Characterization of a Monoclonal Antibody with Wyatt Technology’s MALS and RI Detectors and a Bio-Inert HPLC
Special Issues
Multi-angle light scattering (MALS) represents a uniquely powerful technique to determine the absolute molar masses and sizes of proteins in solution. MALS detectors cover a wide detection range of sizes and masses and enable the characterization of protein molecules as monomers, dimers, or higher order aggregates.
Multi-angle light scattering (MALS) represents a uniquely powerful technique to determine the absolute molar masses and sizes of proteins in solution. MALS detectors cover a wide detection range of sizes and masses and enable the characterization of protein molecules as monomers, dimers, or higher order aggregates.
The plurality of detectors at different angles improves the accuracy and the precision of the results. However, it is not just the number of angles that determines the quality of the measurements, but rather the engineering of the instrument, too. Superior signal-to-noise ratios and sophisticated algorithms for data management are pivotal features of the instrument and software design. As is shown below, these prerequisites are fulfilled by Wyatt Technology's DAWN detectors.
Materials and Methods
Different amounts (0.2 μg to 500 μg) of a monoclonal antibody directed against leukocytic antigens were separated using an Agilent 1260 Infinity Bio-inert LC coupled to a Superdex 200 SEC column. The LC consisted of a 1260 Infinity bio-inert quaternary pump (G5611A), a G5667A bio-inert autosampler, and a 1260 Infinity VLDiode array detector. Concentration was measured using a Wyatt Technology Optilab T-rEX differential refractometer (operating at the same wavelength of light as the DAWN MALS instrument). Light scattering measurements came from Wyatt's DAWN HELEOS II MALS detector. While in many applications no special liquid chromatography (LC) is required, for these experiments the Agilent 1260 Infinity Bio-inert LC was applied because it has a metal-free sample flow path. This prevents unspecific interaction of the analyzed molecule with instrument surfaces.
Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows the signals obtained from the antibody injected into the separation system. The RI detector displays peaks of varying heights, as expected according to the various sample loads of the protein. In contrast, the MALS signal represents the product of the sample's molar mass times the concentration.
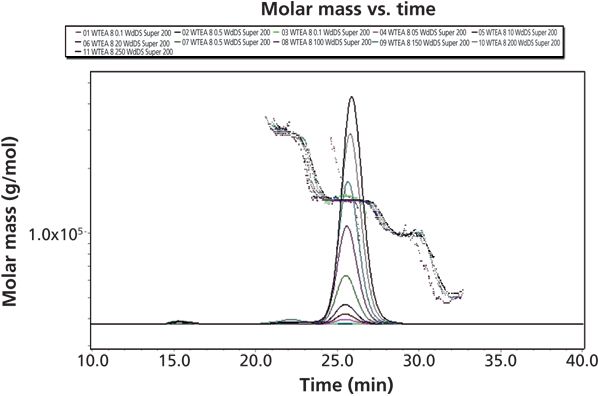
Figure 1: RI and LS signals of 11 measurements of the antibody.
Evaluation of Collected Data
The average molar mass of the antibody using Wyatt's ASTRA software was determined to be 153,650 Da, with a standard deviation of only 1.7%. As can be seen in Figure 2, molar masses were reliably determined over a huge dynamic range that varied by a factor of 2500. For antibody analysis this is highly advantageous. Frequently, there is only a small amount of precious sample available, so high sensitivity is essential to collect meaningful data. However, when performing quality control of therapeutic protein preparations, the solute concentrations are, of course, higher.
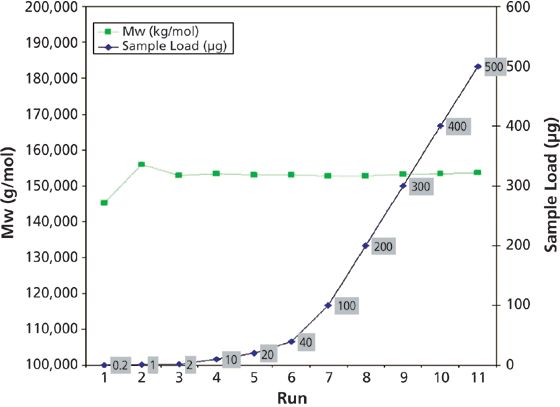
Figure 2: Comparison of sample load and molar mass determinations of the antibody by MALS.
Our data show that the Wyatt MALS and RI detectors combined with Agilent 1260 Infinity Bio-inert LC is a very useful approach that yields highly reproducible results over a wide range of protein injections. It represents the instrumentation of choice for the analysis of therapeutic proteins in numerous pharmacological settings.

Wyatt Technology Corporation
6300 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, California 93117, USA
Tel: +1 (805) 681 9009 fax: +1 (805) 681 0123
Website: www.wyatt.com

New Study Uses MSPE with GC–MS to Analyze PFCAs in Water
January 20th 2025Scientists from the China University of Sciences combined magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) to analyze perfluoro carboxylic acids (PFCAs) in different water environments.
The Next Frontier for Mass Spectrometry: Maximizing Ion Utilization
January 20th 2025In this podcast, Daniel DeBord, CTO of MOBILion Systems, describes a new high resolution mass spectrometry approach that promises to increase speed and sensitivity in omics applications. MOBILion recently introduced the PAMAF mode of operation, which stands for parallel accumulation with mobility aligned fragmentation. It substantially increases the fraction of ion used for mass spectrometry analysis by replacing the functionality of the quadrupole with high resolution ion mobility. Listen to learn more about this exciting new development.
A Guide To Finding the Ideal Syringe and Needle
January 20th 2025Hamilton has produced a series of reference guides to assist science professionals in finding the best-suited products and configurations for their applications. The Syringe and Needle Reference Guide provides detailed information on Hamilton Company’s full portfolio of syringes and needles. Everything from cleaning and preventative maintenance to individual part numbers are available for review. It also includes selection charts to help you choose between syringe terminations like cemented needles and luer tips.
The Complexity of Oligonucleotide Separations
January 9th 2025Peter Pellegrinelli, Applications Specialist at Advanced Materials Technology (AMT) explains the complexity of oligonucleotide separations due to the unique chemical properties of these molecules. Issues such as varying length, sequence complexity, and hydrophilic-hydrophobic characteristics make efficient separations difficult. Separation scientists are addressing these challenges by modifying mobile phase compositions, using varying ion-pairing reagents, and exploring alternative separation modes like HILIC and ion-exchange chromatography. Due to these complexities, AMT has introduced the HALO® OLIGO column, which offers high-resolution, fast separations through its innovative Fused-Core® technology and high pH stability. Alongside explaining the new column, Peter looks to the future of these separations and what is next to come.
Oasis or Sand Dune? Isolation of Psychedelic Compounds
January 20th 2025Magic mushrooms, once taboo, have recently experienced a renaissance. This new awakening is partially due to new findings that indicate the effects of psilocybin, and its dephosphorylated cousin psilocin may produce long lasting results for patients who might be struggling with anxiety, depression, alcohol and drug abuse, and post-traumatic stress disorder. Hamilton Company has developed a methodology for the isolation and identification of 5 common psychedelic compounds used in the potential treatment of disease. The PRP-1 HPLC column resin remains stable in the harsh alkaline conditions ideal for better separations.