Significant Costs Savings Achieved Through the Development of a New Analytical Method for Residual API Analysis with a Kinetex 1.7 µm Core-Shell UHPLC Column
Phenomenex Application Note
This study demonstrates how the ultra-high performance of 1.7 µm core-shell columns can be used in the laboratory in order to realize significant cost savings.
Experimental Conditions
Columns: Kinetex 1.7 µm and 2.6 µm C18, 100 × 2.1 mm
Mobile phase: A: 5 mM Ammonium formate pH 3.25 / Acetonitrile (95:5)
B: 5 mM Ammonium formate pH 3.25 / Acetonitrile (10:90)
Gradient: See Table 1
Flow-rate: 0.4 mL/min
Temperature: 50 °C
Detector: PDA 210-300 nm, extracted channels 225 nm and 280 nm
Instrument: Waters ACQUITY equipped with PDA
Sample:
1. Antidepressant drug (containing a HCl salt); 2. Hormone therapy #1 (containing a salt); 3. SERM drug (containing a basic functional group); 4. CNS drug (containing basic functional group); 5. PPI drug (containing basic functional group); 6. CNS drug (containing basic functional group); 7. CNS drug (containing basic functional group); 8. Hormone therapy #2 (neutral); 9. Oral contraceptive hormone #1 (neutral); 10. Hormone therapy #3 (neutral); 11. Oral contraceptive hormone #2 (neutral); 12. Hormone therapy #4 (neutral); 13. Oral contraceptive hormone (neutral); 14. Hormone therapy #5 (neutral); 15. Hormone therapy #6 (acetate salt of 14); 16. Immunosuppressant drug (macromolecule, containing basic functional group)
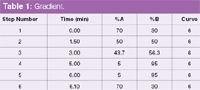
Table 1: Gradient.
Swab Extraction Procedure:
A swab containing residual API from different production surfaces was extracted with 2 mL of a solution containing a mixture of 1:1 acetonitrile/water and shaken for 5 minutes.
Results
The API's (Active pharmaceutical ingredients) used in these experiments are a mixture of organic salts, organic bases and neutral organic compounds. The analysis was performed on a Phenomenex Kinetex 1.7 µm C18 column under gradient conditions with a flow-rate of 0.4 mL/min. Two different UV wavelengths were used for quantification, 225 nm as shown in Figure 1(a) and 280 nm as shown in Figure 1(b).
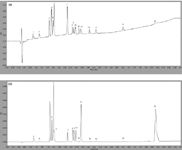
Figure 1: Sample chromatogram at (a) 225 nm; and (b) 280 nm, using a Kinetex C18 1.7 µm, 100 à 2.1 mm.
A reduced run time of 6 minutes compared to the 10–20 min in the original method was achieved. The critical pair for separation was compounds 5 and 6, as the closest eluting peaks. However, molecules 5 and 6 are not in the same class of drug and would not routinely be manufactured on the same equipment set and hence seen in the same sample. Therefore complete resolution was not required.
Conclusion
A new analytical method was developed which is capable of analysing 16 different API residues from production surfaces. It has been shown that the 1.7 µm Kinetex 100 × 2.1 mm column was capable of resolving 16 different chemical entities with a 6 minute run time. This new analytical method will be used to replace 16 older methods thereby facilitating an annualised cost saving for the site of €320000.
For complete details request Laboratory Case Study by Andrew Charles et al.
Phenomenex Inc.
411 Madrid Ave., Torrance, California, USA
tel: +1 310 212 055 fax: +1 310 212 7768
Website: www.phenomenex.com

Separating Impurities from Oligonucleotides Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
February 21st 2025Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) has been optimized for the analysis of 5-, 10-, 15-, and 18-mer oligonucleotides (ONs) and evaluated for its effectiveness in separating impurities from ONs.



















