Restek LC–MS/MS Analysis of Mycotoxins in Peanut Powder in 5.5 Min
- Fast analysis for higher sample throughput
- Excellent separation improves accuracy for 12 regulated mycotoxins
- Quick and easy sample preparation (dilute-filter-shoot)
Certain fungi that can grow on agricultural products produce toxic metabolites known as mycotoxins. Modern food processing procedures cannot completely remove these compounds if they are present, so strict monitoring protocols have been established. Although a universal method for the analysis of mycotoxins would allow highly efficient screening, it is very challenging to develop such a method due to differences in physiochemical properties of mycotoxins, extraction efficiencies, and matrix effects. Zhang and associates published a multi-lab study (1) aimed at providing labs with an analytical procedure that could be broadly applied to the analysis of a variety of mycotoxins in many different matrices. Using that work as inspiration, we developed the following LC–MS/MS method that resolves 12 FDA regulated mycotoxins within the pressure limits of traditional HPLC instruments.
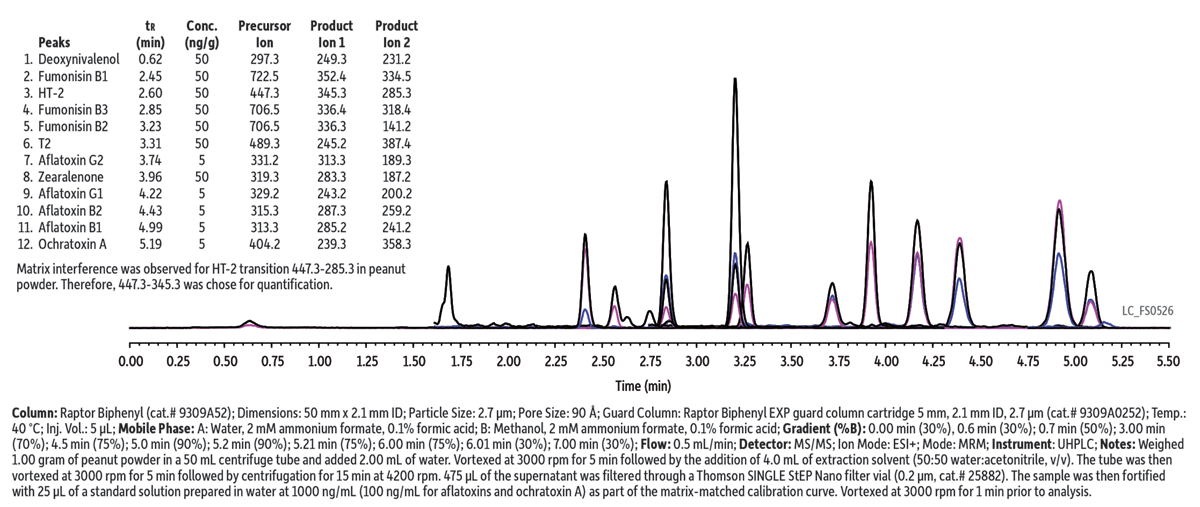
Click here to view full-size graphic
In this example, mycotoxins were analyzed in a peanut powder matrix. The use of a relatively short column format, the selectivity of the Biphenyl stationary phase, and the efficiency of 2.7-µm Raptor superficially porous particles provided excellent separations in a fast 5.5-min analysis (total cycle time of 7 min). A coeluting matrix compound that shared the most abundant MRM transition for mycotoxin HT-2 (447.3-285.3) was observed, so a less abundant transition (447.3-345.3) was selected for quantitation. To increase sensitivity, an ammonium buffer was used to promote better ionization of mycotoxins. The Raptor Biphenyl column worked very well for the 12 mycotoxins studied in the cited work, but for longer compound lists containing isobaric mycotoxins with similar structures, the Raptor FluoroPhenyl phase may be necessary to provide adequate chromatographic resolution. The selectivity of the Raptor Fluorophenyl column is demonstrated in an analysis of 20 mycotoxins that can be found by visiting www.restek.com and entering LC_FS0511 in the search.

This method showed excellent precision and accuracy for the 12 FDA regulated mycotoxins that were evaluated during a validation study that covered a variety of matrices (including multiple sources of cornmeal and brown rice flour, in addition to the peanut powder example shown here).
Click here to view full-size graphic
Restek would like to thank Dr. Zhang for his technical support during this project.
Reference
(1) K. Zhang, M.R. Schaab, G. Southwood, E.R. Tor, L.S. Aston, W. Song, B. Eitzer, S. Majumdar, T. Lapainis, H. Mai, K. Tran, A. El-Demerdash, V. Vega, Y. Cai, J.W. Wong, A.J. Krynitsky, T.H. Begley, J Agr Food Chem, 65(33) 7138–7152 (2017). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27983809.

Restek Corporation
110 Benner Circle, Bellefonte, PA 16823
tel. (800) 356-1688
Website: www.restek.com

New Study Reviews Chromatography Methods for Flavonoid Analysis
April 21st 2025Flavonoids are widely used metabolites that carry out various functions in different industries, such as food and cosmetics. Detecting, separating, and quantifying them in fruit species can be a complicated process.
Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)













