Virus Particle Characterization
The Application Notebook
Viruses are packets of infectious nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protective coat consisting of a large number of protein subunits. Because viruses can cause various diseases - some life-threatening - characterizing virus particles thoroughly in terms of their size distribution, aggregation and absolute counts-per-unit volume is of extreme importance.
Wyatt Technology Corporation, Santa Barbara, California, USA.
Viruses are packets of infectious nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protective coat consisting of a large number of protein subunits. Because viruses can cause various diseases — some life-threatening — characterizing virus particles thoroughly in terms of their size distribution, aggregation and absolute counts-per-unit volume is of extreme importance.
Though size exclusion chromatography (SEC) has been the primary tool for separating aggregates of molecules, it is generally not appropriate for fractionating viruses because viruses and their aggregates are subject to shearing degradation by the stationary phase. Moreover, they can also be caught by the columns because of their large sizes.
The Eclipse, a particle separation system based upon field flow fractionation (FFF), effectively replaces SEC as a perfect alternative for virus characterization. Because it is analogous to an HPLC separation, the Eclipse — combined with MALS — makes a physical separation of the particles and then sizes them directly as they elute.
This application note reports the results obtained from a set of virus particles fractionated by Eclipse and sized by the 18-angle DAWN EOS on-line multi-angle light scattering instrument.
Figure 1 shows the radius measured by the DAWN EOS detector (from initial slope of angular dependence) versus elution time for two different virus strains. The plots show clearly that aggregates were found in both viruses and much more in Virus 2. Results from duplicate injections of Virus 1 show the excellent reproducibility of the Eclipse-MALS system.
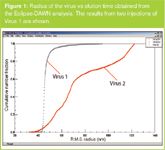
Figure 1
The results are also shown by the cumulative number distribution plots in Figure 2. The cumulative number distribution yields quantitative information on the percentage of aggregates present in each virus strain: 5% for Virus 1 and 95% for Virus 2.

Figure 2
The success of the virus characterization demonstrated above confirms that the Eclipse-MALS approach is an indispensable tool for charactering virus particles — and other colloidal particles — in solution. This approach is especially important when the absolute particle distributions are vital.

Wyatt Technology Corporation
6300 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, California 93117, USA
tel. +1 805 681 9009 fax +1 805 681 0123
Website: www.wyatt.com

Polysorbate Quantification and Degradation Analysis via LC and Charged Aerosol Detection
April 9th 2025Scientists from ThermoFisher Scientific published a review article in the Journal of Chromatography A that provided an overview of HPLC analysis using charged aerosol detection can help with polysorbate quantification.
Analyzing Vitamin K1 Levels in Vegetables Eaten by Warfarin Patients Using HPLC UV–vis
April 9th 2025Research conducted by the Universitas Padjadjaran (Sumedang, Indonesia) focused on the measurement of vitamin K1 in various vegetables (specifically lettuce, cabbage, napa cabbage, and spinach) that were ingested by patients using warfarin. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) equipped with an ultraviolet detector set at 245 nm was used as the analytical technique.
Removing Double-Stranded RNA Impurities Using Chromatography
April 8th 2025Researchers from Agency for Science, Technology and Research in Singapore recently published a review article exploring how chromatography can be used to remove double-stranded RNA impurities during mRNA therapeutics production.














