Determination of Pesticide Residues in Whole Milk by QuEChERS and LC–MS–MS
UCT
This application note describes a cost-effective and easy to use method for the fast determination of pesticide residues in whole milk samples. The method employs the AOAC version of QuEChERS. This procedure provides better analytical results than either the original or EN versions of the QuEChERS procedure in extracting a few sensitive pesticides, such as pymetrozine and hexazinone (Velpar). A sample of 50 mg primary secondary amine (PSA) and 50 mg C18 are used in dSPE for the cleanup of whole milk samples. PSA removes organic acids and carbohydrates, while C18 retains fatty acids and cholesterol. The result is a clean extract for LC–MS–MS analysis.
Extraction and Cleanup Products
QuEChERS Extraction
1) Transfer 15 mL of whole milk into a 50-mL centrifuge tube (RFV0050CT).
2) Add internal standard to all samples, and appropriate amounts of pesticide spiking solution to fortified samples.
3) Add 15 mL of acetonitrile (MeCN) with 1% acetic acid.
4) Cap and shake 1 min at 1000 strokes/min using a Spex 2010 Geno/Grinder.
5) Add salts (6 g MgSO4 and 1.5 g NaOAc) in Mylar pouch (ECMSSA50CT-MP) to each tube, and vortex for 10 s to break up salt agglomerates.
6) Shake for 1 min at 1000 strokes/min using Spex Geno/Grinder.
7) Centrifuge the samples at 3830 rcf for 5 min.

Figure 1: Whole milk samples extracted by the AOAC QuEChERS procedure.
dSPE Cleanup
1) Transfer 1 mL supernatant into a 2-mL dSPE tube (CUMPSC18CT).
2) Shake for 2 min at 1000 strokes/min using Spex Geno/Grinder.
3) Centrifuge at 15300 rcf for 5 min.
4) Transfer 0.3 mL of the cleaned extract into a 2-mL auto-sampler vial.
5) Add 0.3 mL of reagent water, and vortex for 30 s.
6) The samples are ready for LC–MS–MS analysis.
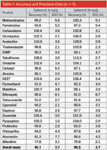
Table 1: Accuracy and Precision Data (n = 5).
Conclusion
A simple, fast, and cost-effective method has been developed to determine pesticide residues in whole milk samples. Pesticide residues in whole milk were extracted using the AOAC version of the QuEChERS approach, followed by dSPE cleanup using MgSO4, PSA, and C18. Excellent accuracy and precision were obtained, even for pymetrozine, a sensitive pesticide with very low recovery when the original or EN version of the QuEChERS approach is employed. The overall analytical run time was 20 min with the overall mean recovery for the 24 pesticides being 96.1% and 98.5% for 10 and 50 ng/mL fortified samples, respectively.
LC–MS–MS conditions and SRM transitions are available upon request.

UCT, Inc.
2731 Bartram Road, Bristol, Pennsylvania19007, USA
Tel: (215) 781 9255
E-mail: methods@unitedchem.com
Website: www.unitedchem.com

New Study Reviews Chromatography Methods for Flavonoid Analysis
April 21st 2025Flavonoids are widely used metabolites that carry out various functions in different industries, such as food and cosmetics. Detecting, separating, and quantifying them in fruit species can be a complicated process.
Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)















