A New Weak Anion-Exchange/Reversed-Phase Mixed-Mode Stationary Phase for Simultaneous Separation of Basic, Acidic and Neutral Pharmaceuticals
LCGC Asia Pacific
Mixed mode chromatography combines aspects of ion exchange chromatography and conventional reversed-phase (RP) chromatography. The combination of both hydrophobic and ion-exchange properties allows for independent control of retention for ionizable and neutral molecules.
Mixed mode chromatography combines aspects of ion exchange chromatography and conventional reversed-phase (RP) chromatography. The combination of both hydrophobic and ion-exchange properties allows for independent control of retention for ionizable and neutral molecules. Therefore, many application challenges involving hydrophilic ionizable compounds that would be difficult for C18 columns, can be easily tackled on a mixed-mode column. We have developed a new silica-based mixed-mode stationary phase, Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX, which provides both weak anion-exchange and RP characteristics facilitated by covalently attaching a hydrophobic alkyl chain with an ionizable terminus to the silica surface. The new column features complete control of selectivity, orthogonal selectivity to RP columns, high capacity and unique selectivity for anionic molecules and multi-mode retention mechanisms (i.e., RP, anion-exchange and HILIC).
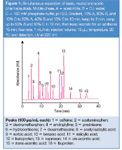
Figure 1
Experimental
Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX (4.6 × 150 mm, dp = 5 ⛤m, Dionex, Sunnyvale, California, USA) columns were used for the separation. Separations were performed on a modular Summit HPLC system (Dionex) equipped with a P680 gradient pump, ASI-100 Autosampler, TCC-100 column oven and UVD 340 detector. Chromeleon 6.70 Chromatography Management Software (Dionex) was used for system control and data processing. All standards were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, Missouri, USA). The chromatographic conditions are given in Figure 1.
Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows separation of a mixture of basic, neutral and acidic pharmaceutical-related compounds using a gradient method. We used a commonly employed mobile phase system containing acetonitrile, D.I. water and a phosphate buffer. All components in the mixture elute not only with symmetrical peaks, but also with good resolution. Unlike conventional RP columns, the unique column chemistry of the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX allows for fast elution of basic molecules with symmetrical peaks, high capacity and good selectivity for anionic molecules, such as acidic drugs and highly hydrophilic organic acids. Meanwhile, neutral molecules, such as steroids retained by hydrophobic interaction, usually elute after bases but before acidic molecules at pH 6. Thus, the separation is easily optimized by adjusting mobile phase ionic strength, pH and organic modifier, either independently or concurrently.
Conclusion
The Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX column provides unique and adjustable selectivity, excellent peak shape for all types of molecules (i.e., acids, bases and neutrals) and multi-mode retention mechanism (i.e., RP, anion-exchange and HILIC). Therefore, it can be used as either a primary column for a broad range of applications including pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, chemical or a complementary column (to conventional RP columns) that provides orthogonal selectivity.

Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale,
California 94088-3603, USA
tel. +1 408 737 0700 fax +1 408 730 9403
Website: www.dionex.com

The Benefits of Custom Bonded Silica
April 1st 2025Not all chromatography resins are created equal. Off-the-shelf chromatography resins might not always meet the rigorous purification requirements of biopharmaceutical manufacturing. Custom bonded silica from Grace can address a wide range of separation challenges, leading to real performance improvements. Discover more about the latest innovations in chromatography silica from Grace, including VYDAC® and DAVISIL®.
5 Things to Consider When Selecting a Chromatography Silica
April 1st 2025Particularly in the pharmaceutical industry, drug purity isn’t just a goal – it’s essential for achieving safety, stability and efficacy. However, purification is easier said than done, especially with challenging molecules like DNA and RNA “oligonucleotides,” due in large part to their diversity and the range of impurities that can be generated during production. Enter DAVISIL® chromatographic silica, with a wide range of pore diameters and particle sizes to meet your specific application, performance and sustainability requirements. Before you choose the chromatography resin for your next purification application, take a look at these 5 considerations.
Automating Protein Purification: Efficiency, Yield, and Reproducibility
March 27th 2025Recent advancements in automated protein purification stress the importance of efficiency, scalability, and yield consistency. This eBook compares different purification platforms, highlighting their impact on downstream applications and demonstrating how automation enhances throughput and process control.


















