LC Analysis of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics Kanamycin and Amikacin
The Application Notebook
Kanamycin and amikacin are aminoglycoside antibiotics used to treat serious bacterial infections. Amikacin is used for infections resistant to other aminoglycosides because it is less susceptible to enzymatic reactions.
Kanamycin and amikacin are aminoglycoside antibiotics used to treat serious bacterial infections. Amikacin is used for infections resistant to other aminoglycosides because it is less susceptible to enzymatic reactions. Purified kanamycin from Streptomyces kanamyceticus is mainly kanamycin A, from which amikacin is synthesized by acylation of the kanamycin A amino group with L-(-)-γ-amino-α-hydroxybutyric acid (L-HABA). Kanamycin A and L-HABA are, therefore, expected impurities in amikacin synthesis.
These antibiotics must meet specified purity criteria before clinical use. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) monographs for the assay of kanamycin and amikacin use high-performance, anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAE-PAD) (1,2). Here we evaluate the USP assays using disposable gold on polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) working electrodes with a 4-potential waveform suitable for use with these electrodes. Disposable electrodes are more convenient than conventional electrodes because they are easier to install and do not require time-consuming electrode polishing. Compared to other disposable gold electrodes, the gold on PTFE electrodes have longer lifetimes and can operate at the hydroxide concentration used in the USP assays.
Experimental
A Dionex ICS-3000 system and Chromeleon® Chromatography Data System software were used in this study. Kanamycin and amikacin (20 μL) were separated using a CarboPac® MA1 (USP L47) column set with 115 mM sodium hydroxide at 0.5 mL/min.
Results
Figure 1 shows the <10 min separation of kanamycin and amikacin. Peak resolution was >4, (exceeding the USP requirement of 3); asymmetry for both antibiotics was 1.1 (USP requirement of <2). Retention time RSDs were 0.16 for kanamycin and 0.07 for amikacin for nine replicate injections (USP requirement of <0.3). Intra- and between-day peak area precisions (RSDs) were 0.99 and 1.3 for kanamycin and 1.2 and 2.3 for amikacin. These values suggest that this method effectively assays these antibiotics without column regeneration, and that using a disposable electrode with its associated waveform meets the current USP assay requirements.
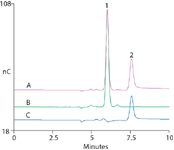
Figure 1: Typical chromatograms of: (A) resolution solution (kanamycin 0.008 mg/mL and amikacin 0.02 mg/mL), (B) commercial kanamycin A sulfate sample, (C) commercial amikacin sample. Peaks: 1. kanamycin (8 μg/mL), 2. amikacin (20 μg/mL).
To demonstrate method capability for stability assays, these antibiotics were studied after exposure to elevated temperatures under acidic or basic conditions. For both antibiotics, most of the degradation products eluted within 10 min. An unidentified late-eluting peak at ~21 min is similar to a late-eluting peak reported for degraded streptomycin (3), which could interfere with quantification if a shorter run time is used. Under basic conditions, amikacin loses its acetylated group resulting in a kanamycin-like molecule.
Conclusion
This method matches and exceeds USP requirements, achieves good sensitivity, and has high sample throughput. Additionally, using disposable electrodes provide shorter equilibrium time and better electrode-to-electrode reproducibility.
References
(1) United States Pharmacopeia (USP), Kanamycin Sulfate, USP34-NF29, 3244.
(2) United States Pharmacopeia (USP), Amikacin Sulfate, USP34-NF29, 1846.
(3) Dionex Corporation, Application Note 181; Sunnyvale, CA.
CarboPac, Chromeleon, and UltiMate are registered trademarks of Dionex Corporation.
Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale CA 94088
tel. (408) 737-0700, fax (408) 730-9403
Website: www.dionex.com

Determining Enhanced Sensitivity to Odors due to Anxiety-Associated Chemosignals with GC
May 8th 2025Based on their hypothesis that smelling anxiety chemosignals can, like visual anxiety induction, lead to an increase in odor sensitivity, a joint study between the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (Erlangen, Germany) and the Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging (Freising, Germany) combined behavioral experiments, odor profile analysis by a trained panel, and instrumental analysis of odorants (gas chromatography-olfactometry) and volatiles (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry).
Investigating 3D-Printable Stationary Phases in Liquid Chromatography
May 7th 20253D printing technology has potential in chromatography, but a major challenge is developing materials with both high porosity and robust mechanical properties. Recently, scientists compared the separation performances of eight different 3D printable stationary phases.
Detecting Hyper-Fast Chromatographic Peaks Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry
May 6th 2025Ion mobility spectrometers can detect trace compounds quickly, though they can face various issues with detecting certain peaks. University of Hannover scientists created a new system for resolving hyper-fast gas chromatography (GC) peaks.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)


















