Determination of Sulfonamide Antibiotics in Bovine Liver Using Agilent SampliQ QuEChERS EN Kits by LC–MS-MS
The procedure involves a rapid and efficient pretreatment with SampliQ QuEChERS kits. The homogenized liver sample was initially extracted in a buffered aqueous/1% acetic acid acetonitrile system with an extraction and partitioning step after the addition of salts.
Limian Zhao and Joan Stevens, Agilent Technologies, Inc.
The procedure involves a rapid and efficient pretreatment with SampliQ QuEChERS kits. The homogenized liver sample was initially extracted in a buffered aqueous/1% acetic acid acetonitrile system with an extraction and partitioning step after the addition of salts. Finally, the sample was cleaned up using dispersive solid-phase extraction (dispersive-SPE). The final extracts were analyzed by the sensitive and selective determination of all compounds in a single run using LC-ESI-MS-MS operating in positive ion multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. Sulfapyridine was selected as the internal standard. The accuracy of the method, expressed as recovery, was between 53 and 93%. The precision, expressed as RSD, was between 2.1 and 16.8%. The established 5 ng/g limits of quantification (LOQ) were much lower than the respective Maximum Residue Limit (MRL) for sulfonamide in animal food products (20-100 ng/g).
Sample Preparation and HPLC Instrument Conditions
Sample preparation and HPLC condtions are available in their entirety within Agilent Technologies publications 5990-5086EN.
Figure 1 shows the MRM chromatograms of the liver control blank and 100 ng/g fortified liver extract. The liver control blank chromatogram indicated that the target analytes were free from any interference.
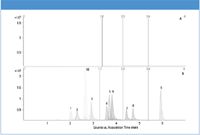
Figure 1: LCâMS-MS Chromatograms of A) liver blank extract, and B) 100 ng/g fortified liver extract. Peaks identification: sulfadizine, 2. sulfathiazole, 3. sulfamerazine, 4. sulfamethizole, 5. sulfamethazine, 6. sulfamethoxypyridazine, 7. sulfachloropyridazine, 8. sulfamethoxazole, 9. sulfadimethoxin, IS (internal standard), sulfapyridine.
Recovery and Reproducibility
The recovery and reproducibility (shown as RSD) data are shown in Table I. The results show that all of the sulfonamides were somewhat low but still at acceptable recoveries (average of 77.8%) and good precision (average of 7.2% RSD). Samples were concentrated during the procedure to optimize sensitivity, which also caused additional matrix effects that possibly contributed to a higher RSD of target compounds at low levels.
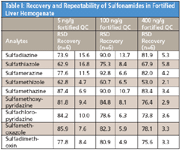
Table I: Recovery and Repeatability of Sulfonamides in Fortified Liver Homogenate
Conclusions
When compared to other sample preparation methods, such as LLE and SPE, QuEChERS methodology is easy, fast, low cost, and does not require automation. In addition, it is labor saving and a "greener" technology. The recovery and reproducibility, based on matrix-spiked standards, were acceptable for multiresidue sulfonamide determination in bovine liver. The impurities and matrix effects from liver were minimal and did not interfere with the quantification of any target compound. The LOQs of the quinolones were much lower than their regulated MRLs in animal food products (20-100 ng/g). This modified QuEChERS procedure is a very promising methodology for the quantitative analysis of sulfonamides in food products of animal origin. This application demonstrates great potential of SampliQ QuEChERS extraction and dispersive-SPE kits, and extend far beyond plant matrices to bio-matrices, such as animal food products and bio-fluid.
Agilent SampliQ QuEChERS EN Extraction kit p/n 5982-5650. Agilent SampliQ QuEChERS EN fatty dispersive-SPE kit for 15 mL p/n 5982-5156.
The complete text of this application first appeared as Agilent Technologies publication 5990-5086EN.

Agilent Technologies, Inc.
2850 Centerville Road, Wilmington, DE 19808
tel. (800)227-9770; fax (302)633-8901
Website: www.agilent.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.















