Chiral Purification with Stacked Injections and Collections Using the Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System
Special Issues
Chiral chromatography has become the preferred tool for enantiomer separations in the early stages of pharmaceutical development for the purpose of accurately identifying single pure enantiomers with pharmacologic, toxicological, and clinical information, as stipulated by the FDA.1
APPLICATION BENEFITS
Implementing the stacked injection mode for chiral purification demonstrates the versatile and flexible collection scheme offered by the Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System. This open-bed platform for collection at atmospheric pressure conditions provides higher efficiency and greater success when multiple detectors are used including a mass detector trigger.
WATERS SOLUTIONS
Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System
2998 Photodiode Array (PDA) Detector
3100 Mass Detector
2767 Sample Manager
Masslynx™ Software
FractionLynx™ Application Manager
Stacked Injection Module
KEY WORDS
Chiral
Prep 100 SFC
Stacked injections
Mass directed
Open-bed collection
INTRODUCTION
Chiral chromatography has become the preferred tool for enantiomer separations in the early stages of pharmaceutical development for the purpose of accurately identifying single pure enantiomers with pharmacologic, toxicological, and clinical information, as stipulated by the FDA.1
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) has proven to be a mainstream technology for chiral separations based on its higher efficiency, throughput, and wide applicability. Chiral SFC has seen increased interest and applicability, in some cases, becoming the method of choice.
Frequently, enantiomeric mixtures contain some significant impurities, which decrease the efficiency of the actual purification process where stacked injection and signal-threshold-based collection strategies (such as UV/PDA detection) are commonly used. In most cases, a pre-cleanup step is necessary but impractical because of resource and labor restrictions. This requires a versatile detection scheme capable of distinguishing the enantiomers from other impurities. The 3100 Mass Detector is an ideal choice in addition to UV/PDA detectors that are widely used in chiral separations.
In this application note, the Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System, with stacked injections and collections on the open-bed platform is demonstrated as a tool in chiral compound purification. The system configuration and methodology for the chiral separation cases are reviewed and presented.
EXPERIMENTAL
Chemicals
CO2 from Airgas (Salem, NH, USA) is supplied in pressurized liquid form at approximately 1100 to 1300 psi through house lines to the Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System.
Methanol and trans-stilbene oxide (TSO, MW196) were provided by Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
SFC columns
ChiralPak AD-H and ChiralCel OD-H (both 21 mm x 250 mm, 5 μm) were supplied by Chiral Technologies (West Chester, PA, USA).
SFC system
Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System was implemented with an additional stacking injector. The 2767 Sample Manager was configured as a simplified, repetitive fraction collector.
METHOD CONDITIONS
SFC gradient and flow program
For all data presented, the maximum total flow of 100 g/min was used with various isocratic modifier programs.
Mass detector conditions
The standard ESI mode for all experiments with the 3100 Mass Detector used the following key parameters:
Capillary voltage: 3.5 KV
Cone voltage: 40.0 V
Extractor voltage: 3.0 V
RF Lens voltage: 0.1 V
Source temp.: 150 °C
Desolvation temp.: 350 °C
Desolvation gas flow: 400 L/hr
Cone gas flow: 60 L/hr
0.1% formic acid in methanol is used as make-up/conditioning flow into MS for improved ionization efficiency.
Data management
MassLynx/FractionLynx, version 4.1
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Scale-up purification with stacking injection mode
A commonly accepted best practice in chiral analyses is to utilize the stacking mode for sample injection and fraction collection, maximizing efficiency and reducing production costs.
The mass-directed-based system has advantages in difficult situations where significant impurities are present, by selectively identifying targets of interest and collecting them while correctly ignoring unwanted impurities; thus, maintaining the high efficiency of chiral SFC for purifications, realizing wider applicability, and becoming the routine mainstream tool for chiral drug development.
To use the mass-directed system for chiral purification to its maximum benefit, certain modifications had to be made on the Prep100 SFC System. These included the addition of a dedicated injector and collection bed layout modifications to accommodate larger containers for repetitive fraction collections of the enantiomers.
Stacking of injection /injector implementation
A Waters® Stacked Injection Module was integrated into the Prep 100 SFC System. Users select "Injection Type," and enter the total number of stacked injections and other related parameters in the software program, as shown in Figures 1 and 2. A customized injector sequence is implemented to run the injector in stacking mode. The injector can draw sample aliquots from a single, bulk sample vessel.
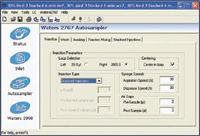
Figure 1. Stacked injection mode is integrated into MassLynx Software.
When not in stacked injection mode, the 2767 Sample Manager maintains its capabilities of performing single injections from the sample racks on the bed, as defined in the Sample List.
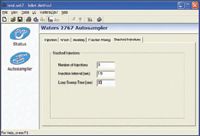
Figure 2. Stacking injection parameters as part of method settings.
Figure 3 shows representative chromatograms from stacked injections of a two-peak mixture. Both UV and MS trace of desired mass are identified correctly, ensuring the reliability and successful fraction collections by either UV or MS trigger. In this case, UV signal was used as the collection trigger; if needed, MS signal can also be used.
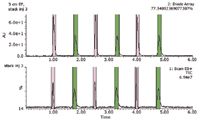
Figure 3. Stacked injections and demonstrated correspondent collection bands.
Customization of collection bed layout for single bottles
The Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System utilizes the 2767 Sample Manager as the dedicated fraction collector. In chiral purifications, since the number of the collected fractions are two (or may be up to four in some cases), larger containers with repetitive back-and-forth collection mode are desired in place of the routine tube rack format in one-to-one fashion.
The 2767 Sample Manager was, therefore, customized by defining the locations of the desired larger containers on the bed, to allow repetitive back-and-forth stacking collection sequences for the same enantiomer from all the stacked injections collected into the same bottle.
As shown in Figure 3, the two enantiomer fractions were collected into bottle 1 (pink band) and bottle 2 (green band), respectively. This was done in a back-and-forth fashion on the 2767 Sample Manager bed from a single injection line in the sequence. This demonstrated that the process was successful, meeting the key criterion using MassLynx Software and FractionLynx Application Manager to correctly identify and collect the enantiomer pair by its signal intensity level.
Figure 4 shows a selective separation and collection that represents a case where an unwanted peak co-existed with the desired enantiomer pair. Only two separated, targeted compounds were collected via targeted mass. This is depicted by colored bands. However, the extra third peak (unwanted impurity) was not collected.
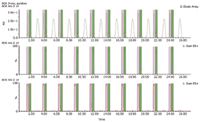
Figure 4. Stacked injection and collection of two peaks from a three-peak mixture.
The MassLynx/FractionLynx AutoPurify™ platform has many advanced detection and collection algorithms that can be adopted for sophisticated workflow, such as Boolean logic of multiple detector signals as triggers. If the sample is sufficiently clean, a user may opt to use UV/PDA for detection. If the sample contains significant portions of impurities, the operator may opt to use combined signal and slope algorithms and specific targeted masses to ensure purer collections.
CONCLUSIONS
The Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System has demonstrated its high efficiency, applicability, and versatility in various pharmaceutical developments. The added feature of stacked injections and collections of the Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System demonstrated here, enables more customized capabilities for chiral separation applications that benefit chromatographers in purification labs such as:
- Multiple and versatile detection modes for a higher success rate.
- The same stacked injection and collection mode on an open-bed platform facilitating ease-of-use.
- A safer lab environment in compliance with industrial and governmental regulations.
The Waters Prep 100 SFC MS Directed System is a powerful tool for chiral purification in drug discovery as well as other preparative chromatography, meeting the increased demand for productivity and greater success.
Reference
1. http://www.fda.gov/cder/guidance/stereo.htm
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street
Milford, MA 01757 U.S.A.
T: 1 508 478 2000
F: 1 508 872 1990

Regulatory Deadlines and Supply Chain Challenges Take Center Stage in Nitrosamine Discussion
April 10th 2025During an LCGC International peer exchange, Aloka Srinivasan, Mayank Bhanti, and Amber Burch discussed the regulatory deadlines and supply chain challenges that come with nitrosamine analysis.











