Automated Off-Line Two-Dimensional LC–MS–MS of Complex Proteomic Samples with the UltiMate 3000 System
LCGC Asia Pacific
Multidimensional liquid chromatography (MDLC) techniques are essential for the separation of highly complex proteomic samples. Advantages of off-line MDLC techniques over on-line approaches include high flexibility in choice of column dimensions and mobile-phase compositions, and the ability to reanalyse sample fractions. Here we present a fully automated off-line two-dimensional chromatographic approach for the analysis of proteomic samples using an UltiMate 3000 system optimized for proteomics MDLC.
Multidimensional liquid chromatography (MDLC) techniques are essential for the separation of highly complex proteomic samples. Advantages of off-line MDLC techniques over on-line approaches include high flexibility in choice of column dimensions and mobile-phase compositions, and the ability to reanalyse sample fractions. Here we present a fully automated off-line two-dimensional chromatographic approach for the analysis of proteomic samples using an UltiMate 3000 system optimized for proteomics MDLC.
Instrumentation and Chromatographic Conditions
Off-line two-dimensional (2D) chromatographic experiments were performed with an UltiMate 3000 system (Dionex) equipped with a dual gradient pump with membrane degasser (DGP3600), flow manager module with active flow-split technology (FLM-3100), autosampler with integrated micro-fraction collector (WPS-3000), and two UV detectors (VWD-3400). The system was coupled on-line to an ion-trap mass spectrometer (HCTultra)
The workflow for automated off-line 2D-LC is as follows: (1) a first-dimension LC separation with fraction collection, followed by (2) repeated cycles of injection of the collected fractions (second-dimension), LC separations and detection of peptides by tandem mass spectrometry. Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the 2D-LC system. The first-dimension separation was performed on a 15 cm × 300 μm i.d. strong cation-exchange column (SCX). After injection of 10 pmol of tryptic peptides from transferrin, bovine serum albumin, β-galactosidase, alcohol dehydrogenase, lysozyme, and cytochrome c, a salt gradient from 0–600 mM NaCl in 5 mM phosphate buffer pH 3 + 5% ACN was applied in 20 min at a flow-rate of 6 μL/min. Detection was achieved with a 45 nL flow cell at 214 nm. Fractions were collected every minute from 10–30 min. The second dimension separation included on-line sample preconcentration and desalting using a monolithic trap column, and separation of peptides on a PepSwift 5 cm, 200 μm i.d. monolithic column applying an acetonitrile gradient from 0–36% in 0.05% TFA in 10 min. Peptides were detected by UV using a 3 nL flow cell and MS–MS detection.
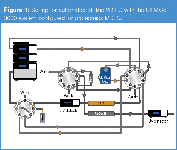
Figure 1
Automated Off-Line MDLC
To minimize dilution of the peptide fractions, the salt gradient was optimized such that 84% of the peptides eluted in single or adjacent fractions, resulting in the chromatogram shown in Figure 2(a). Excellent retention time precision was observed with RSD values <0.1% for three consecutive 2D-LC runs. Using a polystyrene-divinylbenzene monolithic column (PepSwift) and a steep gradient (3.6% ACN/min), a peak capacity of 125 was obtained within 10 min for the second-dimension separation. Figure 2(b) shows a second-dimension separation of the same fraction (#4) obtained in three consecutive MDLC runs. The chromatograms were obtained 12 h apart, (the time required to complete one MDLC analysis). Retention time precision measured for 16 peptides varied between 0.0 and 0.20% RSD. The protein sequence coverage determined with MASCOT was highly reproducible and varied between 43 and 75% for the samples originating from different proteins.
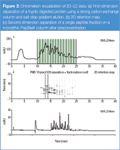
Figure 2
MDLC Data Visualization
As a result of the complex nature of the sample, a special representation was developed that allows easy comparison of the different samples with Chromeleon software. (See Figure 2.) Figure 2(a) shows the first dimension separation; Figure 2(b) shows the consecutive second-dimension separations, using a visualization approach similar to the gel images obtained after 2D-gel electrophoresis (2D-PAGE). A second-dimension separation of a single fraction sampled from the first dimension separation is shown in Figure 2(c).
Concluding Remarks
The UltiMate 3000 MDLC allows automated off-line 2D-LC of complex proteomic samples. The method provides high peak capacity, high resolution and excellent retention time stability.
Pepswift is a trademark and UltiMate and Chromeleon are registered trademarks of Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, California, USA.
HCTultra is a trademark of Bruker Daltonics Incorporated, Billerica, Massachusetts, USA.

Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, Sunnyvale, California 94085, USA
tel. +1 408 737 0700 fax +1 408 730 9403
Website: www.dionex.com
Bas Dolman, Robert van Ling, Evert-Jan Sneekes, Sebastiaan Eeltink and Remco Swart, Dionex, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.

Free Poster: NDSRI Risk Assessment and Trace-Level Analysis of N-Nitrosamines
April 25th 2025With increasing concern over genotoxic nitrosamine contaminants, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have introduced strict guidelines following several high-profile drug recalls. This poster showcases a case study where LGC and Waters developed a UPLC/MS/MS method for quantifying trace levels of N-nitroso-sertraline in sertraline using Waters mass spectrometry and LGC reference standards.
New TRC Facility Accelerates Innovation and Delivery
April 25th 2025We’ve expanded our capabilities with a state-of-the-art, 200,000 sq ft TRC facility in Toronto, completed in 2024 and staffed by over 100 PhD- and MSc-level scientists. This investment enables the development of more innovative compounds, a broader catalogue and custom offering, and streamlined operations for faster delivery. • Our extensive range of over 100,000 high-quality research chemicals—including APIs, metabolites, and impurities in both native and stable isotope-labelled forms—provides essential tools for uncovering molecular disease mechanisms and exploring new opportunities for therapeutic intervention.
New Guide: Characterising Impurity Standards – What Defines “Good Enough?”
April 25th 2025Impurity reference standards (IRSs) are essential for accurately identifying and quantifying impurities in pharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Yet, with limited regulatory guidance on how much characterisation is truly required for different applications, selecting the right standard can be challenging. To help, LGC has developed a new interactive multimedia guide, packed with expert insights to support your decision-making and give you greater confidence when choosing the right IRS for your specific needs.
Using the Carcinogenic Potency Categorisation Approach (CPCA) to Classify N-nitrosamine Impurities
April 25th 2025Learn how to manage nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals with our free infographic. Discover how the CPCA approach establishes acceptable intake limits and guides the selection of NDSRI reference samples. Stay compliant and ensure safety with our ISO-accredited standards.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)












