Separation and Identification of Non-Covalent Metal Complexes from Bacteria by HILIC–MS
The Application Notebook
In this study, we aimed to use a charge modulated HILIC stationary phase (iHILIC®-Fusion) to separate different siderophores of the Pseudomonas taiwanensis VLB120 bacteria.
Pseudomonas bacteria are a genus of rod-shaped, ubiquitous, and gram-negative bacteria, which are resistant against commonly used antibiotics and disinfectants. Pseudomonads are able to survive in extreme conditions (1) and are increasingly used as whole-cell biocatalysts. The range of their biotechnological applications is not limited by the toxicity of used chemicals because of their manifold survival strategies (2).
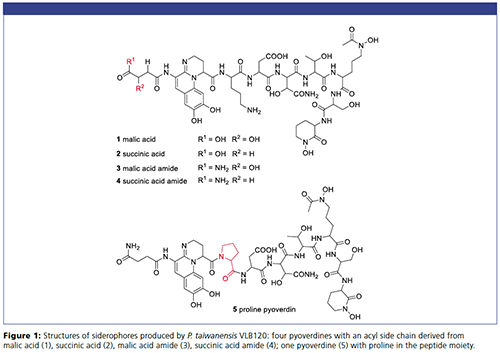
Pseudomonads require iron(III) for metabolism and growth. Under aerobic conditions, the iron(III) is almost insoluble and the pseudomonas bacteria synthesize yellow-green fluorescent molecules called pyoverdines. These molecules can react with iron(III) and form stable hexadentate iron(III)-complexes in the extracellular space and transport the metal (1). The pyoverdines consist of three structural parts: (i) chromophoric unit derived from 2,3-diamino-6,7-dihydroxyqunoline; (ii) strain specific peptide moiety consisting of 6–14 proteinogenic and nonproteinogenic amino acids; (iii) acyl side chain derived from malic acid, succinic acid, their mono amides, α-ketoglutaric acid, or glutamic acid.
Pyoverdines are highly polar molecules that conventional reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is problematic due to insufficient retention. Furthermore, we intended to separate and identify intact metal complexes in our study. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) is well suited for the separation of polar compounds and enables the separation of polar non-covalent metal species (3,4). In this study, we aimed to use a charge modulated HILIC stationary phase (iHILIC®-Fusion) to separate different siderophores of the Pseudomonas taiwanensis VLB120 bacteria.
Experimental
LC–MS System: Agilent 1100er LC system and Q Exactive™ Plus Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap™ mass spectrometer, equipped with a HESI II source, operated in positive ionization mode (ESI+).
Column: 150 × 2.1 mm, 3.5 µm 100 Å, iHILIC®-Fusion (P/N 110.152.0310, HILICON AB, Sweden)
Eluent: A) acetonitrile; B) ammonium bicarbonate (5 mM, pH 7) and acetonitrile (95:5, v/v);
Gradient Elution: 0–0.75 min, 80% A; 0.75–20 min, from 80% A to 40% A; 20–25 min, 40% A; 25–27 min, from 40% A to 80% A; 27–40 min, 80% A
Flow Rate: 0.3 mL/min
Column Temperature: 40 °C
Injection Volume: 5 µL
P. taiwanensis VLB120 Cell Supernatants: Cell supernatants of the P. taiwanensis VLB120 bacteria were provided by Dr. Till Tiso at iAMB (Institute of Applied Microbiology) and ABBt (Aachen Biology and Biotechnology, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany) and purified by solid-phase extraction as described in reference 5. The samples for injection contained five pyoverdines that differ in their acyl side chain and in the peptide moiety (6), shown in Figure 1.
Results and Conclusion
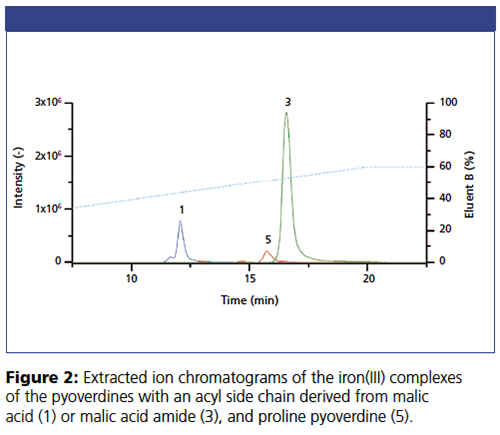
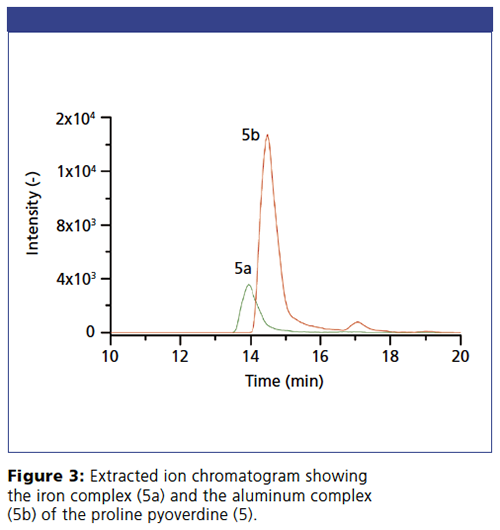
The different siderophores of the P. taiwanensis VLB120 bacteria and their non-covalent iron and aluminium complexes can be simultaneously separated and determined by an iHILIC®-Fusion column hyphenated with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) detection (Figures 2 and 3). Pyoverdines with various acyl side chains exhibit different levels of hydrophilic partitioning and electrostatic interaction with the stationary phase. The extracted ion chromatograms in Figure 3 also demonstrate that the iHILIC®âFusion column is even capable of separating the iron(III) and aluminium(III) complexes of each siderophore. Because of the smaller radius, aluminium has a stronger polarizing effect on the siderophores. Therefore, aluminium(III) complex has higher retention on the HILIC stationary phase. This work demonstrates that intact non-covalent metal complexes can be separated and identified by a HILIC–MS method using an iHILIC®-Fusion column.
References
- C. Cézard, N. Farvacques, and P. Sonnet, Curr. Med. Chem.22, 165–186 (2015).
- J. Volmer, C. Neumann, B. Bühler, and A. Schmid, Appl. Environ. Microbiol.80, 6539–6548 (2014).
- G. Weber, N. von Wiren, and H. Hayen, J. Sep. Sci.31, 1615–1622 (2008).
- J. Köster, R. Shi, N. von Wiren, and G. Weber, J. Chromatogr. A1218, 4934–4943 (2011).
- M. Baune, Y. Qi, K. Scholz, D.A. Volmer, and H. Hayen, BioMetals30, 589–597 (2017).
- K. Scholz, T. Tiso, L.M. Blank, and H. Hayen, BioMetals31, 785–795 (2018).

HILICON AB
Tvistevägen 48, SE-90736, Umeå, Sweden
Tel.: +46 (90) 193469
E-mail: info@hilicon.com
Website: www.hilicon.com

University of Oklahoma and UC Davis Researchers Probe Lipidomic Profiles with RP-LC–HRMS/MS
May 6th 2025A joint study between the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center (Oklahoma City, Oklahoma) and the UC Davis West Coast Metabolomics Center (Davis, California) identified differentially regulated lipids in type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity through the application of reversed-phase liquid chromatography-accurate mass tandem mass spectrometry (RP-LC-accurate MS/MS).
Altering Capillary Gas Chromatography Systems Using Silicon Pneumatic Microvalves
May 5th 2025Many multi-column gas chromatography systems use two-position multi-port switching valves, which can suffer from delays in valve switching. Shimadzu researchers aimed to create a new sampling and switching module for these systems.
Studying Cyclodextrins with UHPLC-MS/MS
May 5th 2025Saba Aslani from the University of Texas at Arlington spoke to LCGC International about a collaborative project with Northwestern University, the University of Hong Kong, and BioTools, Inc., investigating mirror-image cyclodextrins using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS) and vibrational circular dichroism (VCD).

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)










