Fast Analysis with SFC
Special Issues
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) has been used by scientists in laboratories and manufacturing facilities for several decades.
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) has been used by scientists in laboratories and manufacturing facilities for several decades. Historically, interest in SFC has been for chiral applications, natural product separations, and isolation of key active ingredients. Nowadays, analysis and purification of achiral substances are also carried out using SFC technology. As this technique uses mainly carbon dioxide and only small percentages of organic solvents such as methanol, SFC is seen as an environmentally friendly alternative for analysis and compound isolation.
Recent advances in SFC instrumentation combined with the potential for faster analysis and effective separations and sustainability have encouraged scientists to embrace SFC technology. The new Kromasil SFC family of columns is tailor-made for research and development as well as for routine analysis. Among these types of columns, analysts can now take advantage of the new Kromasil SFC 2.5 μm 2-Ethylpyridine column, where the stationary phase is encapped, limiting the interactions with the silica surface and focusing more on the ligand.
Experimental Conditions
The samples used in this work were a) an anticonvulsant mixture containing carbamazepine, phenytoin, and primidone; and b) a hormone mixture containing deoxycorticosterone, corticosterone, cortisone, and hydrocortisone.
The samples were analyzed using a generic linear gradient between 5–30% methanol in carbon dioxide; gradient duration 10 min; flow rate 2 mL/min; 120 bar backpressure; temperature 40 °C; and detection at 220 nm.
Results
Figure 1 shows the chromatographic result for the analysis of the anticonvulsants. There is complete separation and resolution of the three compounds in two minutes. The peaks are sharp and Gaussian.
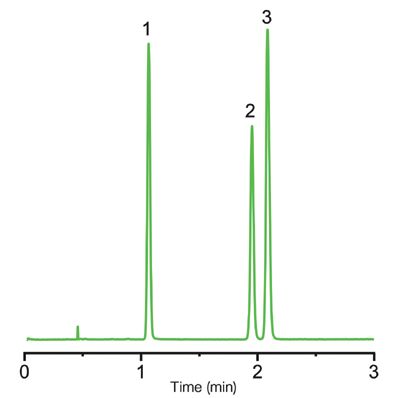
Figure 1: Separation of anticonvulsants using a Kromasil SFC 2.5-2EP 3.0 × 150 mm column. Sample: 1: carbamazepine; 2: phenytoin; and 3: primidone. Conditions: Gradient analysis 5–30% methanol in carbon dioxide in 10 min; flow rate 2 mL/min; 120 bar backpressure; temperature 40 °C; and UV detector at 220 nm.
Figure 2 shows the chromatographic result for the separation of hormones. In this case, baseline resolution was also achieved with the generic run and all the compounds eluted within four minutes. The peaks were also symmetrical. In general, the substances in the hormone mixture are more retained than the anticonvulsants, but it should be noted that the hormones and the anticonvulsants have very different molecular structures. When examining the structure of the four compounds in the hormone mixtures further, it can be seen that hydrocortisone elutes last. This is because it is the most polar compound in the mixture. On the other hand, deoxycorticosterone is the least polar and therefore elutes first. Corticosterone and cortisone have relatively similar structures and elute at similar retention times.
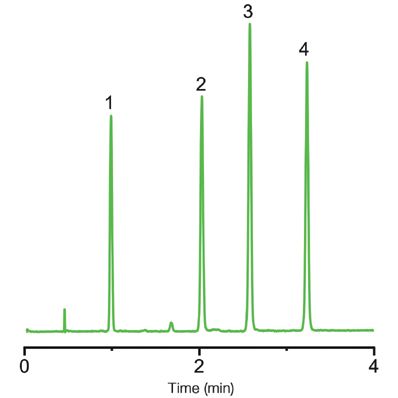
Figure 2: Separation of a hormone mixture using a Kromasil SFC 2.5-2EP 3.0 × 150 mm column. Sample: 1: deoxycorticosterone; 2: corticosterone; 3: cortisone; and 4: hydrocortisone. Conditions: Gradient analysis 5–30% methanol in carbon dioxide in 10 min; flow rate 2 mL/min; 120 bar backpressure; temperature 40 °C ;and UV detector at 220 nm.
The results shown in this work illustrate the benefit of using Kromasil SFC 2.5-2EP columns, encapped for fast and efficient analysis of a variety of compounds. The column employs a linear gradient with mainly carbon dioxide and a low percentage of methanol. Baseline resolution and good peak shapes and symmetries were achieved without optimizing the run conditions.

AkzoNobel Separation Products
SE-445 80 Bohus, Sweden
Website: www.kromasil.com

New Method Explored for the Detection of CECs in Crops Irrigated with Contaminated Water
April 30th 2025This new study presents a validated QuEChERS–LC-MS/MS method for detecting eight persistent, mobile, and toxic substances in escarole, tomatoes, and tomato leaves irrigated with contaminated water.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)











