Fast Analysis of Naproxen Sodium with the Acclaim Trinity P1 Column and Charged Aerosol Detection
The Application Notebook
The characterization of pharmaceutical salts is critical to the drug development process. Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) salts influence the solubility, stability and hygroscopicity of pharmaceuticals and affect the final drug formulation. Traditionally, the analysis of the API and its counterion salt requires separate applications. Nanopolymer silica hybrid (NSH) technology in the Acclaim Trinity P1 column along with the Corona ultra charged aerosol detector (CAD) enables simultaneous analysis of the API and counterion over four orders of magnitude.
Chris Crafts, Bruce Bailey and Ian Acworth, ESA — A Dionex Company Inc., Chelmsford, Massachusetts, USA.
The characterization of pharmaceutical salts is critical to the drug development process. Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) salts influence the solubility, stability and hygroscopicity of pharmaceuticals and affect the final drug formulation. Traditionally, the analysis of the API and its counterion salt requires separate applications. Nanopolymer silica hybrid (NSH) technology in the Acclaim Trinity P1 column along with the Corona ultra charged aerosol detector (CAD) enables simultaneous analysis of the API and counterion over four orders of magnitude.
The analysis of a common API (naproxen sodium) with a 3 min isocratic run (Figure 1) is presented here. The range, reproducibility and accuracy of calculation of sodium salts are demonstrated.
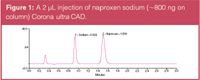
Figure 1
Experimental
A standard HPLC system with a Corona ultra sodium acetate and naproxen sodium were from Sigma-Aldrich.

Results
A calibration curve from 5 ng to 10 μg of sodium acetate on column was generated using a quadratic fit function and the x and y axes were inverted (Figure 2), demonstrating the wide dynamic range of the detector. A second curve, from 80 to 300 ng on column (Figure 2 inset), demonstrates the linearity of the detector over small ranges. Both of these curves returned correlation values > 0.99 and reproducibility ≤ 2% for the three injections at each point. The correlation to the theoretical sodium content in the naproxen was then calculated from each curve using a sample of ~800 ng naproxen sodium on column. Recoveries were within 3% of theoretical for the full range curve and within 1% for the linear curve (Table 1).
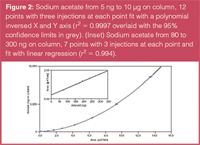
Figure 2
Conclusion
The CAD response curve towards sodium (as acetate salt) shown in Figure 2 illustrates that an excellent correlation can be calculated even when a wide dynamic range (low nanogram to microgram quantities on column) is used. The accuracy and reproducibility data are sufficient for both research and QC environments. This analytical approach provides accurate and reproducible data for both the API and the counterion salt. As a result of the speed of the method there is an opportunity for significant cost savings during the drug development process. The example can be expanded to other APIs containing both inorganic and/or organic salts.
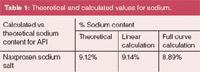
Table 1: Theoretical and calculated values for sodium.
Acclaim, CAD and Corona are registered trademarks and ultra and Trinity are trademarks of Dionex Corporation.

ESA — A Dionex Company Inc.
22 Alpha Road, Chelmsford, Massachusetts 01824, USA
tel. +1 978 250 7000 fax +1 978 250 7087
Websites: www.esainc.com, www.dionex.com

Polysorbate Quantification and Degradation Analysis via LC and Charged Aerosol Detection
April 9th 2025Scientists from ThermoFisher Scientific published a review article in the Journal of Chromatography A that provided an overview of HPLC analysis using charged aerosol detection can help with polysorbate quantification.
Analyzing Vitamin K1 Levels in Vegetables Eaten by Warfarin Patients Using HPLC UV–vis
April 9th 2025Research conducted by the Universitas Padjadjaran (Sumedang, Indonesia) focused on the measurement of vitamin K1 in various vegetables (specifically lettuce, cabbage, napa cabbage, and spinach) that were ingested by patients using warfarin. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) equipped with an ultraviolet detector set at 245 nm was used as the analytical technique.
Removing Double-Stranded RNA Impurities Using Chromatography
April 8th 2025Researchers from Agency for Science, Technology and Research in Singapore recently published a review article exploring how chromatography can be used to remove double-stranded RNA impurities during mRNA therapeutics production.














