A New High-Resolution MAbPac SCX Column for Characterization of Monoclonal Antibody Heterogeneity
The new MAbPacTM SCX-10 column is based on 10 µm nonporous, highly cross-linked styrene-type polymeric media with a proprietary uniform hydrophilic coating that is grafted with sulfonic acid functional groups.
Srinivasa Rao, Yuanxue Hou, Yury Agroskin, and Chris Pohl, Dionex Corporation
The new MAbPac™ SCX-10 column is based on 10 μm nonporous, highly cross-linked styrene-type polymeric media with a proprietary uniform hydrophilic coating that is grafted with sulfonic acid functional groups. An ATRP-based grafting approach is used to control functional group charge density and degree of polymerization. In addition, these particles exhibit a wide range of pH stability with high selectivity and minimal band spreading. The column is available in two formats: 4 × 250 mm analytical column and 4 × 50 mm guard column.
Experimental
A Dionex ICS-3000 HPLC system with a DP pump, VWD absorbance detector, autosampler, and a TCC-100 thermostatted column compartment was used.
Chromatography was controlled by Chromeleon® Chromatography Data System software (Dionex).
Materials
The monoclonal antibody sample was a gift from a biotech company. Other analytical grade chemicals were obtained from Sigma.
Results and Discussion
MAbPac SCX-10 is a strong cation-exchange column specifically developed for characterization of heterogeneity and analysis of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) (1). MAb heterogeneity can be attributed to glycosylation, oxidation, mutation, phosphorylation, amino terminal modifications, incomplete processing of the C-terminus, and asparagine deamidation. These variations in composition occur in MAbs and many other types of proteins and can impact their efficacy, stability, and safety. Monitoring such variations of therapeutic proteins is required by the FDA and other regulatory agencies. Figure 1 shows the MAb separation using the MAbPac SCX column. Acidic variants, lysine truncation, and other basic variants could be resolved. An example separation of the C-terminus lysine truncation variants with and without carboxypeptidase treatment is shown.
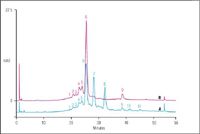
Figure 1: Characterization of acidic, lysine truncation, and other basic variants of a MAb using MAbPac SCX-10 column. Eluents: A: 20 mM MES (pH 5.6) + 60 mM NaCl; B: 20 mM MES (pH 5.6) + 300 mM NaCl; Gradient: 15â36.44%B in 50 min; Flow Rate = 1 mL/min; Injection Volume = 5 μL; detection; UV at 280 nm; Temperature = 30 °C. Samples: A. MAb 900 μg in 100 μL (no carboxypeptidase). Peaks 1â5: Acidic variants; Peaks 6, 7, 8: C-terminal Lys truncation variants of main peak; Peaks 9, 10, 11: C-terminal Lys truncation variants of a minor variant peak. B. MAb 900 μg in 100 μL + carboxypeptidase (CBP) 50 μg in 10 μL (incubation for 3 h at 37 °C). Lysine truncation variant peaks 7 and 8 lose their terminal lysine and combine with peak 6 which has no lysine after CBP treatment. Similarly, minor variant lysine truncation peaks 10 and 11 combine with peak 9 after CBP treatment.
Conclusion
The MAbPac SCX-10 column provides high resolution separation of monoclonal antibody variants in characterization of MAb heterogeneity. This new column is a complimentary addition to the existing ProPac® WCX-10 columns, providing high resolution and orthogonal selectivity for various proteins and MAb charge variant characterization.
References
(1) MAbPac SCX-10 manual and data sheets are available at www.dionex.com.
Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale, CA 94088
tel. (408) 737-0700; fax (408) 730-9403
Website: www.dionex.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)














