Analysis of Impurities in Fine Chemical Octyl-dimethyl-4-aminobenzoate Using the Agilent 1290 Infinity LC and ZORBAX RRHT and RRHD 1.8 μm Columns
The Application Notebook
The Agilent 1290 Infinity LC has significant capabilities for a wide range of HPLC and UHPLC applications. It exhibits a broader power range (that is, the combination of pressure and flow capabilities) than any other commercially available system and has the flexibility to operate with a wide range of column dimensions and particle sizes. Additionally, advanced optical design in the diode array detector allows a wide dynamic range and high sensitivity, both of which are critical in the monitoring of small impurities in fine chemicals.
Michael Woodman, Agilent Technologies Inc., Chemical Analysis Solutions, Wilmington, Delaware, USA.
The Agilent 1290 Infinity LC has significant capabilities for a wide range of HPLC and UHPLC applications. It exhibits a broader power range (that is, the combination of pressure and flow capabilities) than any other commercially available system and has the flexibility to operate with a wide range of column dimensions and particle sizes. Additionally, advanced optical design in the diode array detector allows a wide dynamic range and high sensitivity, both of which are critical in the monitoring of small impurities in fine chemicals.
The combined benefits are demonstrated by a separation of impurities found in a sample of octyl-dimethyl-4-aminobenzoate. The high pressure capability of the system allows the use of methanol, as well as acetonitrile, to explore the selectivity of the two solvents. At 1.5 mL/min, using a simple 2-min gradient and a 3.0 mm × 50 mm 1.8 μm column, the analysis time is only 3 min. The separation of the main components is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Initial separation conditions showing a need for greater resolution and selectivity. Sample: Octyl dimethyl para-aminobenzoate, 1 mg/mL. Gradient: 1.5 mL/min, 40% to 90% ACN/water over 2 minutes. Up to 460 bar on ZORBAX StableBond RRHT C18, 3 mm à 50 mm, 1.8 μm, 40 °C. 0.75 minute retention: 4-amino-benzoic acid; 2.1 minute retention: Octyl dimethyl para-aminobenzoate.
The speed, resolution and flexibility of the system are further demonstrated by a separation of the sample using methanol or acetonitrile with low solvent consumption 2.1 mm i.d., 1.8 μm columns. The flow rate and gradient conditions are optimized for each solvent, to produce a gradient separation with maximum pressure of approximately 850 bar, a conservative setting for the 1200-bar capability of the Agilent 1290 Infinity LC. The separation of the main components, with the two organic solvents, is shown in Figure 2(a) (acetonitrile, top panel) and 2(b) (methanol, lower panel), where the chromatograms are zoomed to the region of peaks shown from approximately 1.2–2.5 min in Figure 1.
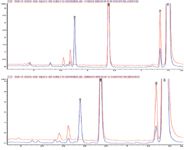
Figure 2: Results using ACN vs MeOH with the same gradient slope on the 1290 Infinity LC. Sample: ODPABA working standard, 1 mg/mL. Conditions: ACN gradient 0.6 mL/min, 40% to 90% ACN/water over 7.4 minutes. Up to 850 bar on ZORBAX StableBond RRHD C18 2.1 mm à 150 mm, 1.8 μm, 40 °C. Methanol gradient 0.52 mL/min, 50% to 100% MeOH/water over 5.7 minutes. Up to 850 bar on ZORBAX StableBond RRHD C18 2.1 mm à 100 mm 1.8 μm, 40 °C. The increased selectivity of methanol allowed a shorter column to be used, decreasing run time and avoiding the use of more expensive acetonitrile mobile phase.
Configuration
- G4220A 1290 Infinity binary pump with integrated vacuum degasser
- G4226A 1290 Infinity autosampler
- G1316C 1290 Infinity thermostatted column compartment
- G4212A 1290 Infinity diode array detector
Conclusion
The combined high flow and high pressure capability of the system allows one to use high efficiency columns, producing rapid separations with remarkable resolution while conserving solvent over the use of 4.6 mm i.d. columns. Impurity detection, as a result of high detector sensitivity and stability, is estimated to be < 0.01%.

Agilent Technologies Inc.,
2850 Centerville Road, Wilmington, Delaware 19808, USA
tel. +1 800 227 9770 fax +1 302 633 7801
E-mail: info_agilent@agilent.com Website: www.agilent.com/chem

Characterizing Plant Polysaccharides Using Size-Exclusion Chromatography
April 4th 2025With green chemistry becoming more standardized, Leena Pitkänen of Aalto University analyzed how useful size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) and asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation (AF4) could be in characterizing plant polysaccharides.
Investigating the Protective Effects of Frankincense Oil on Wound Healing with GC–MS
April 2nd 2025Frankincense essential oil is known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and therapeutic properties. A recent study investigated the protective effects of the oil in an excision wound model in rats, focusing on oxidative stress reduction, inflammatory cytokine modulation, and caspase-3 regulation; chemical composition of the oil was analyzed using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS).













