Investigation of Iron Polysaccharide Complexes by GPC/SEC Using RI- and UV-Detection
The Application Notebook
Gel permeation chromatography (GPC), also known as size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), provides an easy and effective way to measure the molar mass distribution and the amount of free, unbound polysaccharide in iron polysaccharide complexes.
Iron is an essential nutrient in the human body. In case of iron deficiency, complexes of a polysaccharide and iron are applied as drugs to enhance low iron levels. Suitable characterization of these complexes and their formulations are mandatory for regulatory reasons, quality control, and research. In the present investigation, iron polysaccharide complexes from different sources were analyzed on a GPC/SEC system with simultaneous ultraviolet/refractive index (UV/RI) detection.
Experimental Conditions:
GPC/SEC was performed using a PSS BioSECcurity SEC system
PSS SUPREMA, 5 µm, 30 Å + 2 ×1000 Å (8 × 300 mm, each)
PSS SUPREMA precolumn
Results and Discussion:
Figure 1 shows the overlay of the UV-chromatograms of the four different samples A, B, C, and D, while the inset of the figure shows the overlay of the simultaneously measured RI-traces for two of the samples (A and B), which show nearly identical UVâtraces.
Figure 1: Comparison of the UV-traces of four different iron dextran samples used to determine the molar mass distribution of the iron complexes. While the UV-signals for samples A and B are nearly identical, the inset displaying the RI-traces shows that these samples differ in the amount of unbound polysaccharide.
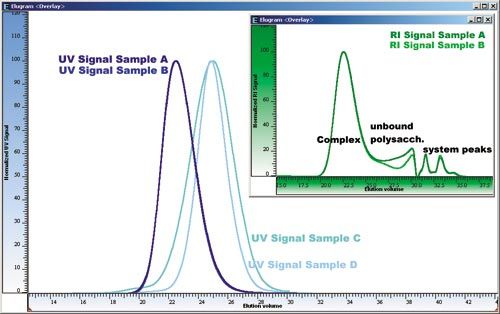
An advantage of this application is that the iron polysaccharide complex is selectively detected by the UV-detector operated at 254 nm (20–26 mL). All complexes reveal well shaped nearly Gaussian peak shapes, indicating that the PSS SUPREMA column combination is ideal for this molar mass separation range. By applying a calibration curve, established using PSS pullulan standards, the relative molar mass distributions as well as the molar mass averages and the polydispersities are derived.
While UV-detection is sufficient to differentiate between three of the four samples, samples A and B render identical elution profiles. However, when comparing the RI-traces of both samples, it becomes clear that sample A contains a significantly higher amount of the unbound polysaccharide.
We can therefore conclude that GPC/SEC with UV- and RIâdetection does not only allow the molar mass distribution of iron polysaccharide complexes to be determined, but also provides information on the amount of free, unbound polysaccharide ensuring a more comprehensive characterization of the samples.

PSS Polymer Standards Service GmbH
In der Dalheimer Wiese 5, D-55120 Mainz, Germany
Tel: +49 6131 962390 fax: +49 6131 9623911
E-mail: info@pss-polymer.com
Website: www.pss-polymer.com

Determining the Effects of ‘Quantitative Marinating’ on Crayfish Meat with HS-GC-IMS
April 30th 2025A novel method called quantitative marinating (QM) was developed to reduce industrial waste during the processing of crayfish meat, with the taste, flavor, and aroma of crayfish meat processed by various techniques investigated. Headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) was used to determine volatile compounds of meat examined.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)
















