Determination and Quantification of Primary Aromatic Amine in Printer Ink
LCGC Asia Pacific
Knauer Application Note
There is an increasing public interest in the analysis of aromatic amines since this class of organic compounds includes many carcinogenic substances.
In recent years other sources of aromatic amines apart from tobacco smoke have gained more and more interest, for example, azo dyes (1). Therefore a fast and reliable method for the determination of aromatic amines in dyes like printer ink was developed. Five primary aromatic amines (PAAs) (aniline, 2-anisidine, 3-chloro-4methoxyanline, 2,4-dimethylaniline, o-toluidine) were chosen for this demonstration.
Method Parameters for Full Mass Scan Tests
The mass spectra of single compound standards are shown in Figure 1. The resulting m/z values manifest the fragmentation patterns of the PAAs. For every PAA the highest intensity was detected for the single charged quasi molecule ion [M+H]+. Therefore this mass was chosen for quantification in all cases.
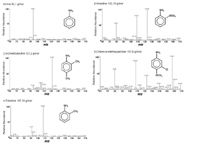
Figure 1: Mass spectra of single standard.
With the calibrated m/z values the extracts of two printer inks were analysed in order to determine PAA composition and concentrations of these five PAAs.
Sample Preparation
Samples were prepared as cold water extracts according to EN 645:1993 from printed paper.
Instrument Configuration
This application was performed on a PLATINblue binary high pressure gradient UHPLC system equipped with degasser, autosampler, column thermostat and MSQ Plus mass detector.
UHPLC Parameters: Column: BlueOrchid 175–1.8 C18, 100 x 2 mm i.d.; Eluent A: water + 0.1% formic acid; Eluent B: methanol + 0.1% formic acid; Gradient: yes (details on request); Flow rate: 0.2 mL/min; Injection volume: 50 µL; Column temperature: 40 °C
MS Detection Parameters: Ionization mode: ESI, positive mode; Needle voltage: 1 kV; Cone voltage: 20 V; Probe temperature: 200 °C
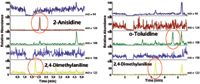
Figure 2: SIC scans of two printer inks (P1 + P2) after sample preparation.
Conclusion
The UHPLC-ESI-MS method presented in this application demonstrates the fast and simultaneous separation, qualification and quantification of five PAAs usually found in printer ink. The limit of detection was in the range between 1 to 5 µg/L (S/N = 3). Only 7 min are required for the analysis of one sample, including a washing step and re-equilibration of the column. Therefore the method is well-suited for routine analyses. Due to the fast separation and low eluent flow rate of this method, only about 1.5 mL of eluent and less than 1 mL of methanol are needed for one run. Thus this method is both economical and environmentally acceptable.
Reference
(1) M.J. Zeilmaker, H.J van Kranen, M.P. van Veen and J. Janus, Cancer risk assessment of azo dyes and aromatic amines from tattoo bands, folders of paper, toys, bed clothes, watch straps and ink. Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu RIVM, 22-Feb-2000.
KNAUER
Wissenschaftliche Gerätebau Dr. Ing. Herbert Knauer GmbH,
Hegauer Weg 38, 14163 Berlin, Germany
tel: +49 30 809727 0 fax: +49 30 801501 0
E-mail: info@knauer.net Website: www.knauer.net

Polysorbate Quantification and Degradation Analysis via LC and Charged Aerosol Detection
April 9th 2025Scientists from ThermoFisher Scientific published a review article in the Journal of Chromatography A that provided an overview of HPLC analysis using charged aerosol detection can help with polysorbate quantification.
Analyzing Vitamin K1 Levels in Vegetables Eaten by Warfarin Patients Using HPLC UV–vis
April 9th 2025Research conducted by the Universitas Padjadjaran (Sumedang, Indonesia) focused on the measurement of vitamin K1 in various vegetables (specifically lettuce, cabbage, napa cabbage, and spinach) that were ingested by patients using warfarin. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) equipped with an ultraviolet detector set at 245 nm was used as the analytical technique.
Removing Double-Stranded RNA Impurities Using Chromatography
April 8th 2025Researchers from Agency for Science, Technology and Research in Singapore recently published a review article exploring how chromatography can be used to remove double-stranded RNA impurities during mRNA therapeutics production.















