Monitoring Worker Exposure of Toxic Chemicals Using Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME) and a Portable GC–MS
Current methods to measure worker exposure to chemicals generally involve collecting samples and sending them to a laboratory for analysis, which can take up to two weeks to obtain results. Tools that can turn samples into on-site information can provide data to make informed decisions when and where they are needed to protect workers.
Current methods to measure worker exposure to chemicals generally involve collecting samples and sending them to a laboratory for analysis, which can take up to two weeks to obtain results. Tools that can turn samples into on-site information can provide data to make informed decisions when and where they are needed to protect workers.
The NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods (NMAM) is a collection of methods for sampling and analysis of contaminants in workplace air. In this example workers in a light industrial building were subjected to nonroutine exposure hazards during a building renovation. Chemicals not normally part of the daily environment started showing up as odors, causing worker concern. To identify the chemicals present, CUSTODION® SPME devices were used to collect air samples that were analyzed with the TRIDION™ -9 person-portable GC–MS.
Experimental Conditions
Sampling was accomplished by exposing SPME fibers coated with polydimethylsiloxane/divinylbenzene (PDMS/DVB) to the ambient air for 5 min. Following sample collection, the SPME syringe was inserted into the TRIDION-9 GC–MS injection port coupled to a low thermal mass GC column (MXT-5, 5 m × 0.1 mm, 0.4 µm df). After an initial 10 s hold at 50 °C, the GC temp was increased at 2 °C/s to 270 °C for a total run time of 2 min. The capillary GC uses a toroidal ion trap mass spectrometer (TMS) detector having a mass range of 43–500 m/z.
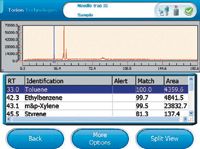
Figure 1: Instrument results.
Results
Figure 1 shows the GC-TMS screen displaying the analytical results of a sample taken closest to the renovation area. Toluene, xylenes, styrene, and several benzene derivatives were detected and identified by the GC-TMS using the instrument's on-board libraries. Current work in the renovation area included painting and carpet gluing. The on-board NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards (NPG) was used to check the exposure levels for the detected chemicals (Figure 2), which in this case worker exposure was below the NIOSH exposure limits.
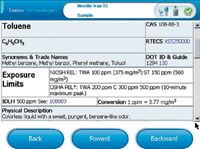
Figure 2: NIOSH NPG
Conclusions
The CUSTODION SPME fiber syringe and TRIDION-9 GC-TMS are uniquely suited for rapid onsite analysis. The primary purpose of on-site analysis is to provide actionable data. This high speed analytical capability provides the information when and where it is needed to make decisions at the samples location.
Feel free to contact a Technical Specialist at Torion to discuss analytical solutions to your specific application at information@torion.com or 801-705-6600.
Acknowledgments
Torion®, CUSTODION® and TRIDION™ are trademarks of Torion Technologies Inc. The CUSTODION SPME Syringes are manufactured and sold under license from SUPELCO under US Patent 5,691,206, and/or any divisions, continuations, or revisions thereof.
Torion Technologies Inc.
796 East Utah Valley Drive, Suite 200
American Fork, UT 84003
Website: www.torion.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)














