagents, and exploring alternative separation modes like HILIC and ion-exchange chromatography. Due to these complexities, AMT has introduced the HALO® OLIGO column, which offers high-resolution, fast separations through its innovative Fused-Core® technology and high pH stability. Alongside explaining the new column, Peter looks to the future of these separations and what is next to come.
Testing Solutions for Metals and PFAS in Water
January 22nd 2025When it comes to water analysis, it can be challenging for labs to keep up with ever-changing testing regulations while also executing time-efficient, accurate, and risk-mitigating workflows. To ensure the safety of our water, there are a host of national and international regulators such as the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), World Health Organization (WHO), and the European Union (EU) that demand stringent testing methods for drinking water and wastewater. Those methods often call for fast implementation and lengthy processes, as well as high sensitivity and reliable instrumentation. This paper explains how your ICP-MS, ICP-OES, and LC-MS-MS workflows can be optimized for compliance with the latest requirements for water testing set by regulations like US EPA methods 200.8, 6010, 6020, and 537.1, along with ISO 17294-2. It will discuss the challenges faced by regulatory labs to meet requirements and present field-proven tips and tricks for simplified implementation and maximized uptime.