Chemical Characterization of Calvados (Apple Brandy) Young Spirits: Separation of Polar and Non-Polar Volatile Compounds
LCGC Asia Pacific
Calvados is an apple-brandy of Normandy (France). Mashed apples are fermented to obtain cider, which is then distilled to give the young spirit.
Calvados is an apple-brandy of Normandy (France). Mashed apples are fermented to obtain cider, which is then distilled to give the young spirit.
Spirit aromas are a subtle balance of various volatile compounds belonging to different chemical classes, having different chemical functionalities and consequently various polarities. They may be acetals, aldehydes, alcohols, carboxylic acids, ketones and phenolic derivatives. In Calvados, esters with fruity descriptors are believed to improve the quality, while carboxylic acids with "rancid, sweat" notes are supposed to decrease the quality.
The aromatic composition can be determined using two techniques, gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (GC–MS) to determine the volatile composition and gas chromatography coupled to olfactometry (GC–O) to determine the corresponding odours.
The GC analysis is typically performed using both a non-polar phase (such as 5% phenyl polysiloxane) and a polar phase (such as a polyethylene glycol) for the separation. In the work reported here, a medium polar phase [14% cyanopropylphenyl polysiloxane (BP10)] was used, as it was found to separate both volatile and semi-volatile compounds (such as a non-polar phase), and polar compounds of close molecular weights (such as a polar phase).
In this study, a detailed identification of the major volatile compounds present in young calvados was performed using GC–MS. Results were correlated to those obtained using GC–O (ODO–I, SGE Analytical Science) to evaluate the most odorant compounds.
More than 120 compounds were identified in liquid–liquid extracts of different samples of calvados. Retention indices were calculated for each of them on the BP-10 stationary phase using a C7 to C31 hydrocarbon mix. Typical chromatograms of three samples of young calvados are given in Figure 1. Each sample contained an average number of 80 volatile compounds, which were correctly separated in approximately 45 minutes.
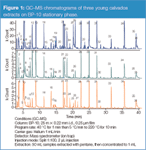
Figure 1
The most represented chemical class was esters with powerful odorants such as ethyl 2-methylpropanoate (peak 5, fruity), ethyl butanoate (peak 8, fruity, alcohol) or 3-methylbutyl acetate (peak 12, banana). The majority of these esters, which are significant for the aroma characteristics of spirits, are produced during either the fermentation, or the distillation step. Some alcohols were also identified such as butan-2-ol (peak 1), butanol (peak 4), isopentanols (peak 7, plastic), hexanol (peak 13, green grass) and octanol (peak 18). These alcohols generally have a high perception threshold and, therefore, only the most concentrated ones could be detected by olfactometry.
The largest peak in the GC–MS chromatogram was for isopentanols, which are known to be characteristic of brandies. Three phenolic derivatives were also detected in a relatively high amount. Of these, 4-ethylphenol (peak 26, animal) and 4-ethylguaiacol (peak 27, floral hyacinth) are considered to be responsible for organoleptic defects in red wines or brandies. Sensory evaluation tests were performed and revealed that the quality of the global aroma of the samples was not decreased by the presence of them. It appears that they need to reach a certain concentration before they cause a significant aromatic defect. Two acetals were also identified. 1,1-Diethoxyethane (peak 2, fruity) is considered as a marker of the presence of ethanal. The odour of 1,1,3-triethoxypropane (peak 16, floral, vegetal) was only perceived in samples with important aromatic defects. This compound is produced by the acetalization and Michael-type addition of acrolein in the presence of an excess of ethanol. This acetal is formed only when acrolein is present in high concentration in the cider prior to distillation. Hexanoic acid (peak 19, yeast-like, cider) was the sole carboxylic acid involved in the aromatic composition.
Summary
The BP-10 column enabled a good separation of the volatile compounds present in extracts of young calvados. More than 80 compounds could be clearly separated and identified using GC–MS. This stationary phase can be a good compromise for the separation of compounds from various chemical functionalities and molecular weights such as those present in beverages.
Jérôme Ledauphin,1Naza Lahoutifard2 and Andrew Gooley,2
1ERPCB — EA 3914, Université de Caen, France, 2SGE Analytical Science, Ringwood, Victoria, Australia.

SGE Analytical Science Pty Ltd
7 Argent Place, Ringwood, Victoria 3134, Australia
tel. +61 3 9837 4200 fax +61 3 9874 5672
E-mail: support@sge.com Website: www.sge.com

Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.
5 Things to Consider When Selecting a Chromatography Silica
April 1st 2025Particularly in the pharmaceutical industry, drug purity isn’t just a goal – it’s essential for achieving safety, stability and efficacy. However, purification is easier said than done, especially with challenging molecules like DNA and RNA “oligonucleotides,” due in large part to their diversity and the range of impurities that can be generated during production. Enter DAVISIL® chromatographic silica, with a wide range of pore diameters and particle sizes to meet your specific application, performance and sustainability requirements. Before you choose the chromatography resin for your next purification application, take a look at these 5 considerations.
Automating Protein Purification: Efficiency, Yield, and Reproducibility
March 27th 2025Recent advancements in automated protein purification stress the importance of efficiency, scalability, and yield consistency. This eBook compares different purification platforms, highlighting their impact on downstream applications and demonstrating how automation enhances throughput and process control.














