Determination of Sulphonamide Antibiotics in Bovine Liver Using Agilent SampliQ QuEChERS EN Kits by LC–MS–MS
The Application Notebook
The procedure involves a rapid and efficient pretreatment with SampliQ QuEChERS kits. The homogenized liver sample was initially extracted in a buffered aqueous/1% acetic acid acetonitrile system with an extraction and partitioning step after the addition of salts. Finally, the sample was cleaned up using dispersive solid-phase extraction (dispersive-SPE). The final extracts were analysed by the sensitive and selective determination of all compounds in a single run using LC–ESI-MS–MS operating in positive ion multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. Sulphapyridine was selected as the internal standard. The accuracy of the method, expressed as recovery, was between 53 and 93%. The precision, expressed as RSD, was between 2.1 and 16.8%. The established 5 ng/g limits of quantification (LOQ) were much lower than the respective maximum residue limit (MRL) for sulphonamide in animal food products (20–100 ng/g).
Limian Zhao and Joan Stevens, Agilent Technologies Inc., Wilmington, Delaware, USA.
The procedure involves a rapid and efficient pretreatment with SampliQ QuEChERS kits. The homogenized liver sample was initially extracted in a buffered aqueous/1% acetic acid acetonitrile system with an extraction and partitioning step after the addition of salts. Finally, the sample was cleaned up using dispersive solid-phase extraction (dispersive-SPE). The final extracts were analysed by the sensitive and selective determination of all compounds in a single run using LC–ESI-MS–MS operating in positive ion multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. Sulphapyridine was selected as the internal standard. The accuracy of the method, expressed as recovery, was between 53 and 93%. The precision, expressed as RSD, was between 2.1 and 16.8%. The established 5 ng/g limits of quantification (LOQ) were much lower than the respective maximum residue limit (MRL) for sulphonamide in animal food products (20–100 ng/g).
Sample Preparation and HPLC Instrument Conditions
Sample preparation and HPLC condtions are available in their entirety within Agilent Technologies publications 5990-5086EN.
Figure 1 shows the MRM chromatograms of the liver control blank and 100 ng/g fortified liver extract. The liver control blank chromatogram indicated that the target analytes were free from any interference.

Figure 1
Recovery and Reproducibility
The recovery and reproducibility (shown as RSD) data are shown in Table 1. The results show that all of the sulphonamides were somewhat low but still at acceptable recoveries (average of 77.8%) and good precision (average of 7.2% RSD). Samples were concentrated during the procedure to optimize sensitivity, which also caused additional matrix effects that possibly contributed to a higher RSD of target compounds at low levels.
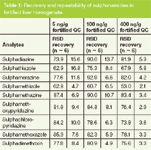
Table 1: Recovery and repeatability of sulphonamides in fortified liver homogenate.
Conclusions
When compared to other sample preparation methods, such as LLE and SPE, QuEChERS methodology is easy, fast, low cost and does not require automation. In addition, it is labour saving and a 'greener' technology. The recovery and reproducibility, based on matrix-spiked standards, were acceptable for multiresidue sulphonamide determination in bovine liver. The impurities and matrix effects from liver were minimal and did not interfere with the quantification of any target compound. The LOQs of the quinolones were much lower than their regulated MRLs in animal food products (20–100 ng/g). This modified QuEChERS procedure is a very promising methodology for the quantitative analysis of sulphonamides in food products of animal origin. This application demonstrates great potential of SampliQ QuEChERS extraction and dispersive-SPE kits, and extend far beyond plant matrices to bio-matrices, such as animal food products and bio-fluid.
Agilent SampliQ QuEChERS EN Extraction kit p/n 5982-5650. Agilent SampliQ QuEChERS EN fatty dispersive-SPE kit for 15 mL p/n 5982-5156.
The complete text of this application first appeared as Agilent Technologies publication 5990-5086EN.

Agilent Technologies Inc.
2850 Centerville Road, Wilmington, Delaware 19808, USA
tel. +1 800 227 9770 fax +1 302 633 8901
Website: www.agilent.com

Determining Enhanced Sensitivity to Odors due to Anxiety-Associated Chemosignals with GC
May 8th 2025Based on their hypothesis that smelling anxiety chemosignals can, like visual anxiety induction, lead to an increase in odor sensitivity, a joint study between the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (Erlangen, Germany) and the Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging (Freising, Germany) combined behavioral experiments, odor profile analysis by a trained panel, and instrumental analysis of odorants (gas chromatography-olfactometry) and volatiles (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry).
Investigating 3D-Printable Stationary Phases in Liquid Chromatography
May 7th 20253D printing technology has potential in chromatography, but a major challenge is developing materials with both high porosity and robust mechanical properties. Recently, scientists compared the separation performances of eight different 3D printable stationary phases.
Detecting Hyper-Fast Chromatographic Peaks Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry
May 6th 2025Ion mobility spectrometers can detect trace compounds quickly, though they can face various issues with detecting certain peaks. University of Hannover scientists created a new system for resolving hyper-fast gas chromatography (GC) peaks.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)












