Saccharide and Polysaccharide Analysis
PSS Application Note
Introduction
Polysaccharides are very important in nature, occurring in food (starches in rice, wheat, etc.) and plants (cellulose). Some polysaccharides are also produced commercially, for example dextrans, which are manufactured through the fermentation of sugar solutions. These are higher molar mass polysaccharides.
Dextrans are used in clinical and technical applications, where molecular weight is critical in determining the properties of the final product. Accurate determination of the molecular weight distribution is vital.
On the other hand, low molar mass saccharides are also very common in food, such as fruits, honey and sweets. Examples of low molar mass sugars are mono- (glucose, fructose), di- (lactose, isomaltose, trehalose) and trisaccharides (maltotriose, isomaltotriose). The separation and identification of low molar mass polysaccharides is a challenge as the compounds have the same chemical formula and only small differences in structure, for example disaccharides maltose, isomaltose, gentiobiose cellobiose and trehalose C12H22O11.
Experimental Conditions:
Eluent: NaNO3 0.1 M
Columns: PSS SUPREMA 5 µm 3 × 100 Å (8 × 300 mm) + precolumn
Data acquisition: PSS WinGPC Unity
Detectors: SECcurity GPC1200 RI
Flow-rate: 0.25 mL/min
Concentration: 4 g/L
Injection volume: 5 µL
Sample Figure 1: Dextran T1, Glucose
Sample Figure 2: Disaccharides
Results and Discussion
A high resolution and therefore a good separation on the column, is necessary for a precise analysis. This is particularly important when new analytical LC coupling methods like GPC/SEC–ESI-MS are used, as the MS detector requires the columns to have a much higher resolution power within an overall smaller column volume.
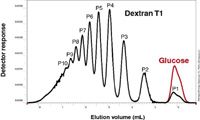
Figure 1: Overlay of elugrams of a glucose (red curve) with a low molar mass Dextran T1 (black curve).
The new SUPREMA column, with a reduced particle size of 5 µm, offers a significant improvement in performance compared to 10 µm materials and provides outstanding additional resolution, especially in the low molecular weight area, which is a major consideration when analysing oligomeric polysaccharides.
The analysis of dextran T1 shows the separation power when a combination of three SUPREMA 5 µm 100 Å columns is used. The oligomers in the low molecular weight are able to be resolved up to P10. A glucose separation is overlaid, as a reference.
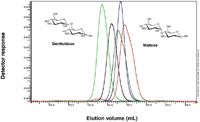
Figure 2: Overlay of elugrams of isomaltose (black), maltose (red), gentiobiose (green), cellobiose (dark green) and trehalose (blue).
The analysis of different disaccharides shows the ability to separate compounds with the same chemical formula and with only small differences in structure and hence size in solution.
PSS SUPREMA 5 µm columns can be used for numerous neutral and anionic aqueous applications in the molecular weight area between 100 Da to around 5 million Da. The columns are available in analytical (i.d. 8 mm) and micro (i.d. 4.6mm) dimensions with different porosities. Linear or mixed columns are also available.
PSS Polymer Standards Service GmbH
In der Dalheimer Wiese 5, D-55120 Mainz, Germany
tel: +49 6131 962390 fax: +49 6131 962390 11
E-mail: info@polymer.de Website: www.polymer.de

Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.

















