Separation of Steviol Glycosides
A robust, selective and sensitive separation method for the determination of four steviol glycosides in stevia plant matrix is demonstrated. In addition to the two calibrated substances two more glycosides could be found in stevia plant extracts by LC–MS. Using a popular Eurospher NH2 phase and applying moderate separation conditions results in an inexpensive and precise analysis method.
René Borstel, Columns and Applications Department, KNAUER, Berlin, Germany
Introduction
Steviol glycosides are responsible for the sweet taste of stevia plant leaves. These compounds are 75 to 450 times sweeter than sucrose without the typical bitter aftertaste of some well-known artificial sweeteners. In the course of the accreditation of these four steviol glycosides by the public health authority a stable and sensitive analytical quantitative separation method is highly recommendable.
Experimental
The separation was performed in isocratic mode on a KNAUER Smartline HPLC system with low pressure gradient capability, degasser, autosampler and column oven.
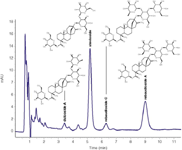
Figure 1: Separation of stevia plant extract on a Eurospher 100-5 NH2, 150 à 3 mm column. Method parameters: mobile phase: acetonitrile/water 80:20 (v/v); flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; injection volume: 10 µL; column temperature: 35 °C; system pressure: 50 bar; detection: UV at 210 nm.
Results
The separation could be achieved in 10 minutes. The limit of detection (LOD, S/N = 3) was determined for stevioside at 7.5 ng and for rebaudioside A at 16.0 ng.
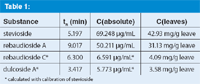
Table 1:
Conclusion
A fast and very good separation of four steviol glycosides in Stevia leaf extract samples with excellent peak symmetry is easily accomplished by reversed-phase HPLC using the Eurospher NH2 column in combination with a Smartline HPLC system. The simple isocratic method with moderate parameters guarantees robust and sensitive results over a long time period. The method allows safe quantification. Contact info@knauer.net for a more detailed version of this application.
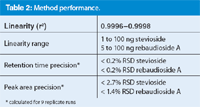
Table 2: Method performance.

Knauer GmbH
Hegauer Weg 38, 14163 Berlin, Germany
tel. +49 30 809727 0 fax +49 30 801501 0
E-mail: info@knauer.net
Website: www.knauer.net

Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.

















