Mass-Directed Preparative SFC: An Orthogonal Tool with Reduced Liquid Solvent Usage for High Throughput Purification
In recent years, improving productivity and cost-savings have become major initiatives in pharmaceutical discovery and development.
APPLICATION BENEFITS
The Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System offers significant benefits in high throughput purification environments. The orthogonality between RPLC and SFC offers potential cost-savings by recovering more compounds from medicinal chemistry for ensuing research and development. Prep 100 SFC MS employs carbon dioxide as the main mobile phase; thereby, reducing liquid solvent consumption and sample dry-down time post purification.
WATERS SOLUTIONS
Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System
2767 Sample Manager
3100 Mass Detector
2998 Photodiode Array (PDA) Detector
Gas-Liquid Separator
MassLynx™ Software
FractionLynx™ Application Manager
KEYWORDS
Open-bed fraction collection
Mass directed prep SFC
High throughput purification
SFC
Purification
INTRODUCTION
In recent years, improving productivity and cost-savings have become major initiatives in pharmaceutical discovery and development. The introduction of new technologies for high throughput synthesis has enabled preparation of up to 48 compounds in the same time frame previously required for a single compound.1 Consequently, there has been increasing pressure for development and implementation of efficient purification platforms to support the overall high throughput process.
Mass-directed reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC) purification has revolutionized the workflow for chemists in drug discovery by enabling one fraction collection per injection, largely due to the specificity that MS detection offers. As a result, mass-directed RPLC has quickly become the most commonly used technique in high throughput purification environments. Considerable effort has been devoted to streamlining the process so that minimal user intervention is required. However, a major limitation in the process is the long dry-down time of aqueous fractions downstream.
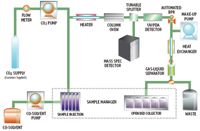
Figure 1. Schematic of Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System.
Adopted primarily for chiral analysis and purification by the pharmaceutical industry in the early 1990s, supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) has experienced a remarkable resurgence in the past decade. In particular, preparative SFC is deemed by many to hold the greatest promise to attain mainstream acceptance. SFC uses CO2 as the primary mobile phase and an organic co-solvent in isocratic or gradient mode of operation. The reduction in liquid solvent consumption and collection in relatively small volumes of volatile organic solvents has led to significant savings on operation costs. For example, Ripka, et al. calculated that 20,000 samples purified by SFC instead of RPLC would realize a 48 time reduction in solvent consumption.2
A mass-directed preparative SFC system, like its counterpart in RPLC, is an ideal platform for high throughput purification of diverse libraries of drug-like compounds. However, proprietary and capacity-limited collection systems along with limited software capability have been some of the key hurdles in using preparative SFC for library compound purification and mass-directed target collection. Waters® Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System overcomes these challenges.
This application note presents the results to illustrate key features of the Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System that demonstrate suitability for high throughput purification. Comparative results on library compound purification using both the AutoPurification™ and the Prep 100 SFC MS systems are also presented to highlight the orthogonality of the two techniques.
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
All preparative experiments were performed on a Waters Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System.
2767 Sample Manager
3100 Mass Detector
2998 Photodiode Array (PDA) Detector
CO2 pump
Liquid pump
515 HPLC Pump
Analytical-2-Prep™ Column Oven
Automated Back Pressure Regulator (ABPR)
Gas-Liquid Separator (GLS)
Tunable Splitter
MassLynx Software
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
To employ preparative SFC for high throughput purification, collection racks with tubes are required. Gaseous mobile phase, CO2, has to be vented and only the liquid solvent with dissolved compound can be collected in open tube format. One of the major challenges in implementing open-bed fraction collection at high flow rates in SFC is CO2 expansion. After exiting the ABPR, high pressure liquid CO2 will decompress to its gaseous form at a volume ratio of ~1:500. This rapid expansion will cause aerosol formation leading to possible sample loss and cross contamination. This challenge is overcome by a proprietary GLS, as shown in Figure 2.
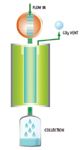
Figure 2. Schematic of the Gas-Liquid Separator (GLS).
The effectiveness of the GLS is demonstrated by the high recoveries and high purities of collected fractions. For example, Aurigemma et al. reported their evaluation of the Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System.3 In their experiment, a mixture of flavone (A), carbamazepine (B), acetaminophen (C), and sulfamethazine (D) with a concentration of 8 mg/mL for each component were injected and collected over three replicate injections as shown in Table 1. Overall, sample recoveries and purities greater than 95% (with the exception of peak C in injection 1) during gradient elution were achieved. In particular, the high purities of two closely eluting components (C and D) indicated a negligible cross contamination between peaks. In a separate experiment, similar evaluations were performed using a mixture of caffeine, sulconazole, and bendroflumethazide. On average, greater than 90% of recovery and greater than 99% purity were achieved for all compounds using UV triggering, MS triggering, and UV+MS triggering, respectively.
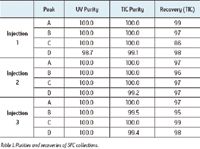
Table I. Purities and recoveries of SFC collections.
It is also important to recognize the cost-savings aspect of implementing the Prep 100 SFC MS system into high throughput purification environments. In addition to the well documented cost-savings resulting from reduction in solvent consumption and dry-down time,2,4 the orthogonality between SFC and RPLC offers additional cost savings by pushing more compounds from medicinal chemistry through the pipeline. SFC is loosely considered a normal-phase chromatographic technique and complements RPLC in selectivity. For example, Figure 3 shows the comparison between mass-directed RPLC and SFC in purifying one real-world pharmaceutical compound directly from combinatorial synthesis; here, the impurity was baseline resolved from the target compound in SFC but not in RPLC. A previous study5 reported a 30% increase in the success rate when combining the two techniques compared to using each technique alone. The same study also reported a 20% reduction in overall batch processing time for SFC compared to RPLC as a result of shorter dry-down time post purification.
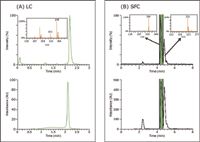
Figure 3. Chromatograms illustrating the different selectivity between RPLC and SFC.
Another example where the combination of system features and software capabilities perform mass selective detection of a small quantity of compound, which may be present in a library and able to trigger collection, is a separation illustrated in Figure 4. Here, two spiked impurities of combined weight of 0.55% wt/wt are isolated around the main peak. The system was able to detect and collect peak 1, carbamazepine 280 ug and peak 3, sulfamethazine 205 ug from the main peak 2, 87.2 mg ketoprofen injected on the column using MS trigger settings.
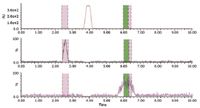
Figure 4. SFC chromatograms illustrating the isolation of a small amount of impurities from the main peak.
CONCLUSIONS
This application note demonstrates the ability of the Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System to be used in applications such as high throughput or library purification where one fraction is desired per injection. Intelligent instrument control meets demanding fraction collection workflow needs with FractionLynx Application Manager derived from MassLynx Software. The orthogonal separation mechanism offers an added dimension to process more diverse compounds. Finally, the liquid solvent savings coupled with reduced dry-down time can have a positive operational impact on the laboratory by increasing throughput while reducing the cost of processing each sample.
References
1. McClain RT, et al. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies, 2009; 32: 483-499.
2. Ripka WC, Barker G, and Krakover J. Drug Discovery Today, 2001 6 (9): 471-477.
3. Aurigemma C, Zulli S, Wang Z, and Lefler JL. poster presentation, LabAutomation, 2009.
4. White C, Burnett J. J.Chromatog. A., 2005; 1074, 175.
5. Mich A, Matthes B, Chen R, and Buehler S. LCGC Europe, The Application Book, March 2010.
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street
Milford, MA01757U.S.A.
T: 1 508 478 2000
F: 1 508 872 1990

Regulatory Deadlines and Supply Chain Challenges Take Center Stage in Nitrosamine Discussion
April 10th 2025During an LCGC International peer exchange, Aloka Srinivasan, Mayank Bhanti, and Amber Burch discussed the regulatory deadlines and supply chain challenges that come with nitrosamine analysis.











