Polyvalent Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine (PNEUMOVAX 23)
An approach was developed to align release and end-expiry specifications for molecular size for the quality control of Merck's polyvalent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PNEUMOVAX 23).
An approach was developed to align release and end-expiry specifications for molecular size for the quality control of Merck's polyvalent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PNEUMOVAX®23). Each of the 23 polysaccharide components of the vaccine were separately subjected to ultrasonication to produce a series of preparations of decreasing weight-average molar mass (Mw ).
These size-reduced polysaccharides were analyzed as monovalent solutions by high-performance size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) with multiangle light scattering (MALS) and refractive index (RI) detection to measure their absolute Mw (1). Analyses were performed with a miniDAWN and Optilab.
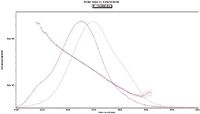
Figure 1: HPSEC/MALS/RI analysis of serotype 19A polysaccharide prior to ultrasonic size reduction (Mw = 270 kDa).
These samples were also analyzed as polyvalent formulations by HPSEC with rate nephelometry (RN) detection to measure their relative molecular size (r-MS) based on chromatographic elution volumes (2). The data from the two distinct molecular size analyses were used to establish a correlation between M w and r-MS for each polysaccharide component of the vaccine. This correlation permitted the determination of each polysaccharide's r-MS end-expiry specification for the final formulated product that is in alignment with the corresponding monovalent polysaccharide M w release specification.
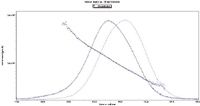
Figure 2: HPSEC/MALS/RI analysis of serotype 19A polysaccharide after 360 min of ultrasonic size reduction (Mw = 110 kDa).
The alignment of specifications provides a high level of assurance that the quality control of the final vaccine product is consistent with that of the polysaccharide starting materials. This work was recently published (3) in Biologicals.
References
(1) B. Bednar and J.P. Hennessey, Jr. Molecular Size Analysis of Capsular Polysaccharide Preparations from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Carbohydr Res 243, 115–130 (1993).
(2) J.A. Sweeney, J.S. Sumner, and J.P. Hennessey, Jr. Simultaneous Evaluation of Molecular Size and Antigenic Stability of PNEUMOVAX®23, a Multivalent Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine. Brown, Corbel, Griffi ths, editors. Physico-Chemical Procedures for the Characterization of Vaccines: Dev Biol 103, 11–26 (2000).
(3) J. MacNair, T. Desai, J. Teyral, C. Abeygunawardana, and J.P. Hennessey, Jr. Alignment of Absolute and Relative Molecular Size Specifi cations for a Polyvalent Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine (PNEUMOVAX®23). Biologicals 33, 49–58 (2005).
This note was graciously submitted by J. MacNair, T. Desai, J. Teyral, C. Abeygunawardana, and J. Hennessey, Jr., Merck Research Laboratories, P.O. Box 4, Sumneytown Pike, West Point, PA.
DAWN®, miniDAWN®, ASTRA®, Optilab®, DynaPro®, Protein Solutions® and the Wyatt Technology logo are registered trademarks of Wyatt Technology Corporation. (c)2011 Wyatt Technology Corporation.
Wyatt Technology Corporation
6300 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, CA 93117
tel. (805) 681-9009, fax (805) 681-0123
Website: www.wyatt.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)














