Analysis of Basic Pharmaceuticals and Peptides on a Multi-Mode ODS Column
Analyzing basic pharmaceuticals and peptides can be challenging with conventional ODS columns.
Bryan Evans and Itaru Yazawa, Imtakt USA (formerly Silvertone Sciences)
Analyzing basic pharmaceuticals and peptides can be challenging with conventional ODS columns. Often times, separating these compounds requires the use of ion-pairing reagents. In this paper, we present an alternative solution using Scherzo SM-C18 (Multi-Mode ODS column).
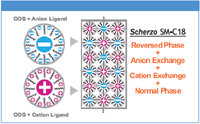
Figure 1: Multi-Mode ODS column structure.
Experimental and Results
All data was generated with a semi-micro HPLC system equipped with UV or ELS detection. Solutes were separated using LC–MS compatible conditions on Unison UK-C18 (conventional ODS) and Scherzo SM-C18 (Multi-Mode ODS consisting of ODS + anion + cation ligands, Figure 1). Figure 2 shows the separation of antidepressant drugs under acidic and neutral conditions. The data shows that ionic interaction between basic solute and the stationary phase increases at higher pH (organic composition was increased to optimize separation). Figure 3 shows the separation of anserine and related compounds. Both L-carnosine and L-anserine contain histidine and show improved retention on the Multi-Mode ODS column due to cation exchange. The nucleotide Inosine 5'-monophosphate shows improved retention due to anion exchange.
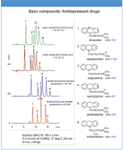
Figure 2: Basic compounds - antidepressant drugs.
Conclusion
Scherzo SM-C18 (Multi-Mode ODS) offers an alternative method to ion-pairing chromatography for basic pharmaceuticals and peptides. Scherzo SM-C18 will be useful for those looking to eliminate ion-pairing chromatography, as well as those who require an ODS column with different selectivity.
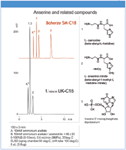
Figure 3: Anserine and related compounds.

Imtakt USA (formerly Silvertone Sciences)
1511 Walnut St., Suite 310, Philadelphia, PA 19102
tel. (215)665-8902; fax (501)646-3497
Email: info@imtaktusa.com; Website: www.imtaktusa.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.















