Oasis HLB SPE Disc for Rapid Multiresidue Determination of Pharmaceuticals in Drinking Water
Waters Application Note
Michael S. Young, Waters Corp., Milford, Massachusetts, USA.
Introduction: Pharmaceuticals in the Environment
A recent poll indicated that millions of consumers were "very" concerned that their public water supplies may be contaminated with trace amounts of pharmaceuticals.1
These compounds enter the water supply in a variety of ways. Drug residues are introduced to wastewater from hospitals and pharmaceutical manufacturers, from consumer disposal of unused drugs and from human waste. Because water and waste treatment plants in the US do not typically remove pharmaceuticals, these compounds may ultimately pass into the drinking water supply.2
Some utilities have begun to test for these compounds using Oasis HLB cartridges.3 This application note describes the UPLC–MS determination of pharmaceutical compounds using Oasis HLB sorbent in a 47 mm SPE disc format. The Oasis HLB disk provides a suitable alternative that can be used for larger sample sizes and for dirtier samples with sufficient particulate matter to hinder cartridge SPE sampling.
Experimental
This application note discusses SPE methodology for determination of most basic, acidic and neutral drugs.
Oasis HLB disc SPE
The disc is first conditioned with methanol (10 mL) and water (10 mL). Then the 1 L sample is loaded followed by a 10 mL water wash. The sample is eluted with methanol (5 mL), 2% ammonia/methanol (12 mL) and 50:50 acetone/methanol (6 mL). The combined eluents are evaporated and reconstituted prior to UPLC–MS analysis.
UPLC
All analyses were performed using an ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 column, 2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm.
Mass spectrometry
The mass spectrometer was a Waters Quattro Premier XE operated in MRM mode using positive electrospray for bases and neutrals and in negative electrospray for acids.
Results/Conclusions
The Oasis HLB disc performs well for the isolation and enrichment of many classes of pharmaceutical and related compounds from water samples. Figure 1 shows UPLC–MS chromatograms obtained for some basic and acidic pharmaceuticals determined in a fortified river water sample. The results were comparable to results obtained using EPA Method 1694.3 Significant advantages of the HLB disc format include the ability to process larger and dirtier water samples than practical using a cartridge format. In addition, the disc format can be used for the extraction of water sample containing a significant amount of particulate matter, which is not possible using a cartridge.
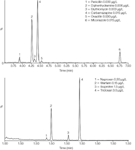
Figure 1: Some group 1 (base/neutrals) and group 3 (acids) compounds extracted at acid pH from river water with spike levels noted.
For the complete application note, visit www.waters.com/30363
References
1. J. Donn, M. Mendoza and J. Pritchard, "AP Probe Finds Drugs in Drinking Water", Associated Press (various outlets) (9 March 2008).
2. D.M. Bauman, Drugs in the Water, Water Technology, 22–24 (May 2008).
3. EPA Method 1694: Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Water, Soil, Sediment, and Biosolids by HPLC–MS–MS, US Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water, EPA-821-R-08-002 (December 2007).
© 2009 Waters Corporation. Waters, The Science of What's Possible, Oasis, ACQUITY UPLC, UPLC, and Quattro Premier are trademarks of Waters Corporation.

Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street, Milford, Massachusetts 01757, USA
tel. +1 508 478 2000 fax +1 508 482 3605
Website: www.waters.com

Understanding FDA Recommendations for N-Nitrosamine Impurity Levels
April 17th 2025We spoke with Josh Hoerner, general manager of Purisys, which specializes in a small volume custom synthesis and specialized controlled substance manufacturing, to gain his perspective on FDA’s recommendations for acceptable intake limits for N-nitrosamine impurities.
University of Rouen-Normandy Scientists Explore Eco-Friendly Sampling Approach for GC-HRMS
April 17th 2025Root exudates—substances secreted by living plant roots—are challenging to sample, as they are typically extracted using artificial devices and can vary widely in both quantity and composition across plant species.
Determining the Serum Proteomic Profile in Migraine Patients with LC–MS
April 17th 2025Researchers used liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) in their proteomic analysis to compare the serum proteome of migraine patients with healthy controls and to identify differentially expressed proteins as potential migraine biomarkers.














