Rapid Separation of Rhodamines
This application note describes a rapid UHPLC method for the separation of Sulforhodamine 101 (Texas Red®) and its three water-soluble derivatives using a column packed with Thermo Scientific Hypersil GOLD™ 1.9 μm particles.
This application note describes a rapid UHPLC method for the separation of Sulforhodamine 101 (Texas Red® ) and its three water-soluble derivatives using a column packed with Thermo Scientific Hypersil GOLD™ 1.9 μm particles.
Rhodamines are a family of 3,6-di(substituted amino)-9-benzoate derivatives of xanthene. Fluorescent molecules from the rhodamine family are widely used in bio-analysis. They are used as dyes and indicators for various metals, and also as fluorescent tracers in histochemistry (1). Due to their polycyclic aromatic structures, rhodamines are hydrophobic, which makes them incompatible for biological applications, so the ability to synthesize water-soluble analogues is an important consideration for biocompatibility.
In order to compare the polarity of such water-soluble rhodamine derivatives with the starting molecules, it is important to have in place a sound analytical methodology. This application note describes a fast LC method that been developed for the separation of Sulforhodamine 101 (Texas Red) and its three derivatives: Alexa Fluor® 594 (Isomer I), Alexa Fluor 594 (Isomer II) and Texas Red water soluble (TR-WS) using a column packed with Hypersil GOLD 1.9 μm particles.
Experimental Conditions
LC System: Thermo Scientific Accela™ High Speed LC
Column: Hypersil GOLD, 1.9 μm, 50 × 2.1 mm
Part Number: 25002-052130
Mobile Phase: A: 0.1M Triethylammonium acetate (TEAA), pH 7; B: Acetonitrile
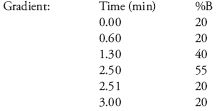
Temperature: 30 °C
Flow Rate: 0.55 mL/min
Injection Volume: 1 μL
UV Detection: 595 nm
Std. Solutions: Alexa Fluor 594 (Isomer I): 1.09 mg in 2.09 g MeCN + 6.79 g water; Alexa Fluor 594 (Isomer II): 0.10 mg in 1.15 g MeCN + 3.81 g water; Texas Red water soluble (TR-WS): 0.25 mg in 1.17 g MeCN + 4.97 g water; Sulforhodamine 101 (Texas Red): 0.25 mg in 1.29 g MeCN + 6.16 g water
Results and Discussion
The use of a short Hypersil GOLD column packed with 1.9 μm particles allows for rapid analysis of the rhodamines. Using the UHPLC method described above, the separation of Sulforhodamine 101 (Texas Red) and its three derivatives can be achieved in under two min (Figure 1). The low dwell volume of the Accela pump means that the gradient is delivered onto the column in a short time and the column can be quickly re-equilibrated. The total analysis time is 3 min sample to sample.
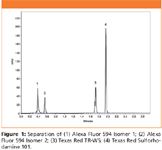
Figure 1
Further optimization of the gradient could potentially lead to a greater ability to separate the ortho-and para-isomers of Texas Red water soluble (TR-WS).
Acknowledgements
This rapid separation was kindly initiated by the provision of the samples and existing methodology using a Hypersil GOLD 150 × 2.1 mm, 5 μm column. Thank you to: Institut de Recherche en Chimie Organique Fine (IRCOF), Equipe de Chimie Bio-Organique, UMR 6014 CNRS, INSA de Rouen et Université de Rouen 76130 Mont Saint Aignan, France.
References
(1) http://www.online-medical-dictionary.org.

Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
112 Chadwick Road, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK WA71PR
tel. (011)44-1928-581-000
Website: www.thermo.com

Automated Sample Preparation (ISO 20122) for MOSH/MOAH in Seasoning Oils
May 6th 2025This work presents an Automated Sample Preparation procedure for MOSH/MOAH analysis of Seasoning Oils. We compare results from a manual epoxidation procedure compliant with DIN 16995 with results based on fully automated sample preparation (epoxidation and saponification) compliant with ISO 20122. In both cases, online clean-up via activated aluminum oxide (AlOx) are used to remove interfering n-alkanes from the MOSH fraction during the HPLC run. Automated data evaluation using a dedicated software (GERSTEL ChroMOH) is presented.
Free Poster: NDSRI Risk Assessment and Trace-Level Analysis of N-Nitrosamines
April 25th 2025With increasing concern over genotoxic nitrosamine contaminants, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have introduced strict guidelines following several high-profile drug recalls. This poster showcases a case study where LGC and Waters developed a UPLC/MS/MS method for quantifying trace levels of N-nitroso-sertraline in sertraline using Waters mass spectrometry and LGC reference standards.
New TRC Facility Accelerates Innovation and Delivery
April 25th 2025We’ve expanded our capabilities with a state-of-the-art, 200,000 sq ft TRC facility in Toronto, completed in 2024 and staffed by over 100 PhD- and MSc-level scientists. This investment enables the development of more innovative compounds, a broader catalogue and custom offering, and streamlined operations for faster delivery. • Our extensive range of over 100,000 high-quality research chemicals—including APIs, metabolites, and impurities in both native and stable isotope-labelled forms—provides essential tools for uncovering molecular disease mechanisms and exploring new opportunities for therapeutic intervention.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)














