Reach Polymer Status Analysis of Polyols
The Application Notebook
Polyols are alcohols with multiple hydroxyl groups. They are used for very different applications, such as, for example, in Feed and Food as sugar substitutes or in polymer chemistry as reactants to produce high quality products.
Friedhelm Gores, PSS Polymer Standards Service GmbH, Mainz, Germany.
Introduction
Polyols are alcohols with multiple hydroxyl groups. They are used for very different applications, such as, for example, in Feed and Food as sugar substitutes or in polymer chemistry as reactants to produce high quality products.
REACH (Registration, Evaluation and Authorization of Chemicals) is a European Union (EU) regulation for the production and use of chemical substances. Companies using polyols need a technical dossier to register under regulation EG No. 1907/2006.
Polymers are "special substances" in terms of REACH. However, companies have to proof that their products/educts ARE polymers. The preferred method to identify whether a substance falls under the definition of a polymer is gel permeation chromatography (GPC). Guidelines on the determination of the molecular weight distribution using GPC are available in the OECD TG118 (1996).
Analytical Conditions
The samples were dissolved in THF.

Results
A polymer molecule in the sense of REACH is a molecule that contains a sequence of at least 3 monomer units (M), covalently bound to at least one other monomer unit or reactant (initiator). This definition is equal with the so called (3M+1)-rule. Additional requirements are:
(a) Over 50 percent of the weight for that substance consists of polymer molecules.
(b) The amount of polymer molecules presenting the same molecular weight must be less than 50 weight percent of the substance.
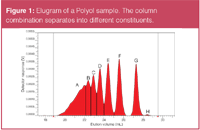
Figure 1
To determine if the above stated requirements are true, a GPC/SEC experiment using high resolution columns is performed. Figure 1 shows the elugram of a Polyol showing separation into individual R-(M)x peaks. The results for the detailed analysis are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1: Content and molar mass average report for a Polyol and comments to the REACH requirements.
Conclusion
The Polyol is a polymer in the context of REACH because:
- Less than 50 weight percent of the sample is below (3M+1), the sample consists mainly of polymer molecules with n >3. The (3M+1)-rule is met.
- None of the different constituents present has a concentration above 50 weight percent.

PSS Polymer Standards Service GmbH
In der Dalheimer Wiese 5, D-55120 Mainz, Germany
tel. +49 6131 96239 50 fax +49 6131 96239 11
E-mail: FGores@polymer.de Website: www.polymer.de

Detecting Hyper-Fast Chromatographic Peaks Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry
May 6th 2025Ion mobility spectrometers can detect trace compounds quickly, though they can face various issues with detecting certain peaks. University of Hannover scientists created a new system for resolving hyper-fast gas chromatography (GC) peaks.
University of Oklahoma and UC Davis Researchers Probe Lipidomic Profiles with RP-LC–HRMS/MS
May 6th 2025A joint study between the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center (Oklahoma City, Oklahoma) and the UC Davis West Coast Metabolomics Center (Davis, California) identified differentially regulated lipids in type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity through the application of reversed-phase liquid chromatography-accurate mass tandem mass spectrometry (RP-LC-accurate MS/MS).
Automated Sample Preparation (ISO 20122) for MOSH/MOAH in Seasoning Oils
May 6th 2025This work presents an Automated Sample Preparation procedure for MOSH/MOAH analysis of Seasoning Oils. We compare results from a manual epoxidation procedure compliant with DIN 16995 with results based on fully automated sample preparation (epoxidation and saponification) compliant with ISO 20122. In both cases, online clean-up via activated aluminum oxide (AlOx) are used to remove interfering n-alkanes from the MOSH fraction during the HPLC run. Automated data evaluation using a dedicated software (GERSTEL ChroMOH) is presented.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)












