Simultaneous Measurement of Anions and Cations: Method Validation
Dedicated instrumentation, multiple columns and time-consuming changeovers are required in order to measure both anions and cations with ion chromatography.
The use of HILIC chromatography and the Corona® Detector with HPLC offers an alternative technique for the analysis of ions. This applications note discusses the validation of this method of analysis.
Dedicated instrumentation, multiple columns and time-consuming changeovers are required in order to measure both anions and cations with ion chromatography.
A new method for ion analysis has been introduced (1) that measures both anions and cations in a single analysis using standard HPLC. This application note describes aspects of method validation.
Materials
A standard HPLC system with a Corona® CAD Detector.
Column: Sequant ZIC®-pHILIC 5 μm, 4.6 × 150 mm, 30 °C
Mobile Phase and Gradient: see reference 2.
Corona: 100 pA, no filter
Flow Rate: 0.5 mL/min.
Injection Volume: 10 μL
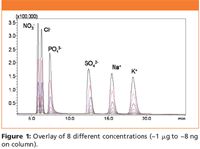
Figure 1
Results
In Figure 1, overlays of eight concentrations of anions and cations are illustrated. The reproducibility and intermediate precision of the analysis was examined for peak areas and retention times of standards using one concentration (~12.5 μg/mL of each ion salt) over the length of the study. Five injections of standard 4 were made on days 1 and 2; six injections on days 4 and 7. The peak area reproducibility, as well as the retention time reproducibility, was examined over the 22-point data set for the six ions. The inter-and intra-day reproducibility results are listed in Table I.
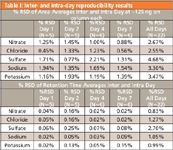
Table I: Inter-and intra-day reproducibility results
Conclusion
The data collected during this study demonstrates that the analysis of ions using the Corona detector can be performed accurately and reproducibly to low nanogram levels. All major validation parameters were tested for chloride, sulfate, sodium, and potassium with only reproducibility reported here. (The analysis did not include all robustness levels according the FDA Q7A). For complete validation information see reference 2. These data illustrate intermediate precision of the detector and method. The validation of this analysis along with the versatility of this ion method makes a viable alternative to traditional approaches.
References
(1) ESA Application note 70-8290 Simultaneous Measurement of an Anion and Cation.
(2) Evaluation of Methods for the Simultaneous Analysis of Cations and Anions Using HPLC with Charged Aerosol Detection and a Zwitterionic Stationary Phase, J. Chromatogr. Sci., 47, 534–539.

ESA Biosciences, Inc.
22 Alpha Road, Chelmsford, MA 01824
tel. (978)250-7000;
Email: info@esainc.com
Website: www.corona-ultra.com

Free Poster: NDSRI Risk Assessment and Trace-Level Analysis of N-Nitrosamines
April 25th 2025With increasing concern over genotoxic nitrosamine contaminants, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have introduced strict guidelines following several high-profile drug recalls. This poster showcases a case study where LGC and Waters developed a UPLC/MS/MS method for quantifying trace levels of N-nitroso-sertraline in sertraline using Waters mass spectrometry and LGC reference standards.
New TRC Facility Accelerates Innovation and Delivery
April 25th 2025We’ve expanded our capabilities with a state-of-the-art, 200,000 sq ft TRC facility in Toronto, completed in 2024 and staffed by over 100 PhD- and MSc-level scientists. This investment enables the development of more innovative compounds, a broader catalogue and custom offering, and streamlined operations for faster delivery. • Our extensive range of over 100,000 high-quality research chemicals—including APIs, metabolites, and impurities in both native and stable isotope-labelled forms—provides essential tools for uncovering molecular disease mechanisms and exploring new opportunities for therapeutic intervention.
New Guide: Characterising Impurity Standards – What Defines “Good Enough?”
April 25th 2025Impurity reference standards (IRSs) are essential for accurately identifying and quantifying impurities in pharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Yet, with limited regulatory guidance on how much characterisation is truly required for different applications, selecting the right standard can be challenging. To help, LGC has developed a new interactive multimedia guide, packed with expert insights to support your decision-making and give you greater confidence when choosing the right IRS for your specific needs.
Using the Carcinogenic Potency Categorisation Approach (CPCA) to Classify N-nitrosamine Impurities
April 25th 2025Learn how to manage nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals with our free infographic. Discover how the CPCA approach establishes acceptable intake limits and guides the selection of NDSRI reference samples. Stay compliant and ensure safety with our ISO-accredited standards.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)














