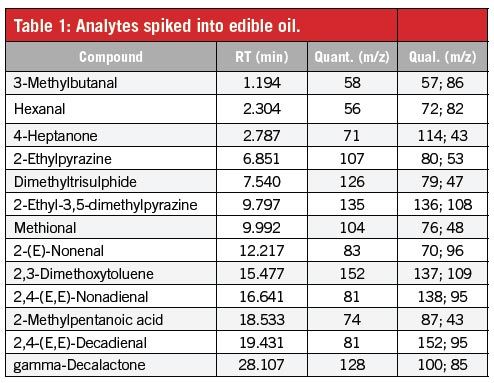
Determining Aroma Compounds in Edible Oils by Direct Thermal Desorption GC–MS Using Microvials
The Application Notebook
The determination of aroma compounds in edible oils is important for the manufacturers and vendors of these products. Off-flavours derived from unsaturated fatty acid degradation such as, for example, hexanal, 2-(E)-nonenal, and 2,4-(E,E)-decadienal are of particular interest. These compounds can compromise the taste and therefore the quality of a product, even in the ng/g concentration range.
Sensitive and fast analysis methods are needed, ideally requiring little or no sample preparation. A highly sensitive analysis method based on direct thermal desorption of the oil in a standard microvial with a purge slit placed just above the sample surface has been developed. Oil samples were placed inside a thermal desorption unit for thermal extraction in close proximity to the trap in which the aroma compounds are subsequently trapped before being transferred for gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) determination.
Instrumentation
Thermal desorption of oil samples placed in microvials inside thermal desorption tubes was performed using a GERSTEL Thermal Desorption Unit (TDU). Analytes were refocused in a GERSTEL Cooled Injection System (CIS 4), a PTV-type inlet, at low temperatures before being transferred to the GC column. A 7890/5975 GC–MS system from Agilent Technologies was used for separation and detection of the analytes of interest. Thermal desorption tubes containing the samples were delivered to the TDU automatically using a GERSTEL MultiPurpose Sampler (MPS).
Analysis Conditions
Sample Preparation
Edible oil was spiked with the analytes listed in Table 1 in the concentration range between 10 and 1000 ng/g. A set of 30 mg samples of the oil were weighed into individual microvials and placed in thermal desorption tubes. Each tube was capped with a transport adapter and placed in the autosampler tray for later desorption.
Measurements
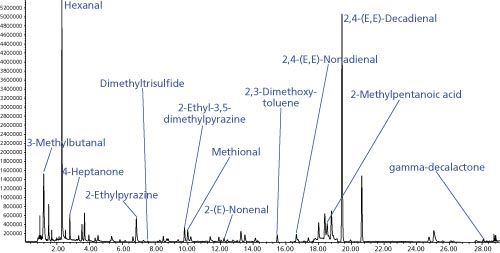
Ten oil samples of 30 mg each were prepared in microvials with a purge slit at 1 cm height measured from the bottom of the microvial and individually desorbed in the TDU to determine the repeatability. A resulting SIM GC–MS chromatogram is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: SIM chromatogram resulting from thermal desorption of a spiked edible oil inside a microvial with slit placed 1 cm from bottom.
Results and Discussion
Thermal extraction of aroma compounds from edible oils employing microvials is highly feasible. The microvial prevents contamination of the analysis system by high boiling matrix compounds while allowing effective transfer of VOCs and SVOCs onto the analytical column. After sample processing the microvial can be disposed of and the desorption tube is ready to take up the next sample. Relative standard deviations for 10 repeat measurements were between 7.2–16.8% with a median of 9.7%. This is highly acceptable considering the complex matrix, the low concentrations, and the straightforward sample preparation. A longer desorption time would likely improve the relative standard deviations further.
Reference
- GERSTEL AppNote-2014-03: Analysis of Aroma Compounds in Edible Oils by Direct Thermal Desorption GC/MS using Slitted Microvials (http://www.gerstel.com/pdf/p-gc-an-2014-03.pdf)

Gerstel GmbH & Co.KG
Eberhard-Gerstel-Platz 1, 45473 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany
Tel: +49 (0)208 7 65 03 0 Fax. +49 (0)208 7 65 03 33
E-mail: gerstel@gerstel.com
Website: http://www.gerstel.com

Determining the Link Between Prenatal Cannabis Use and Symptoms of Depression Using LC–MS/MS
April 16th 2025Researchers investigating the relationship between cannabis use during pregnancy and depressive symptoms—and whether continued use beyond the first trimester or higher levels of use were linked to increased symptoms—used liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) to confirm the presence of 11-nor-9-carboxy-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC-COOH) in urine samples.
Common Challenges in Nitrosamine Analysis: An LCGC International Peer Exchange
April 15th 2025A recent roundtable discussion featuring Aloka Srinivasan of Raaha, Mayank Bhanti of the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), and Amber Burch of Purisys discussed the challenges surrounding nitrosamine analysis in pharmaceuticals.
Identifying PFAS in Alligator Plasma with LC–IMS-HRMS
April 15th 2025A combination of liquid chromatography ion mobility spectrometry, and high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC–IMS-HRMS) for non-targeted analysis (NTA) was used to detect and identify per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in alligator plasma.


















