Why are C18s So Different? A Focus on the Contributions of Steric Selectivity
One of the fundamental tenets of chromatography is the interaction between an analyte and stationary phase. We often assume that this should be consistent between different columns with the same stationary phase, but this is not always the case. With C18 columns, this highlights the contribution of factors other than hydrophobicity, such as electrostatic interaction, when a column has exposed unreacted surface silanols, or steric selectivity, which is related to surface ODS density (Figure 1).
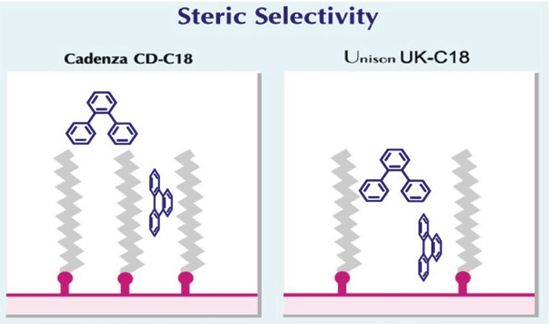
Figure 1: How ODS ligand density can improve steric selectivity
Experimental Conditions are shown in each figure.
Result and Discussion
Figure 2 shows that the columns tested had significantly different separation profiles for o-terphenyl and triphenylene, despite having nearly identical hydrophobic resolution (α = 1.4–1.5, data not shown). This comparison shows how steric selectivity can contribute to variation, with Brand XB (α=1.4) having the least resolution, followed by Cadenza CD-C18 (α=1.6), then Cadenza CX-C18 (α=2.2), with Dacapo DX-C18 (α=2.5) having the highest.
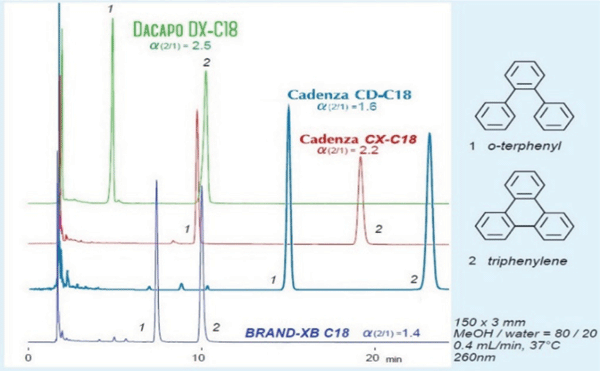
Figure 2: Standard steric selectivity test of four columns
Conclusion
We first discovered how to improve steric selectivity with the development of our Cadenza CD-C18 column. In Figure 1 you can see that, by having a higher ligand density, this creates a narrower space between the C18 chains, which presents a different geometry of interaction for molecules that are more planar. We have developed this technology further with Cadenza CX-C18 and Dacapo DX-C18, improving steric selectivity to α values of 2.2 and 2.5, respectively. The advantage of high steric selectivity can be seen in Figure 3, where four steroids with only minor differences were baseline resolved. In this case, the differences were minute, as with hydrocortisone vs. prednisolone, where a single bond is replaced by a double bond, and in cortisone vs. hydrocortisone, where a ketone is replaced by an alcohol.
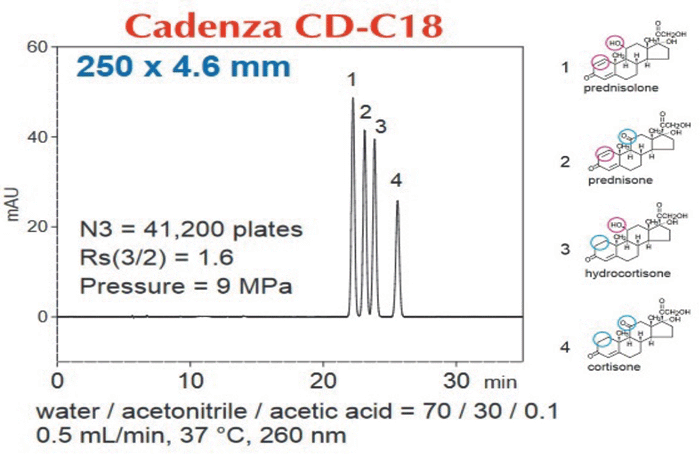
Figure 3: High steric selectivity is needed when the differences between analytes is not hydrophobic.
In summary, we have shown here that four ODS columns can have very different retention characteristics, despite all having the same ligand, with steric selectivity significantly contributing to this variation. We have also shown the importance of steric selectivity in providing separation of compounds that are very similar to each other. This suggests that the use of a high steric selectivity ODS column should be considered when separating compounds such as isomers or impurities, which may have very little difference between them.

Imtakt USA
2892 NW Upshur St., Portland, OR 97210
tel. (215) 665-8902, toll free (888) 456-HPLC, fax (501) 646-3497
Website:ImtaktUSA.com

A Guide to (U)HPLC Column Selection for Protein Analysis
April 16th 2025Analytical scientists are faced with the task of finding the right column from an almost unmanageable range of products. This paper focuses on columns that enable protein analysis under native conditions through size exclusion, hydrophobic interaction, and ion exchange chromatography. It will highlight the different column characteristics—pore size, particle size, base matrices, column dimensions, ligands—and which questions will help decide which columns to use.
Automating Protein Purification: Efficiency, Yield, and Reproducibility
March 27th 2025Recent advancements in automated protein purification stress the importance of efficiency, scalability, and yield consistency. This eBook compares different purification platforms, highlighting their impact on downstream applications and demonstrating how automation enhances throughput and process control.













