Fast, Sensitive, and Simultaneous Analysis of Multiple Steroids in Human Plasma by UHPLC–MS–MS
Special Issues
Accurate steroid measurement is essential for the diagnosis of various disorders, for example in sexual differentiation or gonadal function.
Accurate steroid measurement is essential for the diagnosis of various disorders, for example in sexual differentiation or gonadal function. The study of steroid metabolism is also relevant in the early detection and treatment of a number of diseases, such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia, Cushing's disease, primary aldosteronism, endometriosis, and many more.
As the metabolism of steroids is regulated by several mechanisms (Figure 1), a panel analysis can be of great advantage to obtain a complete profile. Immunoassays used for this purpose suffer from limitations in throughput and a lack of specificity, and cannot be applied to multiple steroids in one sample. This can cause problems, particularly when there is only a low volume of sample available for analysis, for example in pediatric diagnosis.
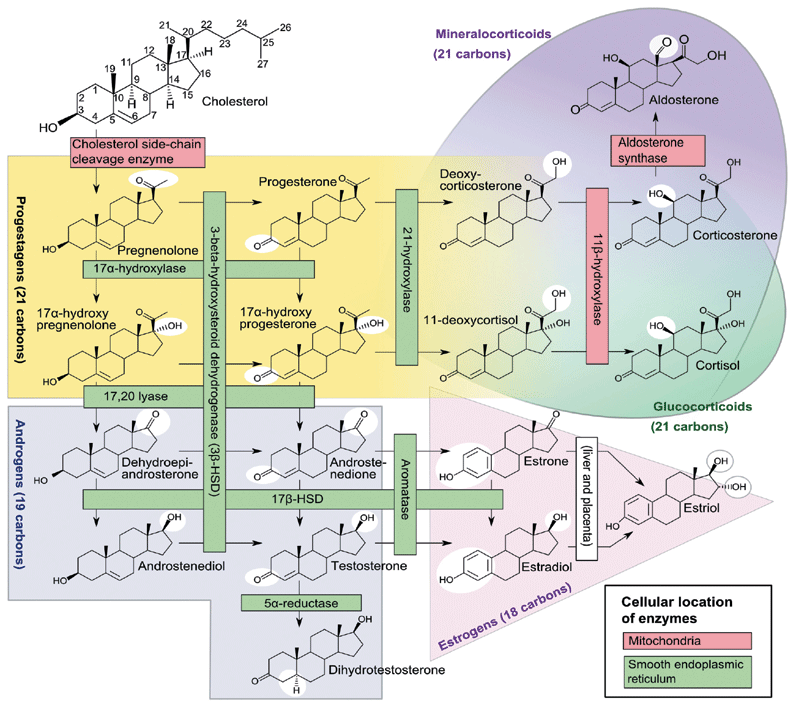
Figure 1: Human steroidogenesis: Häggström M, Richfield D (2014). "Diagram of the pathways of human steroidogenesis". Wikiversity Journal of Medicine 1(1). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.005. ISSN 20018762). (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Steroidogenesis.png)
With the combination of specificity, precision, sensitivity, automation, low sample volume, and high throughput liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS–MS) is the ideal tool for quick and simple profiling of steroids and their conjugates. A highly sensitive analytical method for the simultaneous determination of 15 steroids by ultrahigh-performance LC–MS–MS was developed to support research or clinical studies in this field.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals
Water and methanol were of ULC/MS quality (Biosolve). Dichloromethane was of LV-GC quality (Biosolve). Certified steroid standard solutions and stable isotope labelled steroid solutions were provided by Cerilliant (Sigma-Aldrich).
Calibration Standards and Quality Control
A double charcoal stripped human plasma pool (6 donors, 3 male and 3 female) from whole blood collected on EDTA-K3 (Seralab, UK) was used to prepare the calibration standards. Plasma aliquots were spiked using the same spiking volume at all levels, representing not more than 0.5% of the total volume. A calibration curve ranging from 0.5 to 15000 pg/mL for all compounds was prepared. The lowest limit of quantification was determined a posteriori for each compound with a signal-to-noise ratio of 10.
Sample Preparation
Samples were prepared using supported liquid extraction (SLE). Standards, quality control probes, and samples (550 μL) were spiked with 10 μL of internal standard solution (each at a final concentration of 1 ng/mL) and diluted with 550 μL of ultrapure water. A total of 1000 μL of diluted sample was directly loaded onto a SLE+ cartridge (1 mL, Biotage). After complete loading, the sample was left in contact with the sorbent for at least 5 min. The compounds were then eluted with 5 mL of dichloromethane. After evaporation to dryness under a stream of nitrogen at room temperature, the extracts were reconstituted in 50 μL of water/methanol (1:1), transferred to a vial with glass insert and stored at 5 °C prior to analysis.
UHPLC–MS–MS Conditions
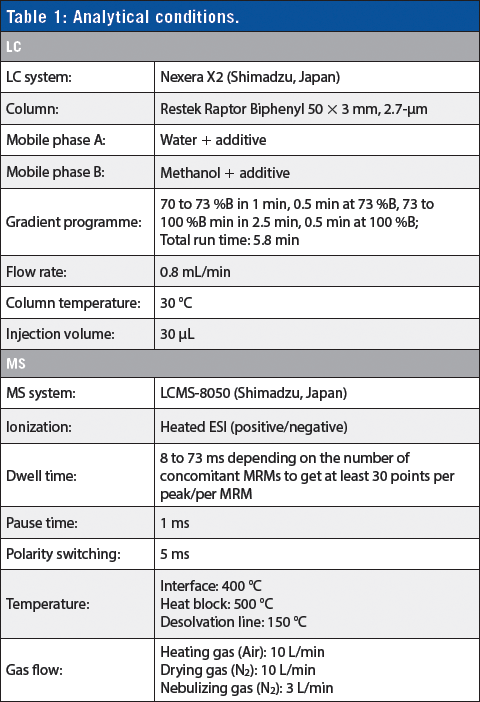
Analytical conditions are reported in Table 1. Two multiple reaction monitoring (MRMs) were selected for target compounds and one MRM for the internal standard. MRMs were recorded in relevant time segments.
Results
A total number of 15 different steroids could be determined in one 6 min LC–MS–MS run with the use of 11 different internal standards for the most sensitive and accurate quantification of all analytes of interest (Figure 2).
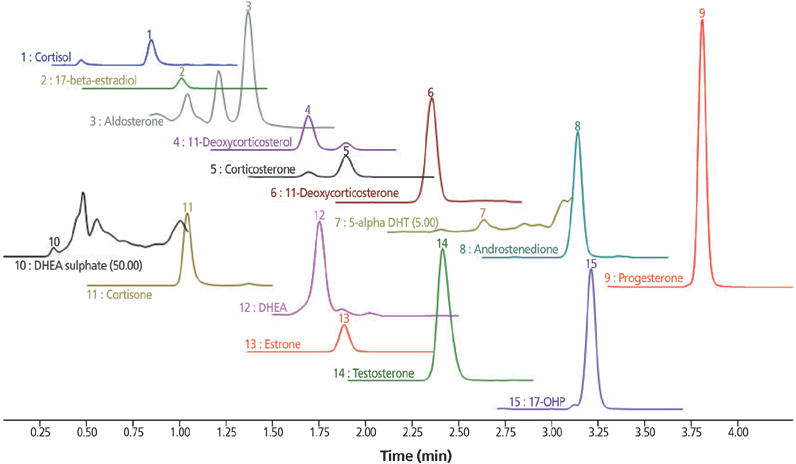
Figure 2: Plasma standard with spiked steroid level of 10 ng/mL.
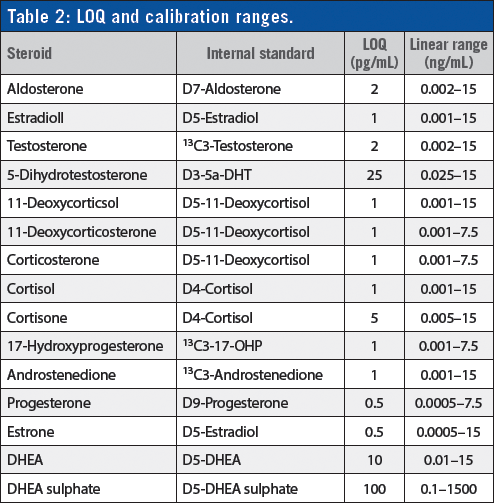
Linear range and limits of quantification for all 15 steroids are displayed in Table 2.
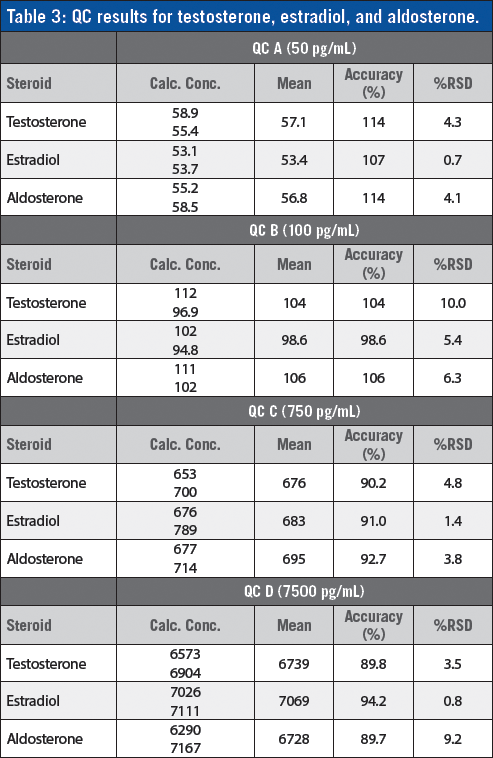
A detailed account of the results of QC samples for the determination of testosterone, estradiol, and aldosterone with spiked steroid concentrations of 50, 100, 750, and 7500 pg/ml is shown in Table 3.
Conclusion
A fast and robust LC–MS–MS method for steroid panel analysis was established. The highly sensitive assay allows for small sample volumes and enables the monitoring of deficiency disease levels. Simple sample preparation and fast analysis are ideally suited for high throughput analysis in research laboratories or clinical studies.

Shimadzu Europa GmbH
Albert-Hahn-Str. 6–10, D-47269 Duisburg, Germany
Tel: +49 203 76 87 0 fax: +49 203 76 66 25
E-mail: shimadzu@shimadzu.eu
Website: www.shimadzu.eu

Determining the Effects of ‘Quantitative Marinating’ on Crayfish Meat with HS-GC-IMS
April 30th 2025A novel method called quantitative marinating (QM) was developed to reduce industrial waste during the processing of crayfish meat, with the taste, flavor, and aroma of crayfish meat processed by various techniques investigated. Headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) was used to determine volatile compounds of meat examined.
University of Tasmania Researchers Explore Haloacetic Acid Determiniation in Water with capLC–MS
April 29th 2025Haloacetic acid detection has become important when analyzing drinking and swimming pool water. University of Tasmania researchers have begun applying capillary liquid chromatography as a means of detecting these substances.
Using GC-MS to Measure Improvement Efforts to TNT-Contaminated Soil
April 29th 2025Researchers developing a plant microbial consortium that can repair in-situ high concentration TNT (1434 mg/kg) contaminated soil, as well as overcome the limitations of previous studies that only focused on simulated pollution, used untargeted metabolone gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to measure their success.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)













