Analysis of Synthetic Opiates and Novel Analgesics in Urine Using SPE and HPLC–MS/MS
The Application Notebook
Opiate abuse is drastically on the rise in the United States. In addition to traditional naturally occurring opiate compounds, forensic toxicologists also need to be able to rapidly identify synthetic opioid-like drugs. A rapid, three-step solid-phase extraction (SPE) procedure for the identification and quantification of fentanyl and its major urinary metabolite norfentanyl, in addition to four “designer” compounds, U-47700, W-18, W-15, and furanyl fentanyl, is presented here. As a result of the rapid use and abuse of fentanyl in medical and recreational settings, respectively, it is important to develop a method that can accurately extract this Schedule II drug from any other novel compounds that may be present.
Danielle Mackowsky, UCT, LLC
Summary
Opiate abuse is drastically on the rise in the United States. In addition to traditional naturally occurring opiate compounds, forensic toxicologists also need to be able to rapidly identify synthetic opioid-like drugs. A rapid, three-step solid-phase extraction (SPE) procedure for the identification and quantification of fentanyl and its major urinary metabolite norfentanyl, in addition to four “designer” compounds, U-47700, W-18, W-15, and furanyl fentanyl, is presented here. As a result of the rapid use and abuse of fentanyl in medical and recreational settings, respectively, it is important to develop a method that can accurately extract this Schedule II drug from any other novel compounds that may be present.
Procedure
1. Sample Pretreatment:
To 1 mL of urine sample, add 1 mL of 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH = 6) and an appropriate amount of internal standard.
2. Sample Extraction:
Apply the sample to the SPE cartridge (if required, use a low vacuum to draw the sample through at ≤3 mL/min).
3. Wash Cartridge:
a) 1 × 3 mL D.I. H2O
b) 1 × 3 mL 100 mM acetic acid
c) Dry column under full vacuum or pressure for 10 min.
4. Elution:
a) 1 × 3 mL methanol containing 2% ammonium hydroxide (methanol:NH4OH, 98:2 v/v).
b) Evaporate the sample to dryness under a gentle stream of nitrogen.
c) Reconstitute in 100 µL 95:5 D.I. H2O:methanol and vortex for 1 min.
d) Transfer sample to autosampler vial containing a low volume insert.
Instrumental
LC–MS/MS: Thermo Scientific™ Dionex™ Ultimate™ 3000 UHPLC and TSQ Vantage™ (MS/MS)
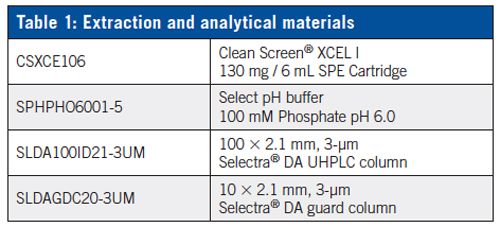
Column: 100 × 2.1 mm, 3-μm UCT Selectra® DA HPLC column
Guard Column: 10 × 2.1 mm, 3-μm UCT Selectra® DA guard column
Injection Volume: 5 μL
Mobile Phase A: D.I. H2O 0.1% formic acid
Mobile Phase B: Methanol 0.1% formic acid
Column Flow Rate: 0.30 mL/min
Results
Conclusion
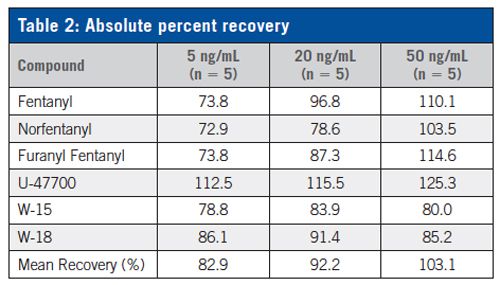
A fast and effective method was developed for the determination of six designer opiates in urine samples. All analytes of interest were extracted using a Clean Screen® XCEL I column. Analysis of the samples was performed by LC–MS/MS utilizing a Selectra® DA HPLC column, which allowed for improved separation of furanyl fentanyl and fentanyl, when compared to other column phases. Absolute recoveries ranged from 72.9–125.3% for all three control levels tested. With the unfortunate (and often unaware) abuse of synthetic opiates throughout the United States, it is critical that forensic laboratories have accurate and rapid SPE methods for the identification of this class of compounds. This method will be of great use as drugs with similar structures start to be found in casework.

UCT, LLC
2731 Bartram Road, Bristol, Pennsylvania 19007, USA
Tel: (800) 385 3153
E-mail: methods@unitedchem.com Website: www.unitedchem.com
Best of the Week: Food Analysis, Chemical Migration in Plastic Bottles, STEM Researcher of the Year
December 20th 2024Top articles published this week include the launch of our “From Lab to Table” content series, a Q&A interview about using liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC–HRMS) to assess chemical hazards in plastic bottles, and a piece recognizing Brett Paull for being named Tasmanian STEM Researcher of the Year.
Using LC-MS/MS to Measure Testosterone in Dried Blood Spots
December 19th 2024Testosterone measurements are typically performed using serum or plasma, but this presents several logistical challenges, especially for sample collection, storage, and transport. In a recently published article, Yehudah Gruenstein of the University of Miami explored key insights gained from dried blood spot assay validation for testosterone measurement.
Determination of Pharmaceuticals by Capillary HPLC-MS/MS (Dec 2024)
December 19th 2024This application note demonstrates the use of a compact portable capillary liquid chromatograph, the Axcend Focus LC, coupled to an Agilent Ultivo triple quadrupole mass spectrometer for quantitative analysis of pharmaceutical drugs in model aqueous samples.
