Analysis of Intact Proteins on a Thermo Scientific Accucore 150 C4 HPLC Column
LCGC Asia Pacific
Thermo Scientific Application Note
This application note demonstrates the analysis of intact proteins using a Thermo Scientific Accucore 150-C4 (150 Å pore diameter) HPLC column. Analysis of six proteins ranging in mass from 6 to 45 kDa is carried out in 15 min with pressures compatible with conventional HPLC instrumentation.
Accucore™ HPLC columns use Core Enhanced Technology™ to facilitate fast and high efficiency separations. The 2.6 μm diameter particles have a solid core and a porous outer layer. The optimized phase bonding creates a series of high-coverage, robust phases. The tightly controlled 2.6 μm diameter of Accucore particles results in much lower back pressures than typically seen with sub 2 μm materials. For the analysis of large biomolecules the Accucore pore size has been further optimized and a C4 phase with reducedhydrophobic retention has been prepared. This 150 Å pore size enables the effective analysis of molecules unable to penetrate into smaller diameter pores, whilst the low hydrophobicity C4 phase results in protein separation by hydrophobicity.
Chromatographic separation of proteins at the intact level prior to MS analysis is desirable for reducing sample complexity and maintaining global protein information. In this application note we demonstrate the excellent performance of an Accucore 150-C4 HPLC column for the chromatographic separation of six intact proteins (6–45 kDa).
Thermo Scientific Column and Consumables
Accucore 150-C4, 2.6 μm, 100 × 2.1 mm Vials and closures (P/N MSCERT 4000-34W)
Thermo Scientific Accela HPLC System
Flow rate: 400 μL/min
Run time: 15 min
Column temperature: 40 °C
Injection details: 2 μL (10 pmol/μL solution of each protein) UV detector wavelength: 214 nm
Back pressure at starting conditions: 185 bar (c.f. 320 bar on sub 2 μm material)
Data Processing
Software: Thermo Scientific Xcalibur 2.0 SR2
Mobile Phase
Mobile phase A: 0.1 % TFA in 30:70 acetonitrile:water
Mobile phase B: 0.1 % TFA in 98:2 acetonitrile:water
Gradient: 0–30% B in 8 min, 30–95% B in 2 min, hold at 95% B for 1 min and re-equibrilate for 4 min
Results
Under these conditions, six proteins covering the mass range of 6 to 45 kDa can be separated on an Accucore 150-C4 HPLC column in less than 15 min with back pressures compatible with conventional HPLC equipment. The chromatography is shown in Figure 1 with all of the proteins eluting with sharp symmetrical peaks and being baseline resolved, with the exception of an impurity from carbonic anhydrase which co-elutes with lysozyme.
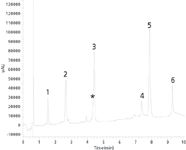
Figure 1: Chromatogram for six proteins separated on an Accucore 150-C4 HPLC column. 1. insulin 2. cytochrome c 3. lysozyme 4. myoblobin 5. carbonic anhydrase 6. ovalbumin * carbonic anhydrase impurity.
Conclusion
- Accucore 150-C4 HPLC columns show excellent separation of six test proteins of differing mass (6–45 kDa) within 15 min.
- Good peak shape is observed for all proteins.
- The back pressure is compatible with use on a conventional HPLC system.
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Tudor Road, Manor Park, Runcorn, Cheshire WA7 1TA, UK
tel. +44 (0) 1928 534110

Thermodynamic Insights into Organic Solvent Extraction for Chemical Analysis of Medical Devices
April 16th 2025A new study, published by a researcher from Chemical Characterization Solutions in Minnesota, explored a new approach for sample preparation for the chemical characterization of medical devices.
Sorbonne Researchers Develop Miniaturized GC Detector for VOC Analysis
April 16th 2025A team of scientists from the Paris university developed and optimized MAVERIC, a miniaturized and autonomous gas chromatography (GC) system coupled to a nano-gravimetric detector (NGD) based on a NEMS (nano-electromechanical-system) resonator.
Miniaturized GC–MS Method for BVOC Analysis of Spanish Trees
April 16th 2025University of Valladolid scientists used a miniaturized method for analyzing biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs) emitted by tree species, using headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC–QTOF-MS) has been developed.
A Guide to (U)HPLC Column Selection for Protein Analysis
April 16th 2025Analytical scientists are faced with the task of finding the right column from an almost unmanageable range of products. This paper focuses on columns that enable protein analysis under native conditions through size exclusion, hydrophobic interaction, and ion exchange chromatography. It will highlight the different column characteristics—pore size, particle size, base matrices, column dimensions, ligands—and which questions will help decide which columns to use.















