Fast Methods for Structurally Similar Compounds Using Carbon HPLC Columns
Carbon-clad zirconia phases offer dramatically different chromatographic selectivity for structurally similar compounds when compared to traditional silica-based bonded phases.
Carbon-clad zirconia phases offer dramatically different chromatographic selectivity for structurally similar compounds when compared to traditional silica-based bonded phases. This note shows baseline separation of six structurally similar sulfate-steroid conjugates using a zirconia-based ZirChrom®-CARB HPLC column.
Method development in reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC) has traditionally been difficult for molecules which are geometric isomers or structurally very similar. In bonded-phase silicas, the partition mechanism responsible for retention in RPLC often does not offer adequate chemical selectivity for such compounds. On the other hand, carbon-based phases can provide retention in RPLC through an adsorption mechanism which increases the chromatographic selectivity, especially for differences involving aromatic rings, and dramatically increase the chances of resolving critical pairs.
The ZirChrom®-CARB phase is a zirconia particle that has been carbon-clad, using patented chemical vapor deposition technology, with an elemental layer of graphitized carbon. The resulting phase contains only C-C surface bonds, which are extremely resistant to chemical and thermal attack, allowing ZirChrom®-CARB to be stable throughout the pH range (1–14) and up to 200 °C.
Experimental
A mixture of sulfate-steroid conjugates was separated at elevated temperature using a ZirChrom®-CARB column. The separation conditions were as follows:
Column: ZirChrom®-CARB, 100 mm × 4.6 mm
Mobile Phase: Gradient elution from 55/5/40 to 90/5/5 A/B/C from 0 to 4.5 min.
A: Acetonitrile
B: Tetrahydrofuran
C: 25 mM Ammonium fluoride, 10 mM Ammonium acetate, pH 5.6
Temperature: 80 °C
Injection Vol.: 10 µl
Flow rate: 3.0 mL/min
Pressure Drop: 195 bar
Detection: UV at 270 n
This method is an excellent example of how the enlarged zirconia method development "tool box" can be used to overcome the toughest separation challenges. Using temperature, the unique surface chemistry of ZirChrom®-CARB, and a gradient, baseline resolution of these six structurally similar sulfate-steroid conjugates was achieved in under 5 min (see Figure 1). The critical pair, dihydroequilin sulfate and equilin sulfate, which differ in structure by only a hydrogen, are well resolved.
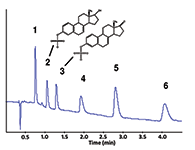
Figure 1: Steroid conjugate selectivity. 1 = Dihydroestradiol sulfate, 2 = Dihydroequilin sulfate, 3 = Equilin sulfate, 4 = Estrone sulfate, 5 = Equilenin sulfate, 6 = Dihydroequilenin sulfate.
This method can be tailored to your specific application needs. ZirChrom method developers can help you optimize and transfer this method to your site. Please contact ZirChrom technical support at 1-866-STABLE1 or support@zirchrom.com for details.
ZirChrom phases offer unique selectivity for ionic compounds, high efficiency, and excellent chemical and thermal stability.

ZirChrom Separations, Inc.
617 Pierce Street, Anoka, MN 55303
tel. 1-866-STABLE-1, email: support@zirchrom.com
Website: www.zirchrom.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.















