Expediting Achiral SFC Method Development Using a Multi-Channel SFC System with MS Detection
Special Issues
In the past decade, supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) has been established as a cost-effective, sustainable, and green purification technology for pharmaceutical and related industries.
APPLICATION BENEFITS
This application note demonstrates the workflow of an achiral SFC method development using the Waters® Resolution X5 SFC MS System. In multichannel mode, five columns were simultaneously screened and the optimal column was identified. The throughput in method development was improved five-fold. In single-channel mode, the 3100 Mass Detector provided mass confirmation of the analytes, which is typically required in achiral SFC method development.
WATERS SOLUTIONS
Resolution X5 SFC MS System
2998 Photodiode Array (PDA) Detector
2489 Tunable UV/Visible (TUV) Detector
3100 Mass Detector
MassLynx™ Software
Viridis™ SFC Column
KEYWORDS
SFC
Method development
Achiral
INTRODUCTION
In the past decade, supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) has been established as a cost-effective, sustainable, and green purification technology for pharmaceutical and related industries. For example, Ripka et al. calculated that 20,000 samples purified by SFC instead of reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC) would yield a 48-time reduction in solvent consumption.1 Improved productivity resulting from reduced dry-down time post purification was reported by McClain et al. by adopting an SFC-based purification platform in a high throughput purification environment.2 A comparative study by Buehler et al.3 also revealed the orthogonality between SFC and RPLC, which enabled chemists to recover more compounds from medicinal chemistry for ensuing research and development.
One bottleneck in SFC applications is the extensive method development required because of the lack of a universal column, especially achiral applications of analytes possessing a wide polarity range and/or complex matrices. Trial-and-error screening of a set of stationary phases has been the predominant approach to achiral SFC method development. However, the whole process is time-consuming because each column has to be tested individually in a temporal manner. To circumvent this problem, parallel screening approaches4-5 have been introduced where an injected sample was carried by the mobile phase and, simultaneously, divided into multiple columns. Existing systems primarily focus on chiral separations where a UV detector generally suffices, but are inadequate for achiral separations due to sample complexity.
In this application note, the Resolution X5 SFC MS System is introduced, a multichannel SFC system with MS detection seamlessly integrated with MassLynx Software. SFC method development of a five-component mixture in multi-channel mode and mass confirmation of structurally similar compounds in single channel is demonstrated.
Chromatographic conditions
The key experimental parameters for the multi-channel experiments were as follows:
Flow rate: 20 mL/min
System pressure: 120 bar
Temp.: 40 °C
Injection volume: 50 μL
Co-solvent: Methanol
Gradient: 5% to 30% in 5 min, hold at 30% for 1 min, return to 5% in 2 min, and hold at 5% for 2 min
2489 TUV wavelength: 254 nm
2998 PDA
wavelength range: 210 to 400 nm
MS mode: APCI, ± switching
The key experimental parameters for the single-channel (channel 5) experiments were as follows:
Flow rate: 4 mL/min
System pressure: 120 bar
Temp.: 40 °C
Injection volume: 10 μL
Co-solvent: Methanol
Gradient: 5% to 30% in 5 min, hold at 30% for 1 min, return to 5% in 2 min, and hold at 5% for 2 min
2998 PDA
wavelength range: 190 to 350 nm
MS mode: APCI, ± switching
EXPERIMENTAL
All experiments were performed on the Resolution X5 SFC MS System (X5-MS), which consists of a Fluid Delivery Module (FDM) with a flow rate up to 30 mL/min, an Alias Autosampler, an Analytical-2-Prep™ 10-port column oven, an Automated Back Pressure Regulator (ABPR), four 2489 UV/Vis detectors (channels 1 to 4), a 2998 Photodiode Array (PDA) Detector (channel 5), a LabAlliance 10 Series I Make-Up Pump, and a 3100 Mass Detector. The system was controlled by MassLynx Software. The schematic of the system is shown in Figure 1.
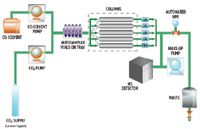
Figure 1. Resolution X5 SFC MS System schematic.
All chemicals were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and their structures are shown in Figure 2. A stock solution of 1 mg/mL for each compound was made in methanol. The five columns used were (in order of channel number): Viridis SFC 2-Ethyl Pyridine, Viridis SFC Silica, diol, cyano and propylpyridyl urea (PPU) columns from Princeton Chromatography, Inc. (Cranberry, NJ, USA). All five columns were 4.6 x 150 mm in dimension with 5 μm particle size.
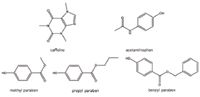
Figure 2. Chemical structures of the compounds used in this study.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Figure 3 shows SFC UV chromatograms of the five-component mixture obtained using a generic gradient in multi-channel mode. It is clear that the PPU column offered a complete resolution of all five compounds. However, the TUV and PDA detectors were unable to differentiate the identities of the eluting compounds, especially for the structurally similar parabens whose UV spectra were almost identical, as shown in Figure 4. Nevertheless, multi-channel screening was sufficient as a first-pass screening tool to identify the suitable column for further method optimization.

Figure 3. SFC chromatgrams of the five-component mixture obtained in multi-channel mode.
Next, we switched to the PPU column in single channel mode by selecting the preset method. Note that this switching was realized via fully software-controlled proprietary valve configuration and did not involve any hardware change. Figure 5 shows the SFC-UV chromatogram (bottom trace) and the extracted ion chromatograms (XICs) of the three parabens, with their respective mass spectra shown in the inserts. It is evident that the 3100 Mass Detector provided necessary mass confirmation of the paraben analogues.

Figure 4. UV spectra of three parabens.
Finally, it is noteworthy that the system is seamlessly integrated with MassLynx Software, the same software platform used for the Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System. This software continuity enables users to effortlessly transfer their analytical method for ensuing purification.
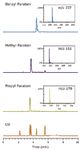
Figure 5. SFC UV chromatogram of the five-component mixture and extracted ion chromatograms (XICs) of the three parabens. Inserts are mass spectra of the parabens.
CONCLUSIONS
In this application note, the workflow for achiral SFC method development using the Resolution X5 SFC MS System was demonstrated. In multi-channel mode, five columns were simultaneously screened and the optimal column was identified; hence, a five-fold increase in throughput. The mass confirmation is often necessary in achiral applications of complex samples and analytes of similar structures with or without chromophores.
References
1. Ripka WC, Barker G, and Krakover J. Drug Discovery Today, 2001; 6(9): 471-477.
2. McClain RT, Dudkina A, Barrow J, Hartman G, and Welch CJ. J. Liquid Chromatog. & Related Tech., 2009; 32: 483-499.
3. Mich A, Matthes B, Chen R, and Buehler S. LCGC Europe: The Application Notebook, 2010; 12-13.
4. Zeng L, Xu R, Laskar DB, and Kassel DB. J. Chromatogr. A., 2007; 1169: 193-204.
5. Subbarao L, Wang Z, and Chen R. LCGC Europe, Apps. Book, 2009; 24-25.
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street
Milford, MA 01757 U.S.A.
T: 1 508 478 2000
F: 1 508 872 1990

Silvia Radenkovic on Her Research and Passion for Scientific Collaboration
April 3rd 2025Radenkovic is a PhD candidate at KU Leuven and a member of FeMS. Her research focuses on inborn metabolic disorders (IMD), like congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG), omics techniques such as tracer metabolomics, and different disease models.
Evaluating Natural Preservatives for Meat Products with Gas and Liquid Chromatography
April 1st 2025A study in Food Science & Nutrition evaluated the antioxidant and preservative effects of Epilobium angustifolium extract on beef burgers, finding that the extract influenced physicochemical properties, color stability, and lipid oxidation, with higher concentrations showing a prooxidant effect.










