Accurate Pain Management Analysis in Under 5 Min on Raptor™ Biphenyl Superficially Porous Particle LC Columns
The Application Notebook
Pain management LC analyses can be difficult to optimize because of the limited selectivity of C18 and phenyl-hexyl phases. In contrast, the selectivity of Raptor™ Biphenyl superficially porous particle (SPP) LC columns provides complete resolution of isobaric pain medications with a total cycle time of 5 min.
Accurate, reliable analysis of pain medications is a key component in monitoring appropriate medical use and preventing drug diversion and abuse. As the demand for fast, multicomponent methods grows, LC–MS–MS methods are increasingly desired for pain management and therapeutic drug monitoring because of the low detection limits that can be achieved with this highly sensitive and selective technique. However, despite the selectivity offered by mass spectrometry, hydrophilic matrix components can still interfere with early-eluting drug compounds resulting in ion suppression. In addition, isobaric pairs must be chromatographically separated for positive identification. The need for highly selective and accurate methods makes LC column selection critical.
While C18 and phenyl-hexyl phases are frequently used for bioanalytical LC–MS–MS applications, Restek’s Biphenyl phase offers better aromatic retention and selectivity for pharmaceutical and drug-like compounds, giving it a significant advantage over other phases for the analysis of pain management medications or other drugs of abuse. The Biphenyl phase, originally developed a decade ago by Restek, has recently been combined with Raptor™ SPP (“core–shell”) silica particles to allow for faster separations without the need for expensive UHPLC instrumentation. Here, we demonstrate the fast, selective separation of commonly tested pain drugs that can be achieved using the new Raptor™ SPP Biphenyl LC column.
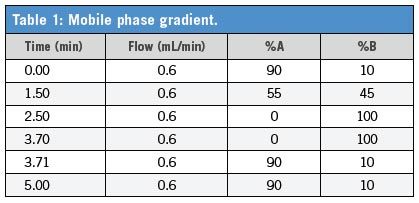
Experimental Conditions
A standard containing multiple pain management drugs was prepared in blank human urine and diluted with mobile phase as follows, urine:mobile phase A:mobile phase B (17:76:7). The final concentration for all analytes was 10 ng/mL except for lorazepam, which was 100 ng/mL. Samples were then analyzed by LC–MS–MS using an AB SCIEX API 4000™ MS–MS in ESI+ mode. Chromatographic conditions, retention times, and mass transitions are presented here and in Tables 1 and 2:
Results
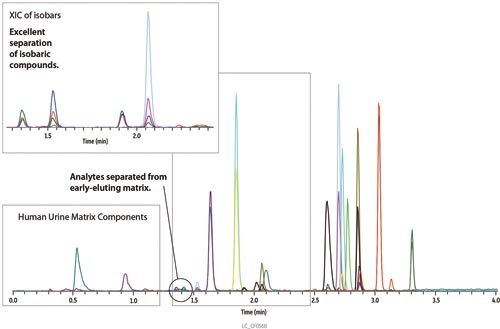
As shown in Figure 1, 18 commonly tested pain management drugs were analyzed, with the last compound eluting in less than 3.5 min, giving a total cycle time of 5 min on Restek’s Raptor™ SPP Biphenyl LC column. Analyte retention times are presented in Table 2. Important isobaric pairs (morphine/hydromorphone and codeine/hydrocodone) were completely resolved and eluted as symmetrical peaks, allowing accurate identification and integration. In addition, early-eluting compounds such as morphine, oxymorphone, and hydromorphone are separated from hydrophilic matrix interferences, resulting in decreased ion-suppression and increased sensitivity. Similar analyses on C18 and phenyl-hexyl columns often exhibit poor peak shape and resolution (for example, peak tailing between closely eluting isobars), which makes identification and accurate quantification more difficult.
Figure 1: Baseline resolution of isobaric pain management drugs in sub-5-min runs on the Raptor™ Biphenyl column.
Conclusions
Complete separation of critical pain management drug analytes from hydrophilic matrix components and isobaric interferences was achieved using the new Raptor™ SPP Biphenyl LC column in less than 5 min. The fast, complete separations produced in this method allow accurate quantification of pain management drugs and support increased sample throughput and improved lab productivity.
To learn more, visit www.restek.com/raptor

Restek Corporation
110 Benner Circle, Bellefonte, Pennsylvania 16823, USA
Tel: (800) 356 1688 fax: (814) 353 1309
Website: www.restek.com/raptor

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)












